Intro
Discover the 5 uses of Metformin, a medication for type 2 diabetes, also used for weight loss, PCOS treatment, insulin resistance, and anti-aging benefits, offering a holistic approach to health management.
Metformin is a medication that has been widely used for decades to treat type 2 diabetes. Its effectiveness in managing blood sugar levels has made it a cornerstone in the treatment of this condition. However, metformin's benefits extend beyond its primary use, and it has been found to have a significant impact on various other health aspects. In this article, we will delve into the 5 uses of metformin, exploring its role in treating conditions beyond diabetes and its potential to improve overall health.
The importance of metformin cannot be overstated, given its widespread use and the significant impact it has on the lives of millions of people worldwide. By understanding the full scope of metformin's uses, individuals can better appreciate the potential benefits it offers and how it can be a valuable tool in maintaining good health. Whether you are living with diabetes or are simply interested in learning more about this versatile medication, this article aims to provide a comprehensive overview of metformin's applications and its potential to improve health outcomes.
Metformin's mechanism of action is complex and multifaceted, involving the reduction of glucose production in the liver, improvement of insulin sensitivity, and enhancement of glucose uptake by muscles. These effects combined make metformin an effective drug for managing type 2 diabetes. However, its influence on various bodily processes also positions it as a potential treatment for other conditions. As research continues to uncover the full range of metformin's effects, its use is being explored in a variety of medical contexts, offering new hope for the treatment of several diseases and conditions.
Introduction to Metformin
Metformin is a biguanide antidiabetic agent that has been in use for over six decades. Initially derived from the French lilac, metformin has undergone significant development to become the synthetic compound used today. Its primary function is to decrease glucose production by the liver, increase insulin sensitivity, and thereby lower blood sugar levels. This action makes metformin particularly useful for individuals with type 2 diabetes, who often exhibit insulin resistance and elevated hepatic glucose output.
How Metformin Works
Metformin's working mechanism is distinct from other antidiabetic drugs. It does not increase insulin secretion but instead reduces the amount of glucose released into the bloodstream by the liver. Additionally, metformin enhances the body's response to insulin, making it easier for glucose to enter cells. This dual action helps to lower blood glucose levels without causing hypoglycemia, a common side effect of many diabetes medications.Metformin for Weight Loss

One of the notable side effects of metformin is weight loss. Many individuals taking metformin for diabetes management experience a reduction in body weight. This effect is believed to be due to metformin's influence on appetite and metabolism. By reducing glucose levels in the bloodstream, metformin can lead to a decrease in appetite, resulting in lower calorie intake. Furthermore, metformin may enhance the burning of fat for energy, contributing to weight loss.
Benefits for Non-Diabetic Individuals
For individuals without diabetes, metformin's potential for weight loss has sparked interest. However, it is crucial to note that metformin should only be used under medical supervision, as it is a prescription medication. While some studies suggest that metformin may aid in weight loss for non-diabetic individuals, its use for this purpose is not universally recommended and requires careful consideration of potential risks and benefits.Metformin and Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS)
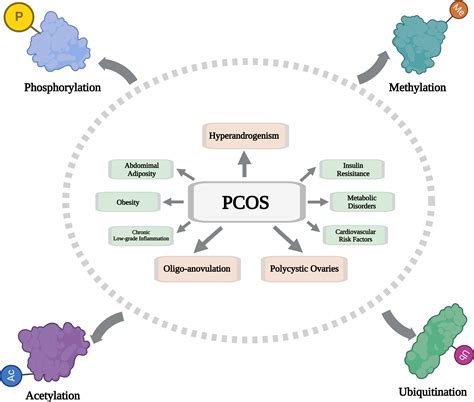
Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) is a condition characterized by irregular menstrual periods, cysts on the ovaries, and often, insulin resistance. Given metformin's ability to improve insulin sensitivity, it has been used off-label to treat PCOS. By reducing insulin resistance, metformin can help regulate menstrual cycles, improve ovulation, and even reduce the appearance of acne and hirsutism, common symptoms of PCOS.
Treatment Considerations
The use of metformin in treating PCOS is not without controversy. While it can be effective for some women, especially those with significant insulin resistance, it may not address all symptoms of PCOS. Moreover, metformin's effects on fertility can be variable, and its use should be carefully considered in the context of overall PCOS management, which may include lifestyle modifications, hormonal treatments, and other interventions.Metformin for Anti-Aging and Longevity

