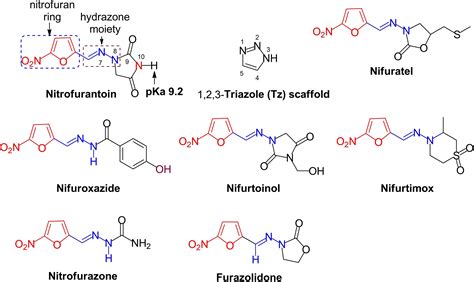
Intro
Discover Nitrofurantoin uses for treating urinary tract infections, including acute cystitis and pyelonephritis, with its antibacterial properties and effectiveness against E. coli and other bacteria, providing relief from UTI symptoms.
The importance of understanding antibiotic uses and their applications cannot be overstated, especially when it comes to treating various bacterial infections. One such antibiotic that has garnered significant attention is Nitrofurantoin, a medication that has been widely used for decades to combat urinary tract infections (UTIs). The efficacy and safety profile of Nitrofurantoin make it a preferred choice among healthcare professionals for managing UTIs, particularly in patients who are susceptible to these types of infections. As we delve into the world of Nitrofurantoin uses, it becomes clear that this antibiotic plays a critical role in the treatment and prevention of UTIs, offering patients a reliable and effective solution for alleviating symptoms and promoting recovery.
The prevalence of UTIs is a significant concern, affecting millions of people worldwide each year. These infections can range from mild to severe, often requiring prompt medical attention to prevent complications. Nitrofurantoin, with its unique mechanism of action, has proven to be an invaluable asset in the fight against UTIs. By understanding the uses of Nitrofurantoin, patients and healthcare providers can work together to develop effective treatment plans, ensuring that UTIs are managed properly and reducing the risk of recurrence. Moreover, the versatility of Nitrofurantoin, which can be used to treat a variety of UTIs, including those caused by susceptible strains of E. coli, makes it an essential component of many antibiotic regimens.
The application of Nitrofurantoin in clinical practice is multifaceted, reflecting its broad spectrum of activity against Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria. Its ability to concentrate in the urinary tract, achieving high levels that are bactericidal, makes it particularly effective for treating UTIs. Furthermore, the development of resistance to Nitrofurantoin is relatively low compared to other antibiotics, which is a significant advantage in the context of increasing antimicrobial resistance globally. As researchers and clinicians continue to explore the full potential of Nitrofurantoin, its role in managing UTIs and potentially other infections is likely to expand, offering new hope for patients seeking effective and safe treatments.
Nitrofurantoin Mechanism of Action
Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics
The pharmacokinetics of Nitrofurantoin involves its absorption, distribution, metabolism, and excretion. When administered orally, Nitrofurantoin is well absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract and undergoes extensive metabolism in the liver. The drug and its metabolites are then excreted primarily through the kidneys, achieving high concentrations in the urine, which is crucial for its antibacterial effects in the urinary tract. Understanding the pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of Nitrofurantoin is essential for optimizing its use, ensuring that patients receive the most effective doses while minimizing the risk of side effects.Nitrofurantoin Uses in Clinical Practice
Treatment of Urinary Tract Infections
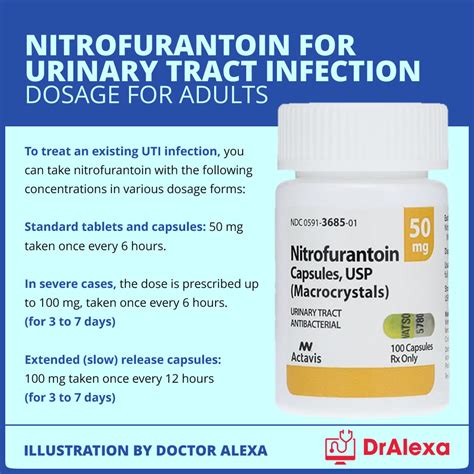
