Intro
Discover if meth is a stimulant, exploring its effects, addiction, and classification as a central nervous system stimulant, affecting dopamine and serotonin levels, with related substance abuse and dependency implications.
Methamphetamine, commonly referred to as meth, is a potent and highly addictive substance that affects the central nervous system. It is classified as a stimulant due to its ability to increase alertness, energy, and activity levels in individuals who use it. However, meth's effects extend beyond typical stimulant properties, as it can also produce hallucinations, paranoia, and other symptoms associated with psychosis. The unique combination of stimulant and psychoactive effects makes meth a particularly dangerous and unpredictable drug.
The importance of understanding meth as a stimulant cannot be overstated, given its widespread abuse and the severe health, social, and economic consequences associated with its use. Methamphetamine use is linked to a range of serious health issues, including cardiovascular problems, dental issues, and increased risk of infectious diseases. Moreover, the psychological effects of meth use, such as anxiety, depression, and cognitive impairment, can have long-lasting impacts on an individual's quality of life and ability to function in society.
Comprehending the stimulant properties of meth and how it interacts with the brain and body is crucial for developing effective prevention and treatment strategies. Meth works by releasing large amounts of dopamine, a neurotransmitter associated with pleasure, reward, and motivation, which reinforces drug-taking behavior and contributes to addiction. Understanding this mechanism can help in the design of interventions aimed at reducing meth use and mitigating its harmful effects.
What is Methamphetamine?

Methamphetamine is a synthetic drug that can be manufactured through various chemical processes, making it widely available and contributing to its popularity among drug users. It is known by several street names, including meth, ice, and crystal, depending on its appearance and purity. Meth can be ingested orally, smoked, snorted, or injected, with each method of administration having different onset times and durations of effect.
The chemical structure of methamphetamine is similar to that of amphetamine, another stimulant drug, but meth has a more potent effect on the brain. This potency, combined with its relatively low cost and ease of production, has made meth a significant public health concern worldwide. Efforts to combat methamphetamine production and distribution are ongoing, but the drug remains widely available, highlighting the need for continued education and intervention.
How Does Methamphetamine Work?
Methamphetamine's stimulant effects are primarily due to its ability to increase the release of dopamine and other neurotransmitters in the brain. This leads to enhanced alertness, concentration, and energy, as well as feelings of euphoria. However, the excessive release of dopamine can also lead to the depletion of this neurotransmitter over time, contributing to the development of addiction and withdrawal symptoms when the drug is not used.The psychoactive effects of meth, including hallucinations and paranoia, are thought to result from the drug's impact on serotonin and norepinephrine systems in the brain. These effects can vary widely among users and are influenced by factors such as the dose of meth taken, the method of administration, and individual differences in brain chemistry and metabolism.
Benefits and Risks of Methamphetamine
While methamphetamine has limited medical uses, such as in the treatment of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) and narcolepsy under the brand name Desoxyn, its potential for abuse and dependence far outweighs any therapeutic benefits for most individuals. The risks associated with meth use are significant and can include:
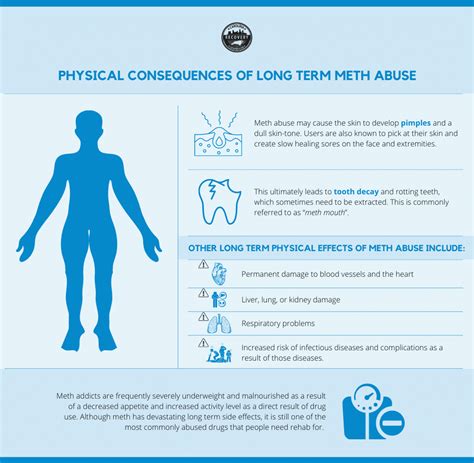
- Cardiovascular problems, such as high blood pressure and heart attack
- Dental issues, known as "meth mouth," which can lead to severe tooth decay and gum disease
- Increased risk of infectious diseases, such as HIV and hepatitis, due to shared needle use
- Severe psychological effects, including anxiety, depression, and psychosis
The benefits of methamphetamine are largely overshadowed by its risks, especially when considering its non-medical use. For individuals prescribed methamphetamine for legitimate medical purposes, the benefits can include improved focus and concentration, as well as management of symptoms associated with ADHD and narcolepsy.
Methamphetamine Addiction and Treatment
Methamphetamine addiction is a complex condition that requires comprehensive treatment approaches. Behavioral therapies, such as cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) and contingency management, have been shown to be effective in treating meth addiction. These therapies help individuals understand the motivations behind their drug use, develop coping skills, and learn to manage triggers and cravings.Medications, such as bupropion and naltrexone, are being studied for their potential in treating methamphetamine addiction, although more research is needed to fully understand their efficacy. Support groups, such as Narcotics Anonymous, can also play a crucial role in the recovery process by providing a community of peers who understand the challenges of addiction and recovery.
Prevention Strategies

