Intro
Discover key Atorvastatin facts, including its role in cholesterol reduction, statin benefits, and potential side effects, to understand this lipid-lowering medications impact on heart health and cardiovascular disease prevention.
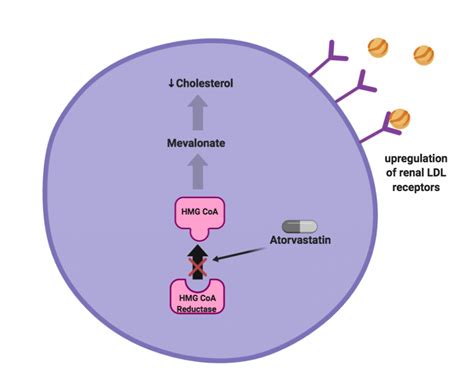
Atorvastatin, commonly known by its brand name Lipitor, is one of the most widely prescribed medications for lowering cholesterol levels. It belongs to a class of drugs called statins, which work by inhibiting the enzyme HMG-CoA reductase. This enzyme plays a crucial role in the production of cholesterol in the liver. By blocking this enzyme, atorvastatin reduces the amount of cholesterol produced in the liver, thereby lowering the overall levels of cholesterol in the blood. This is particularly important for individuals at risk of heart disease, as high cholesterol levels can lead to the buildup of plaque in the arteries, increasing the risk of heart attacks and strokes.
The importance of managing cholesterol levels cannot be overstated. High cholesterol is a major risk factor for cardiovascular disease, which is one of the leading causes of death worldwide. By controlling cholesterol levels, individuals can significantly reduce their risk of developing heart disease. Atorvastatin has been proven to be highly effective in this regard, with numerous studies demonstrating its ability to lower LDL (bad) cholesterol levels and reduce the risk of cardiovascular events. Moreover, atorvastatin has been shown to be safe for long-term use, making it a reliable option for individuals who need to manage their cholesterol levels over an extended period.
The mechanism of action of atorvastatin, like other statins, is complex and involves not only the reduction of cholesterol production in the liver but also effects on other lipid parameters and potentially anti-inflammatory properties. Understanding how atorvastatin works can provide insights into its benefits and potential side effects. Furthermore, knowing how to take atorvastatin, including the appropriate dosage and potential interactions with other medications, is crucial for maximizing its effectiveness and minimizing risks. As with any medication, it's essential to follow the prescription guidelines carefully and to discuss any concerns or questions with a healthcare provider.
Introduction to Atorvastatin
Benefits of Atorvastatin
The benefits of atorvastatin extend beyond its cholesterol-lowering effects. It has been shown to reduce the risk of major cardiovascular events, such as heart attacks, strokes, and the need for coronary revascularization procedures. This is particularly significant for individuals with established cardiovascular disease or those at high risk of developing it. Additionally, atorvastatin may have pleiotropic effects, including anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties, which could contribute to its overall cardiovascular protective benefits.How Atorvastatin Works
Atorvastatin Dosage and Administration
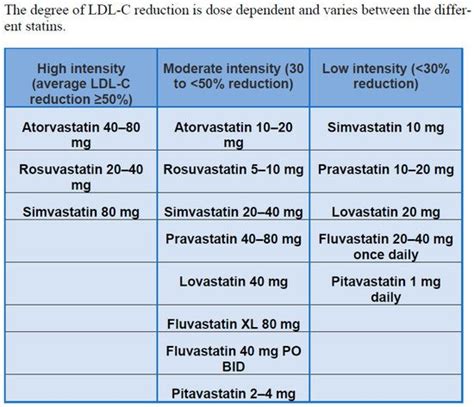
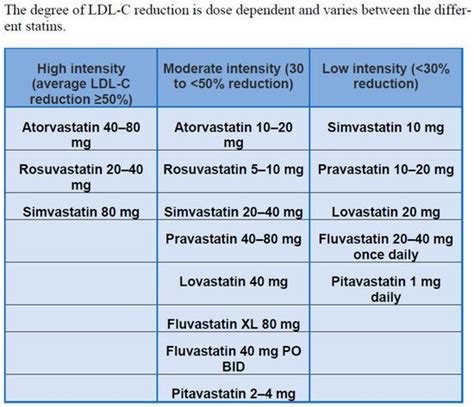
The dosage of atorvastatin can vary depending on the individual's response to treatment, the severity of their hyperlipidemia, and their risk of cardiovascular disease. Typically, treatment is initiated with a low to moderate dose, which can be titrated upwards based on lipid profiles and tolerability. It is essential to follow the prescribed dosage and to take the medication as directed to achieve optimal benefits and minimize potential side effects.Side Effects and Interactions

Contraindications and Precautions
