Intro
Maintaining optimal blood sugar levels is crucial for overall health, and one key indicator of blood sugar control is Hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c). HbA1c is a blood test that measures the average level of glucose in the blood over the past 2 to 3 months. It's a vital tool for diagnosing and managing diabetes, as well as assessing the risk of developing complications related to diabetes. In this article, we will delve into the importance of low Hemoglobin A1c, its benefits, and how to achieve and maintain optimal levels.
The significance of HbA1c cannot be overstated, as it provides a comprehensive picture of an individual's blood sugar control. By monitoring HbA1c levels, healthcare providers can assess the effectiveness of treatment plans, identify potential issues, and make informed decisions about adjustments to medication, diet, or exercise. Moreover, research has shown that maintaining low HbA1c levels can significantly reduce the risk of complications associated with diabetes, such as heart disease, kidney damage, and nerve damage.
Achieving and maintaining low HbA1c levels requires a multifaceted approach that incorporates lifestyle modifications, medication, and regular monitoring. A healthy diet, regular physical activity, and stress management are essential components of a comprehensive plan to manage blood sugar levels. Additionally, medications such as metformin, sulfonylureas, and insulin therapy may be prescribed to help regulate blood sugar levels. By working closely with healthcare providers and making informed lifestyle choices, individuals can effectively manage their HbA1c levels and reduce the risk of diabetes-related complications.
Understanding Hemoglobin A1c
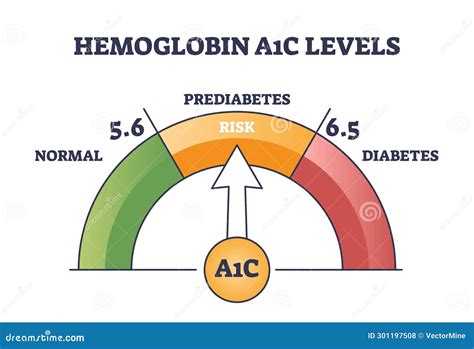
Benefits of Low Hemoglobin A1c
The benefits of maintaining low HbA1c levels are numerous and well-documented. Some of the most significant advantages include: * Reduced risk of heart disease and stroke * Lower risk of kidney damage and disease * Decreased risk of nerve damage and neuropathy * Improved blood flow and circulation * Enhanced overall health and well-being By achieving and maintaining low HbA1c levels, individuals can significantly reduce their risk of developing these complications and improve their overall quality of life.Factors That Affect Hemoglobin A1c

Strategies for Achieving Low Hemoglobin A1c
Achieving and maintaining low HbA1c levels requires a comprehensive approach that incorporates lifestyle modifications, medication, and regular monitoring. Some effective strategies include: * Eating a balanced diet that is low in sugar, refined carbohydrates, and saturated fats * Engaging in regular physical activity, such as walking, jogging, or yoga * Practicing stress-reducing techniques, such as meditation or deep breathing * Getting adequate sleep and maintaining a consistent sleep schedule * Monitoring blood sugar levels regularly and adjusting medication or lifestyle habits as neededMonitoring and Managing Hemoglobin A1c

Common Mistakes to Avoid
When managing HbA1c levels, it's essential to avoid common mistakes that can hinder progress. Some mistakes to avoid include: * Not testing frequently enough: Infrequent testing can make it difficult to identify trends and make informed decisions about treatment. * Not adjusting medication: Failing to adjust medication based on HbA1c levels can lead to poor blood sugar control and increased risk of complications. * Not making lifestyle changes: Failing to make lifestyle changes, such as dietary modifications or increased physical activity, can hinder progress and make it difficult to achieve optimal HbA1c levels.Conclusion and Next Steps

We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences with managing Hemoglobin A1c levels in the comments below. Have you found any particularly effective strategies for achieving and maintaining low HbA1c levels? What challenges have you faced, and how have you overcome them? By sharing your insights and experiences, you can help others who may be struggling with similar issues.
What is a normal Hemoglobin A1c level?
+A normal Hemoglobin A1c level is typically considered to be less than 5.7%. However, the target range may vary depending on individual factors, such as age and medical history.
How often should I test my Hemoglobin A1c levels?
+Hemoglobin A1c levels should be tested at least twice a year, or more frequently if levels are not well-controlled. Your healthcare provider may recommend more frequent testing based on your individual needs.
What are the risks of high Hemoglobin A1c levels?
+High Hemoglobin A1c levels can increase the risk of diabetes-related complications, such as heart disease, kidney damage, and nerve damage. It's essential to work with your healthcare provider to achieve and maintain optimal HbA1c levels.
