Intro
Discover the Loop Electrosurgical Excision Procedure, a minimally invasive technique for removing abnormal cervical cells, using electrosurgery and LEEP methods for diagnosis and treatment of cervical dysplasia and precancerous lesions.
The Loop Electrosurgical Excision Procedure, commonly referred to as LEEP, is a medical procedure used to treat abnormal cell growth on the cervix. This procedure has become a crucial tool in the prevention and early detection of cervical cancer. With the advancement of medical technology and the increasing awareness of women's health, LEEP has gained significant attention in recent years. In this article, we will delve into the world of LEEP, exploring its benefits, working mechanisms, and the steps involved in the procedure.
The importance of LEEP cannot be overstated, as it provides a safe and effective way to remove abnormal cell growth from the cervix. This procedure is typically recommended for women who have undergone a Pap test and have been diagnosed with abnormal cell growth. The LEEP procedure is usually performed in a doctor's office or a clinic, and it typically takes about 10-15 minutes to complete. The procedure is relatively painless, and most women are able to resume their normal activities immediately after.
The LEEP procedure is a vital tool in the fight against cervical cancer. According to the American Cancer Society, cervical cancer is one of the most common types of cancer affecting women worldwide. However, with the help of LEEP and other screening methods, the incidence of cervical cancer has decreased significantly over the years. The procedure is not only effective in treating abnormal cell growth but also provides a sense of relief and peace of mind for women who have been diagnosed with abnormal cell growth.
What is LEEP?
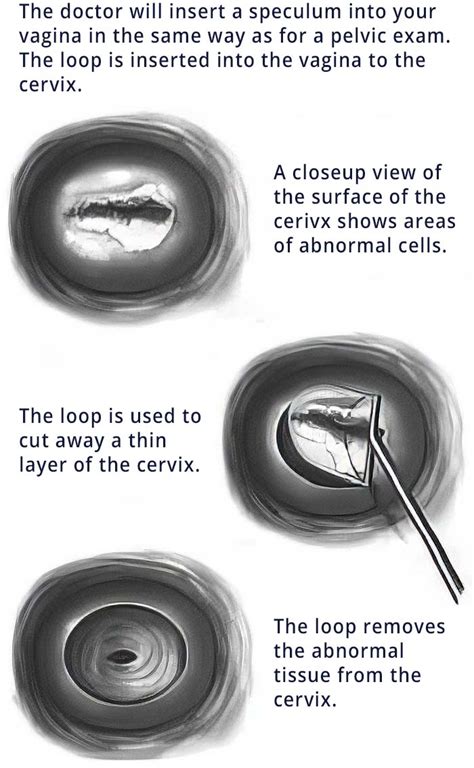
How Does LEEP Work?
The LEEP procedure works by using a combination of electricity and heat to remove the abnormal cells from the cervix. The procedure typically begins with the insertion of a speculum into the vagina, which helps to hold the cervix in place. The doctor will then use a specialized instrument to apply a local anesthetic to the cervix, which helps to numb the area. Once the area is numb, the doctor will use the LEEP device to remove the abnormal cells.Benefits of LEEP

Who is a Candidate for LEEP?
LEEP is typically recommended for women who have been diagnosed with abnormal cell growth on the cervix. This can include women who have undergone a Pap test and have been diagnosed with: * Mild dysplasia * Moderate dysplasia * Severe dysplasia * Carcinoma in situSteps Involved in LEEP

Risks and Complications of LEEP
While LEEP is generally a safe procedure, there are some risks and complications to be aware of. These can include: * Bleeding or spotting * Infection * Scarring * Cervical stenosis * Preterm labor (in pregnant women)After the Procedure
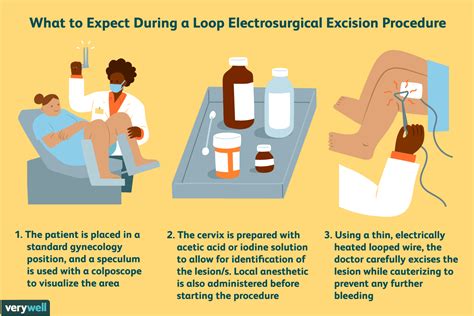
Follow-up Care
Follow-up care is crucial after the LEEP procedure. Your doctor will typically schedule a follow-up appointment to check on your healing progress and remove any stitches. You may also need to undergo additional Pap tests to monitor your cervical health.FAQs

What is the purpose of LEEP?
+The purpose of LEEP is to treat abnormal cell growth on the cervix, which can help prevent the development of cervical cancer.
Is LEEP a painful procedure?
+LEEP is typically a relatively painless procedure, although some women may experience mild discomfort or cramping.
How long does it take to recover from LEEP?
+Recovery time from LEEP is usually quick, and most women are able to resume their normal activities immediately after the procedure.
Conclusion and Next Steps

