Intro
Discover lidocaine uses and benefits, including pain relief, numbing, and anti-inflammatory effects, for medical and cosmetic procedures, such as dermatology and dentistry applications.
Lidocaine is a local anesthetic and antiarrhythmic drug that has been widely used in medical settings for several decades. It is a versatile medication that offers a range of benefits and uses, from numbing skin and mucous membranes to treating certain types of arrhythmias. In this article, we will delve into the world of lidocaine, exploring its uses, benefits, and mechanisms of action.
Lidocaine is commonly used as a local anesthetic, which means it is applied directly to the skin or mucous membranes to numb the area. This makes it an ideal medication for minor surgical procedures, such as biopsies, skin grafts, and dental procedures. Lidocaine works by blocking the nerve signals that transmit pain, allowing patients to undergo procedures without feeling discomfort or pain. Additionally, lidocaine has antiarrhythmic properties, which make it useful for treating certain types of irregular heartbeats, such as ventricular tachycardia.
The importance of lidocaine cannot be overstated, as it has revolutionized the way medical professionals approach pain management and arrhythmia treatment. With its ability to numb skin and mucous membranes, lidocaine has made it possible for patients to undergo procedures that would otherwise be too painful to tolerate. Furthermore, its antiarrhythmic properties have saved countless lives by helping to regulate irregular heartbeats and prevent life-threatening complications.
Lidocaine Uses
Types of Lidocaine
There are several types of lidocaine, including: * Lidocaine hydrochloride: This is the most common form of lidocaine and is available in various concentrations. * Lidocaine base: This form of lidocaine is less acidic than lidocaine hydrochloride and is often used for spinal anesthesia. * Lidocaine patches: These are transdermal patches that release lidocaine over a prolonged period, providing long-lasting pain relief.Lidocaine Benefits
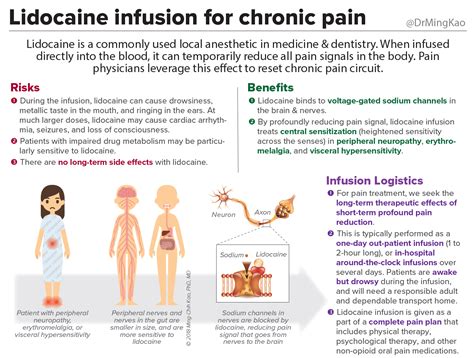
Lidocaine Mechanism of Action
Lidocaine works by blocking the sodium channels in nerve cells, which prevents the transmission of pain signals to the brain. This results in a numbing effect that can last for several hours, depending on the concentration and route of administration. Additionally, lidocaine has antiarrhythmic properties, which help to regulate irregular heartbeats by blocking the potassium channels in the heart.Lidocaine Side Effects

Lidocaine Interactions
Lidocaine can interact with other medications, including: * Beta blockers: Lidocaine can interact with beta blockers, which can increase the risk of cardiac arrhythmias. * Calcium channel blockers: Lidocaine can interact with calcium channel blockers, which can increase the risk of cardiac arrhythmias. * Antiarrhythmic medications: Lidocaine can interact with other antiarrhythmic medications, which can increase the risk of cardiac arrhythmias.Lidocaine Dosage

Lidocaine Administration
Lidocaine can be administered via various routes, including: * Topical application: Lidocaine can be applied topically to the skin or mucous membranes. * Injection: Lidocaine can be administered via injection, either locally or intravenously. * Transdermal patches: Lidocaine can be administered via transdermal patches, which release the medication over a prolonged period.Lidocaine Precautions
Lidocaine Warnings
Lidocaine can cause serious side effects, including: * Cardiac arrhythmias: Lidocaine can cause cardiac arrhythmias, especially when used in high concentrations. * Respiratory depression: Lidocaine can cause respiratory depression, especially when used in high concentrations. * Seizures: Lidocaine can cause seizures, especially when used in high concentrations.What is lidocaine used for?
+Lidocaine is used as a local anesthetic and antiarrhythmic medication. It is commonly used to numb skin and mucous membranes, as well as to treat certain types of irregular heartbeats.
What are the benefits of using lidocaine?
+The benefits of using lidocaine include rapid onset of action, long-lasting effects, low toxicity, and versatility. Lidocaine can be administered via various routes and is generally well-tolerated.
What are the side effects of lidocaine?
+The side effects of lidocaine include numbness or tingling, dizziness or lightheadedness, headache, and allergic reactions. Lidocaine can also interact with other medications and cause serious side effects, such as cardiac arrhythmias and respiratory depression.
In summary, lidocaine is a versatile medication that offers a range of benefits and uses. From numbing skin and mucous membranes to treating certain types of irregular heartbeats, lidocaine has revolutionized the way medical professionals approach pain management and arrhythmia treatment. While lidocaine is generally safe, it can cause side effects and interact with other medications. As such, it is essential to use lidocaine with caution and under the guidance of a medical professional. We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences with lidocaine in the comments below, and to explore our other articles on related topics.