The treatment of UTIs with Nitrofurantoin typically involves a short course of therapy, usually 5 to 7 days for uncomplicated infections. The dosage may vary depending on the patient's renal function and the severity of the infection. It is crucial to complete the full treatment course as prescribed, even if symptoms improve before finishing the medication, to ensure that the infection is fully cleared and to reduce the risk of resistance development.Nitrofurantoin Side Effects and Interactions
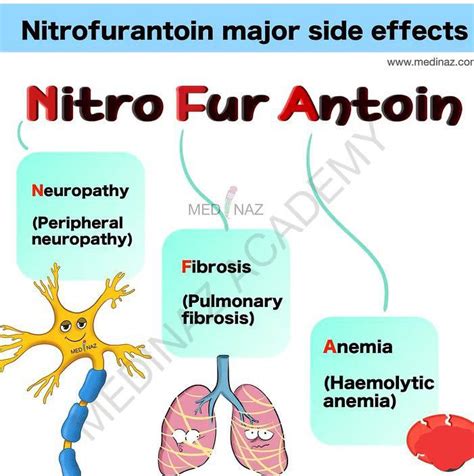
Contraindications and Precautions
Nitrofurantoin is contraindicated in patients with a history of hypersensitivity to the drug, as well as in those with significant renal impairment. Caution is advised when prescribing Nitrofurantoin to patients with hepatic dysfunction, pulmonary disease, or neurological disorders. Pregnant women, especially those at term, should avoid using Nitrofurantoin due to the risk of neonatal hemolysis. Breastfeeding mothers can use Nitrofurantoin, but with careful monitoring of the infant for potential side effects.Nitrofurantoin Resistance and Future Directions
Public Health Implications
The public health implications of Nitrofurantoin use are significant, particularly in the context of UTIs, which are among the most common bacterial infections. By promoting the appropriate use of Nitrofurantoin and other antibiotics, healthcare providers can help reduce the burden of UTIs, decrease the risk of complications, and slow the spread of antibiotic resistance. Public awareness campaigns and educational programs are essential for informing patients about the proper use of antibiotics and the importance of completing full treatment courses.Nitrofurantoin in Special Populations
Pediatric Use
The use of Nitrofurantoin in children is supported by clinical evidence, demonstrating its efficacy and safety in this population. However, the dosage must be tailored to the child's age and renal function to minimize the risk of side effects. Parents and caregivers should be educated on the proper administration of Nitrofurantoin to children and the importance of completing the full treatment course.Nitrofurantoin Dosage and Administration

Administration Considerations
Nitrofurantoin should be administered orally, and patients should be advised to take the medication at the same time each day to maintain consistent drug levels. The drug should not be crushed or chewed, as this can alter its pharmacokinetics. Patients with difficulty swallowing can use the liquid formulation of Nitrofurantoin.Conclusion and Future Perspectives

To further engage with this topic, we invite readers to share their experiences or questions about Nitrofurantoin and its uses in the comments below. Additionally, for those interested in learning more about the management of UTIs or the broader context of antibiotic use, we recommend exploring related articles and resources. By working together, we can foster a deeper understanding of these critical issues and contribute to the development of more effective and sustainable healthcare practices.
What is Nitrofurantoin used for?
+Nitrofurantoin is primarily used for the treatment of urinary tract infections (UTIs), including acute uncomplicated cystitis, recurrent cystitis, and acute pyelonephritis.
How does Nitrofurantoin work?
+Nitrofurantoin works by inhibiting the growth of bacteria in the urinary tract, ultimately leading to their death. It achieves this by interfering with vital bacterial enzymes and cellular processes.
What are the common side effects of Nitrofurantoin?
+Common side effects of Nitrofurantoin include gastrointestinal disturbances such as nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea, as well as allergic reactions like rash and pruritus. Rare but serious side effects can include pulmonary reactions, hepatotoxicity, and neuropathy.
