Intro
Learn 5 ways to check blood sugar levels, including glucose meters, continuous monitoring, and alternative methods, to manage diabetes and maintain healthy blood glucose levels with ease.
Monitoring blood sugar levels is a crucial aspect of managing diabetes and maintaining overall health. With the advancements in medical technology, there are now various methods to check blood sugar levels, each with its own advantages and disadvantages. In this article, we will delve into the different ways to check blood sugar levels, exploring their mechanisms, benefits, and practical applications.
The importance of monitoring blood sugar levels cannot be overstated, especially for individuals with diabetes. By keeping track of blood glucose levels, individuals can make informed decisions about their diet, exercise, and medication, ultimately reducing the risk of complications associated with diabetes. Moreover, regular monitoring can help identify patterns and trends in blood sugar levels, enabling individuals to adjust their treatment plans accordingly.
For individuals without diabetes, monitoring blood sugar levels can also provide valuable insights into their overall health. By tracking blood glucose levels, individuals can identify potential health risks, such as insulin resistance or prediabetes, and take proactive steps to prevent or manage these conditions. Furthermore, monitoring blood sugar levels can help individuals optimize their diet and exercise routines, leading to improved overall health and well-being.
Introduction to Blood Sugar Monitoring
Method 1: Fingerstick Testing
Fingerstick testing is a relatively simple and inexpensive method of monitoring blood sugar levels. However, it can be painful, especially for individuals who need to test their blood sugar levels frequently. Additionally, fingerstick testing may not provide accurate results if the test strip is not used correctly or if the blood sample is contaminated.
Benefits of Fingerstick Testing
The benefits of fingerstick testing include: * Convenience: Fingerstick testing can be done anywhere, at any time, making it a convenient option for individuals with busy schedules. * Cost-effective: Fingerstick testing is a relatively inexpensive method of monitoring blood sugar levels, especially when compared to other methods. * Quick results: Fingerstick testing provides quick results, allowing individuals to make informed decisions about their treatment plans.Method 2: Continuous Glucose Monitoring

CGM provides a more comprehensive picture of blood sugar levels, allowing individuals to identify patterns and trends. This method is particularly useful for individuals with type 1 diabetes or those who experience frequent hypoglycemic episodes. However, CGM can be expensive, and the sensors need to be replaced every few days.
Benefits of Continuous Glucose Monitoring
The benefits of CGM include: * Comprehensive data: CGM provides a detailed picture of blood sugar levels, allowing individuals to identify patterns and trends. * Improved accuracy: CGM is more accurate than fingerstick testing, especially for individuals with fluctuating blood sugar levels. * Reduced fingerstick testing: CGM reduces the need for frequent fingerstick testing, making it a more convenient option for individuals with busy schedules.Method 3: Flash Glucose Monitoring

FGM is similar to CGM, but it does not require calibration with fingerstick testing. This method is particularly useful for individuals with type 2 diabetes or those who are newly diagnosed with diabetes. However, FGM can be expensive, and the sensors need to be replaced every few days.
Benefits of Flash Glucose Monitoring
The benefits of FGM include: * Convenience: FGM is a convenient option for individuals with busy schedules, as it eliminates the need for frequent fingerstick testing. * Improved accuracy: FGM is more accurate than fingerstick testing, especially for individuals with fluctuating blood sugar levels. * Reduced cost: FGM can be less expensive than CGM, especially for individuals with type 2 diabetes.Method 4: Urine Testing

Benefits of Urine Testing
The benefits of urine testing include: * Non-invasive: Urine testing is a non-invasive method of monitoring blood sugar levels, making it a convenient option for individuals who are sensitive to pain. * Cost-effective: Urine testing is a relatively inexpensive method of monitoring blood sugar levels, especially when compared to other methods. * Easy to use: Urine testing is easy to use, as it requires only a urine sample and a test strip.Method 5: Interstitial Fluid Testing
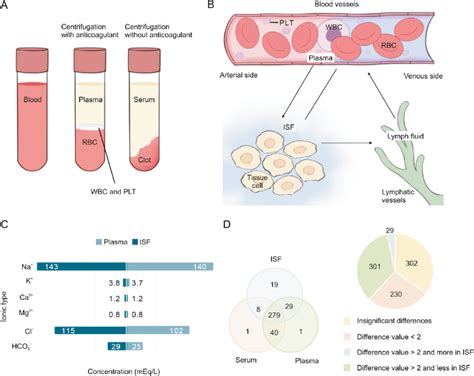
Benefits of Interstitial Fluid Testing
The benefits of interstitial fluid testing include: * Improved accuracy: Interstitial fluid testing is more accurate than fingerstick testing, especially for individuals with fluctuating blood sugar levels. * Reduced fingerstick testing: Interstitial fluid testing reduces the need for frequent fingerstick testing, making it a more convenient option for individuals with busy schedules. * Comprehensive data: Interstitial fluid testing provides a detailed picture of blood sugar levels, allowing individuals to identify patterns and trends.What is the best method for monitoring blood sugar levels?
+The best method for monitoring blood sugar levels depends on individual needs and preferences. Fingerstick testing is a convenient and cost-effective option, while CGM and FGM provide more comprehensive data. Urine testing and interstitial fluid testing are also useful methods, especially for individuals who have difficulty with fingerstick testing.
How often should I monitor my blood sugar levels?
+The frequency of monitoring blood sugar levels depends on individual needs and treatment plans. Individuals with type 1 diabetes or those who experience frequent hypoglycemic episodes may need to monitor their blood sugar levels more frequently, while individuals with type 2 diabetes may need to monitor their blood sugar levels less frequently.
What are the risks associated with monitoring blood sugar levels?
+The risks associated with monitoring blood sugar levels include infection, scarring, and pain. Individuals who use CGM or FGM may experience skin irritation or allergic reactions to the sensors. Urine testing and interstitial fluid testing are generally safe, but may not provide accurate results if the test strips are not used correctly.
In conclusion, monitoring blood sugar levels is a crucial aspect of managing diabetes and maintaining overall health. The various methods of monitoring blood sugar levels, including fingerstick testing, CGM, FGM, urine testing, and interstitial fluid testing, each have their own advantages and disadvantages. By understanding the different methods and their benefits, individuals can make informed decisions about their treatment plans and take proactive steps to manage their blood sugar levels. We invite you to share your experiences with monitoring blood sugar levels and ask any questions you may have about this topic.