Recent research has explored metformin's potential role in promoting longevity and anti-aging. The drug's ability to influence cellular energy metabolism, reduce oxidative stress, and improve insulin sensitivity may contribute to its anti-aging effects. Additionally, metformin's impact on the cellular processes that underlie aging, such as autophagy and mitochondrial function, has garnered significant attention. While the evidence is still preliminary, metformin's potential to extend healthspan and possibly lifespan is an exciting area of investigation.
Future Directions
The concept of using metformin as an anti-aging drug is speculative at this stage, and more research is needed to fully understand its effects on human longevity. However, the existing body of evidence suggests that metformin may have a role to play in healthy aging, potentially by mitigating the risks associated with age-related diseases such as cardiovascular disease, cancer, and cognitive decline.Metformin and Cancer Prevention

There is growing interest in metformin's potential to reduce the risk of certain cancers, particularly those associated with insulin resistance and metabolic syndrome, such as breast, prostate, and colorectal cancers. The mechanisms by which metformin may exert anti-cancer effects include its ability to reduce insulin levels, inhibit cell proliferation, and induce apoptosis (cell death) in cancer cells.
Clinical Evidence
While observational studies and clinical trials suggest a potential link between metformin use and reduced cancer risk, the evidence is not yet conclusive. Ongoing research aims to clarify metformin's role in cancer prevention and treatment, including its potential as an adjuvant therapy to enhance the effectiveness of existing cancer treatments.Metformin for Cardiovascular Health

Metformin's benefits extend to cardiovascular health, with evidence suggesting that it can reduce the risk of heart disease in individuals with type 2 diabetes. This effect is attributed to metformin's ability to lower blood pressure, improve lipid profiles, and reduce inflammation, all of which are risk factors for cardiovascular disease.
Risk Reduction Strategies
For individuals with diabetes, managing cardiovascular risk is crucial. Metformin, as part of a comprehensive treatment plan that includes lifestyle modifications and, when necessary, other medications, can play a significant role in reducing the risk of heart disease. By addressing the root causes of cardiovascular risk, such as insulin resistance and hyperglycemia, metformin contributes to a holistic approach to health management.What are the common side effects of metformin?
+Common side effects of metformin include gastrointestinal symptoms such as diarrhea, nausea, and abdominal pain. These effects are usually mild and temporary.
Can metformin be used for weight loss in non-diabetic individuals?
+While metformin can aid in weight loss, its use for this purpose in non-diabetic individuals is not widely recommended and should be considered on a case-by-case basis under medical supervision.
Is metformin effective in preventing cancer?
+The evidence suggesting metformin's role in cancer prevention is promising but not yet conclusive. Ongoing research is needed to fully understand its potential in reducing cancer risk.
In conclusion, metformin's applications extend far beyond its traditional use in managing type 2 diabetes. Its potential benefits in weight loss, treatment of PCOS, anti-aging, cancer prevention, and cardiovascular health make it a versatile medication with a wide range of uses. As research continues to uncover the full extent of metformin's effects, it is likely that its role in healthcare will expand, offering new avenues for the treatment and prevention of various diseases. Whether you are a healthcare professional, a researcher, or simply an individual interested in learning more about metformin, this article has provided a comprehensive overview of its uses and potential benefits, highlighting its significance in modern medicine.
We invite you to share your thoughts, experiences, or questions about metformin in the comments below. Your engagement can help foster a community of individuals committed to understanding and promoting health through the informed use of medications like metformin. By sharing this article with others, you can contribute to the dissemination of valuable information that may improve health outcomes for many. Together, we can explore the complexities of metformin and its role in enhancing our well-being.
