Intro
Discover common Lisinopril side effects, including dizziness, cough, and fatigue. Learn about ACE inhibitor risks, blood pressure medication interactions, and managing hypertension symptoms.
Lisinopril, a medication belonging to the class of angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors, is widely prescribed to treat conditions such as high blood pressure and heart failure. Its effectiveness in managing these conditions has made it a staple in cardiovascular medicine. However, like all medications, lisinopril can cause side effects, some of which can be severe. Understanding these side effects is crucial for patients to make informed decisions about their treatment and to recognize when they need to seek medical help.
High blood pressure, or hypertension, affects millions of people worldwide and can lead to serious health issues if not properly managed. Lisinopril works by relaxing blood vessels, making it easier for the heart to pump blood, which in turn lowers blood pressure. This mechanism of action not only helps in reducing the risk of heart attack and stroke but also in slowing the progression of kidney disease in diabetic patients. Despite its benefits, patients should be aware of the potential side effects associated with lisinopril, as they can impact the quality of life and, in some cases, necessitate a change in medication.
The importance of monitoring side effects cannot be overstated, especially for medications like lisinopril that are taken long-term. While many patients tolerate lisinopril well, others may experience side effects that range from mild to severe. Being informed about these potential side effects can help patients manage their expectations and communicate more effectively with their healthcare providers. This article delves into five significant side effects of lisinopril, exploring their causes, symptoms, and management strategies, to provide a comprehensive understanding of what patients might experience during their treatment.
Lisinopril and Coughing
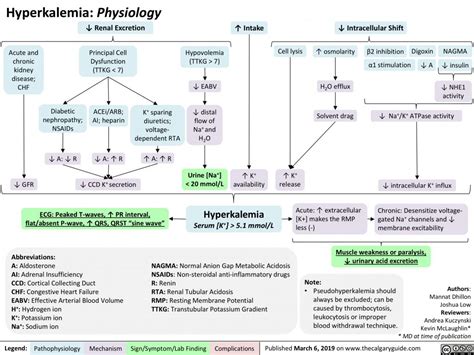
Hyperkalemia: Elevated Potassium Levels
Dizziness and Lightheadedness
Increased Urination
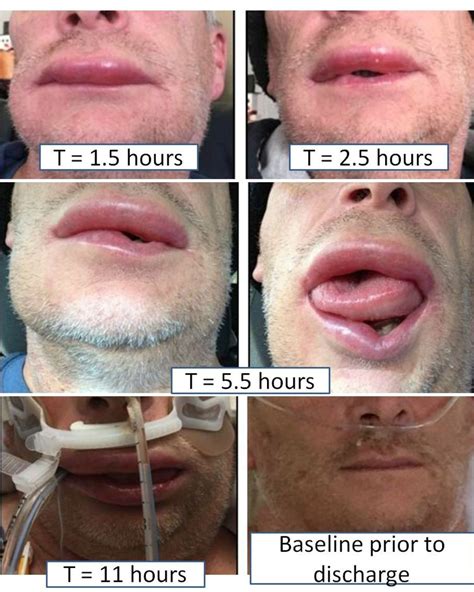
Angioedema: A Rare but Serious Side Effect
Managing Side Effects
While side effects can be a significant concern for patients taking lisinopril, there are steps that can be taken to manage them. Regular communication with a healthcare provider is key, as they can adjust the dosage or switch to a different medication if side effects become unbearable. Lifestyle changes, such as maintaining a healthy diet, exercising regularly, and limiting alcohol intake, can also help mitigate some side effects. Furthermore, understanding the potential interactions between lisinopril and other medications or supplements is crucial to prevent adverse reactions.In conclusion, while lisinopril is an effective medication for managing high blood pressure and heart failure, it is essential for patients to be aware of the potential side effects. By understanding the causes, symptoms, and management strategies for these side effects, patients can better navigate their treatment plan and work closely with their healthcare providers to achieve optimal health outcomes.
What is the most common side effect of lisinopril?
+The most common side effect of lisinopril is a dry, persistent cough, affecting up to 20% of patients.
Can lisinopril cause serious heart problems?
+Yes, lisinopril can cause hyperkalemia (elevated potassium levels), which can lead to serious heart problems, including arrhythmias and cardiac arrest.
How can I manage dizziness caused by lisinopril?
+To manage dizziness, stand up slowly, avoid standing for long periods, and ensure adequate fluid intake to stay hydrated.
Is angioedema a common side effect of lisinopril?
+No, angioedema is a rare but potentially life-threatening side effect of lisinopril, characterized by rapid swelling of the skin and mucous membranes.
Should I stop taking lisinopril if I experience side effects?
+No, do not stop taking lisinopril without consulting your healthcare provider. They can help manage side effects or switch you to a different medication if necessary.
We hope this comprehensive guide to lisinopril side effects has been informative and helpful. If you have any personal experiences or questions regarding lisinopril or its side effects, please do not hesitate to share them in the comments below. Your insights can help others better understand their treatment options and navigate the complexities of managing high blood pressure and heart failure. Additionally, if you found this article useful, consider sharing it with friends or family members who might benefit from this information. Together, we can promote awareness and support for those living with cardiovascular conditions.