Atorvastatin is contraindicated in certain situations, including active liver disease, significant elevations in liver enzymes, and during pregnancy and breastfeeding. Caution is also advised when prescribing atorvastatin to individuals with a history of liver disease, those who consume large amounts of alcohol, and in cases where the patient is taking medications that may interact with atorvastatin.Atorvastatin in Special Populations

Atorvastatin and Diet
A healthy diet is an essential component of managing cholesterol levels and reducing the risk of cardiovascular disease. When taking atorvastatin, it is recommended to follow a diet low in saturated fats, trans fats, and cholesterol. Increasing the intake of soluble fiber, found in foods such as oats, barley, fruits, and vegetables, can also help lower LDL cholesterol levels. Additionally, maintaining a healthy weight, exercising regularly, and not smoking can further contribute to the overall effectiveness of atorvastatin therapy.Monitoring and Follow-Up
Long-Term Use of Atorvastatin
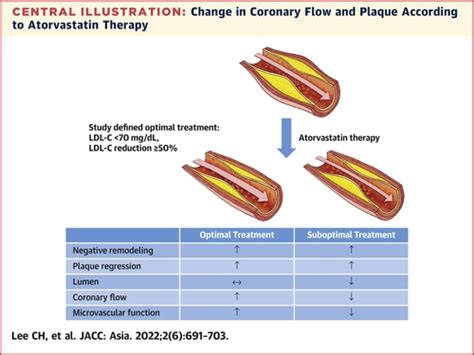
The long-term use of atorvastatin is generally safe and effective for most individuals. However, ongoing monitoring is necessary to ensure that the benefits of therapy continue to outweigh the risks. This includes regular check-ups with a healthcare provider, adherence to a healthy lifestyle, and prompt reporting of any side effects or concerns.Atorvastatin and Cardiovascular Risk Reduction
Atorvastatin in Clinical Practice
In clinical practice, atorvastatin is often used as a first-line treatment for hyperlipidemia due to its efficacy, safety profile, and availability in a range of doses. Its use is guided by clinical guidelines that recommend statin therapy for individuals with elevated cardiovascular risk. The choice of atorvastatin over other statins may depend on factors such as the patient's specific lipid profile, the presence of other medical conditions, and potential drug interactions.Future Directions and Research
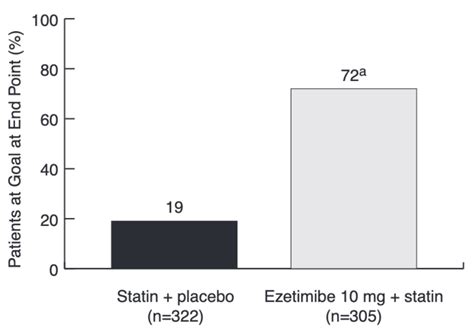
Conclusion and Final Thoughts
In conclusion, atorvastatin is a highly effective medication for lowering cholesterol levels and reducing the risk of cardiovascular disease. Its benefits are well-documented, and it has become a cornerstone in the management of hyperlipidemia. However, like all medications, it must be used judiciously, with careful consideration of its potential side effects and interactions. By understanding how atorvastatin works, its benefits, and its risks, individuals can make informed decisions about their treatment and work closely with their healthcare providers to achieve optimal cardiovascular health.As you consider the role of atorvastatin in your health care, we invite you to share your thoughts and questions about this medication. Whether you are currently taking atorvastatin or are considering it as part of your treatment plan, your experiences and insights can help others. Please feel free to comment below, and let's continue the conversation about how atorvastatin and other statins are shaping the landscape of cardiovascular health.
What is atorvastatin used for?
+Atorvastatin is used to lower cholesterol levels and reduce the risk of cardiovascular disease.
How does atorvastatin work?
+Atorvastatin works by inhibiting the enzyme HMG-CoA reductase, which is involved in the production of cholesterol in the liver.
What are the common side effects of atorvastatin?
+Common side effects of atorvastatin include muscle pain, liver enzyme elevations, and gastrointestinal symptoms.
Can atorvastatin be used in combination with other medications?
+Yes, atorvastatin can be used in combination with other medications, but it's essential to consult with a healthcare provider to discuss potential interactions and benefits.
Is atorvastatin safe for long-term use?
+Atorvastatin is generally safe for long-term use, but ongoing monitoring is necessary to ensure that the benefits of therapy continue to outweigh the risks.
