Intro
Discover the top 10 NSAIDs list, featuring top nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs like ibuprofen, aspirin, and naproxen, to relieve pain, reduce inflammation, and manage conditions like arthritis and muscle soreness.
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, commonly referred to as NSAIDs, are a class of medications widely used to reduce inflammation, relieve pain, and lower fever. They work by inhibiting the production of prostaglandins, which are chemicals in the body that mediate inflammation, pain, and fever. NSAIDs are available over-the-counter (OTC) or by prescription, depending on their strength and the condition being treated. The effectiveness and side effect profile can vary significantly among different NSAIDs, making the choice of which one to use dependent on various factors including the specific condition, patient health, and potential drug interactions.
The use of NSAIDs is a common approach for managing various conditions such as arthritis, menstrual cramps, and other types of pain. However, it's crucial for patients to be aware of the potential side effects and risks associated with NSAID use, such as gastrointestinal complications, increased risk of heart attack or stroke, and kidney damage. Given the diversity of NSAIDs available, understanding the differences and specific uses of each can help in making informed decisions about their use.
NSAIDs have become an integral part of modern medicine due to their effectiveness in providing relief from pain and inflammation. Their role in managing chronic conditions like arthritis and their utility in treating acute pain make them a staple in many healthcare regimens. Despite their benefits, the selection of an appropriate NSAID should be tailored to the individual's health status, the nature of their condition, and under the guidance of a healthcare provider to minimize adverse effects.
Introduction to NSAIDs

NSAIDs are not only used for their analgesic, antipyretic, and anti-inflammatory properties but also for their role in reducing inflammation in conditions like rheumatoid arthritis and other autoimmune diseases. The mechanism of action of NSAIDs involves the inhibition of cyclooxygenase (COX) enzymes, which are crucial in the synthesis of prostaglandins. There are two main types of COX enzymes: COX-1 and COX-2. Traditional NSAIDs are non-selective, meaning they inhibit both COX-1 and COX-2, whereas some newer NSAIDs are selective, primarily inhibiting COX-2 to reduce gastrointestinal side effects.
Top 10 NSAIDs List
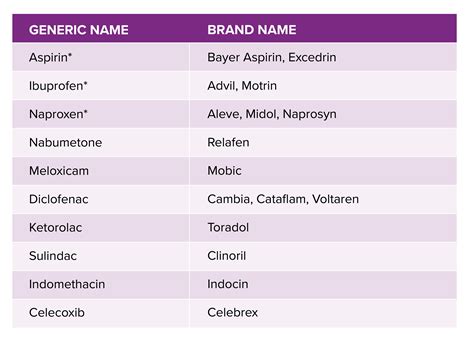
- Ibuprofen: Available over-the-counter, ibuprofen is used for pain relief, to reduce inflammation, and to lower fever. It's commonly found in medications like Advil and Motrin.
- Naproxen: Also available OTC, naproxen is known for its longer-lasting effects compared to ibuprofen and is found in medications like Aleve.
- Aspirin: One of the oldest NSAIDs, aspirin is used for pain relief and as an antiplatelet agent to prevent heart attacks and strokes.
- Diclofenac: Available by prescription, diclofenac is used to treat mild to moderate pain and is also available in topical forms for localized pain and inflammation.
- Celecoxib: A COX-2 inhibitor, celecoxib is used for the treatment of pain, inflammation, and stiffness associated with osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, and ankylosing spondylitis.
- Meloxicam: Another prescription NSAID, meloxicam is used for the treatment of osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, and juvenile rheumatoid arthritis.
- Indomethacin: Used for moderate to severe pain and inflammation, indomethacin is particularly effective in treating gout and other inflammatory conditions.
- Ketoprofen: Available in both oral and topical forms, ketoprofen is used for its anti-inflammatory and analgesic properties.
- Piroxicam: Known for its long half-life, piroxicam provides sustained relief from pain and inflammation, making it suitable for conditions like osteoarthritis.
- Etodolac: Used for the treatment of osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis, etodolac is notable for its efficacy in managing pain and inflammation.
Benefits of NSAIDs
The benefits of NSAIDs are multifaceted, including their ability to provide quick relief from pain and reduce inflammation, which can significantly improve the quality of life for individuals suffering from chronic conditions. They are also versatile, with various formulations available for different needs, such as oral, topical, and injectable forms. Furthermore, NSAIDs can be used to treat a wide range of conditions, from acute injuries to chronic diseases like arthritis.
Common Uses of NSAIDs
- Pain relief: NSAIDs are effective in relieving various types of pain, including headache, toothache, and menstrual cramps. - Reduction of inflammation: They are used to treat inflammatory conditions such as arthritis, bursitis, and tendinitis. - Fever reduction: NSAIDs can help lower fever in adults and children.Risks and Side Effects of NSAIDs
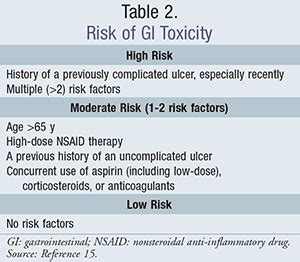
While NSAIDs are beneficial, they also come with potential risks and side effects. The most common side effects include gastrointestinal issues such as stomach ulcers and bleeding, increased risk of heart attack and stroke, and kidney damage. It's essential for individuals to discuss their health history and current medications with their healthcare provider before starting NSAID treatment to minimize these risks.
Minimizing Risks
- Use the lowest effective dose for the shortest duration necessary. - Consider alternative pain relievers for individuals at high risk of NSAID complications. - Monitor for signs of gastrointestinal bleeding and kidney dysfunction.Conclusion and Future Directions

In conclusion, NSAIDs play a vital role in managing pain and inflammation but should be used judiciously, considering their potential side effects. As research continues, the development of safer NSAIDs with fewer side effects is a promising area of focus. For now, patients and healthcare providers must weigh the benefits against the risks and explore all available treatment options to find the best approach for each individual's needs.
Final Thoughts

The future of NSAID therapy looks promising, with ongoing research into more selective inhibitors that can reduce side effects while maintaining efficacy. Additionally, the development of personalized medicine approaches may allow for more tailored NSAID treatment plans, further enhancing their safety and effectiveness.
Engagement and Sharing

We invite readers to share their experiences with NSAIDs, ask questions, or suggest topics for future discussion in the comments below. Your engagement helps us create more informative and relevant content. If you found this article helpful, consider sharing it with others who might benefit from the information.
What are the most common side effects of NSAIDs?
+The most common side effects include stomach ulcers, bleeding, increased risk of heart attack and stroke, and kidney damage.
Can NSAIDs be used for chronic pain management?
+Yes, NSAIDs can be used for chronic pain management, but their use should be carefully monitored by a healthcare provider due to the risk of long-term side effects.
Are there any alternatives to NSAIDs for pain relief?
+Yes, alternatives include acetaminophen, physical therapy, lifestyle changes, and in some cases, prescription pain relievers or corticosteroids.