Preventing methamphetamine use is critical, given the drug's high potential for addiction and the severe consequences associated with its use. Prevention strategies can include:
- Education and awareness campaigns to inform the public about the risks of meth use
- Community-based programs that provide support and resources for individuals at risk of drug use
- School-based interventions that teach children and adolescents about the dangers of drug use and how to resist peer pressure
- Family-based therapies that help improve communication and relationships within families, reducing the risk of drug use among family members
Early intervention is also key in preventing the progression from casual meth use to addiction. Identifying and addressing underlying issues, such as mental health disorders or trauma, can help individuals avoid drug use as a coping mechanism.
Law Enforcement and Policy Efforts
Law enforcement and policy efforts play a significant role in combating methamphetamine production and distribution. These efforts include:- Enforcement of laws related to methamphetamine production and possession
- Interdiction of methamphetamine shipments and distribution networks
- Regulation of precursor chemicals used in meth production
- International cooperation to address global methamphetamine trafficking
Policy initiatives, such as drug courts and diversion programs, aim to reduce recidivism and provide alternatives to incarceration for non-violent drug offenders. These approaches recognize the complexity of drug addiction and the need for comprehensive solutions that address both the supply and demand sides of the drug problem.
Societal Impact of Methamphetamine

The societal impact of methamphetamine use is profound, affecting not only individuals who use the drug but also their families, communities, and society as a whole. Meth use can lead to increased crime rates, as individuals may engage in criminal activity to support their drug habit. It can also result in significant economic burdens, including costs associated with healthcare, law enforcement, and lost productivity.
Furthermore, methamphetamine use can have devastating effects on families, leading to child neglect, domestic violence, and the breakdown of family structures. Community-based initiatives and support services are essential in mitigating these effects and helping families affected by meth use to rebuild and recover.
Global Perspective on Methamphetamine
Methamphetamine is a global problem, with its use and production reported in almost every region of the world. The ease of manufacturing meth, combined with its high potency and addictive potential, has made it a drug of choice for many users. International cooperation and information sharing are critical in addressing the global methamphetamine problem, as drug trafficking networks often operate across borders.Efforts to combat methamphetamine globally include international treaties and agreements, such as the United Nations Convention Against Illicit Traffic in Narcotic Drugs and Psychotropic Substances, which aim to regulate the production and distribution of precursor chemicals and to enhance cooperation among countries in drug enforcement efforts.
Future Directions in Methamphetamine Research

Future research directions in methamphetamine include the development of effective medications for treating meth addiction, as well as a better understanding of the long-term effects of meth use on the brain and body. Studies on the genetic and environmental factors that contribute to methamphetamine addiction can also inform prevention and treatment strategies.
Additionally, research into the social and economic determinants of meth use can help in the development of targeted interventions and policies aimed at reducing drug use and its consequences. The integration of technology, such as mobile health applications and telemedicine, into drug treatment and prevention services is another area of potential growth, offering increased accessibility and convenience for individuals seeking help.
Conclusion and Call to Action
In conclusion, methamphetamine is a highly addictive and dangerous drug with significant stimulant properties. Its use is associated with a range of severe health, social, and economic consequences. Addressing the methamphetamine problem requires a comprehensive approach that includes prevention, treatment, law enforcement, and policy efforts. By working together and supporting research, education, and community initiatives, we can reduce the harm caused by methamphetamine and help individuals and communities affected by drug use to recover and thrive.We invite readers to share their thoughts and experiences related to methamphetamine use and addiction. Your insights can help inform strategies for prevention, treatment, and support. Together, we can make a difference in the lives of those affected by methamphetamine and work towards a healthier, safer community for all.
What are the short-term effects of methamphetamine use?
+The short-term effects of methamphetamine use can include increased energy and alertness, enhanced concentration, and feelings of euphoria. However, meth use can also lead to negative effects such as anxiety, agitation, and increased heart rate and blood pressure.
How is methamphetamine addiction treated?
+Methamphetamine addiction is typically treated with behavioral therapies, such as cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) and contingency management. Medications may also be used to help manage withdrawal symptoms and cravings. Support groups can provide additional help and community during the recovery process.
What are the long-term effects of methamphetamine use?
+The long-term effects of methamphetamine use can include severe dental problems, cardiovascular issues, and increased risk of infectious diseases. Meth use can also lead to significant psychological effects, such as depression, anxiety, and cognitive impairment. Additionally, long-term use can result in changes to the brain's structure and function.
