Intro
Learn about MMR 2nd dose timing for adults, including booster shot schedules, vaccine efficacy, and measles, mumps, and rubella prevention strategies, to ensure optimal immunity and protection.
The measles, mumps, and rubella (MMR) vaccine is a crucial component of preventive care, providing immunity against three serious diseases. For adults, the MMR vaccine is particularly important, as it helps prevent outbreaks and protects vulnerable populations, such as young children and individuals with weakened immune systems. One key aspect of the MMR vaccine is the timing of the second dose, which is essential for ensuring optimal protection against these diseases.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) and other health organizations recommend that adults receive two doses of the MMR vaccine, spaced at least 28 days apart. This recommendation is based on studies that have shown that two doses of the vaccine provide greater protection against measles, mumps, and rubella than a single dose. The second dose is particularly important, as it helps to boost the immune system and provide long-term protection against these diseases.
In recent years, there has been an increase in outbreaks of measles and mumps, highlighting the importance of vaccination. These outbreaks have often occurred in communities with low vaccination rates, emphasizing the need for adults to ensure they are up to date on their MMR vaccinations. By receiving the recommended two doses of the MMR vaccine, adults can help prevent the spread of these diseases and protect themselves and their loved ones from serious illness.
Understanding the MMR Vaccine
The MMR vaccine is a live, attenuated vaccine, which means it contains weakened forms of the measles, mumps, and rubella viruses. The vaccine works by stimulating the immune system to produce antibodies against these viruses, providing protection against infection. The MMR vaccine is typically administered in two doses, with the first dose given to children at 12-15 months of age and the second dose given at 4-6 years of age. However, adults who did not receive the vaccine as children or who have not received the recommended two doses may need to receive the vaccine as well.
Benefits of the MMR Vaccine
The benefits of the MMR vaccine are numerous. Not only does it provide protection against measles, mumps, and rubella, but it also helps to prevent the spread of these diseases in communities. By receiving the MMR vaccine, adults can help protect vulnerable populations, such as young children and individuals with weakened immune systems, who may be at increased risk of serious illness or complications from these diseases.Some of the key benefits of the MMR vaccine include:
- Protection against measles, mumps, and rubella
- Prevention of outbreaks and spread of disease in communities
- Protection of vulnerable populations, such as young children and individuals with weakened immune systems
- Boosting of the immune system to provide long-term protection against these diseases
MMR 2nd Dose Timing for Adults

The timing of the second dose of the MMR vaccine is critical for ensuring optimal protection against measles, mumps, and rubella. The CDC recommends that adults receive the second dose of the MMR vaccine at least 28 days after the first dose. This allows the immune system to fully respond to the vaccine and provides the best protection against these diseases.
It's essential to note that the timing of the second dose may vary depending on individual circumstances. For example, adults who are traveling to areas with high rates of measles, mumps, or rubella may need to receive the second dose earlier, typically within 2-4 weeks of the first dose. Additionally, adults who have been exposed to these diseases may need to receive the second dose as soon as possible, ideally within 72 hours of exposure.
Factors Affecting MMR 2nd Dose Timing
Several factors can affect the timing of the second dose of the MMR vaccine, including: * Travel plans: Adults traveling to areas with high rates of measles, mumps, or rubella may need to receive the second dose earlier. * Exposure to disease: Adults who have been exposed to these diseases may need to receive the second dose as soon as possible. * Immune status: Adults with weakened immune systems may need to receive the second dose earlier or more frequently. * Pregnancy: Pregnant women should not receive the MMR vaccine, but women who are planning to become pregnant should ensure they are up to date on their MMR vaccinations before becoming pregnant.Side Effects and Contraindications

Like all vaccines, the MMR vaccine can cause side effects, although these are typically mild and temporary. Common side effects include:
- Pain, redness, or swelling at the injection site
- Fever
- Headache
- Fatigue
- Muscle or joint pain
In rare cases, the MMR vaccine can cause more serious side effects, such as allergic reactions or seizures. It's essential to discuss any concerns or allergies with a healthcare provider before receiving the vaccine.
Contraindications to the MMR vaccine include:
- Pregnancy
- Severe allergic reactions to previous doses of the vaccine or to components of the vaccine
- Weakened immune system due to certain medical conditions or treatments
- Recent blood transfusions or other blood products
Special Considerations
Certain individuals may require special consideration when it comes to the MMR vaccine, including: * Pregnant women: Should not receive the MMR vaccine, but women who are planning to become pregnant should ensure they are up to date on their MMR vaccinations before becoming pregnant. * Breastfeeding women: Can receive the MMR vaccine, but should discuss any concerns with a healthcare provider. * Individuals with weakened immune systems: May need to receive the vaccine earlier or more frequently, and should discuss their individual needs with a healthcare provider.Boosting Immunity with the MMR Vaccine
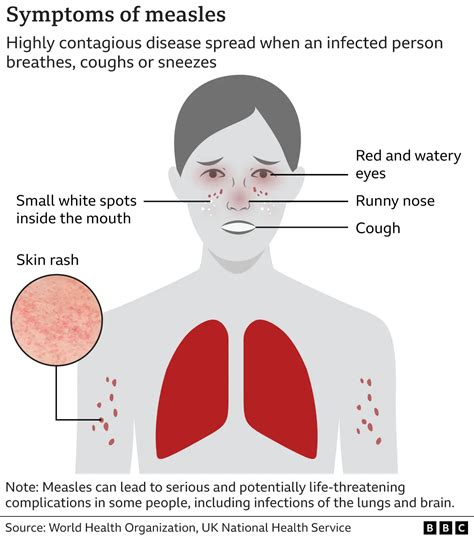
The MMR vaccine plays a critical role in boosting immunity against measles, mumps, and rubella. By receiving the recommended two doses of the vaccine, adults can help ensure they have optimal protection against these diseases. Additionally, the vaccine can help boost the immune system, providing long-term protection against these diseases.
Some of the ways the MMR vaccine boosts immunity include:
- Stimulating the production of antibodies against measles, mumps, and rubella
- Activating immune cells, such as T-cells and B-cells, to recognize and respond to these viruses
- Providing long-term protection against these diseases, reducing the risk of serious illness or complications
Importance of Herd Immunity
Herd immunity plays a critical role in preventing the spread of measles, mumps, and rubella. When a sufficient percentage of a population is immunized against these diseases, it helps to prevent outbreaks and protect vulnerable populations, such as young children and individuals with weakened immune systems.The importance of herd immunity cannot be overstated, as it:
- Prevents outbreaks and spread of disease in communities
- Protects vulnerable populations, such as young children and individuals with weakened immune systems
- Reduces the risk of serious illness or complications from these diseases
Conclusion and Next Steps
In conclusion, the MMR vaccine is a crucial component of preventive care, providing immunity against measles, mumps, and rubella. The timing of the second dose is critical for ensuring optimal protection against these diseases, and adults should receive the second dose at least 28 days after the first dose. By understanding the benefits, side effects, and contraindications of the MMR vaccine, adults can make informed decisions about their health and help prevent the spread of these diseases in their communities.
We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences with the MMR vaccine in the comments below. Have you received the MMR vaccine? Do you have any questions or concerns about the vaccine? Let's start a conversation and work together to promote public health and prevent the spread of measles, mumps, and rubella.
What is the recommended timing for the second dose of the MMR vaccine for adults?
+The CDC recommends that adults receive the second dose of the MMR vaccine at least 28 days after the first dose.
Can I receive the MMR vaccine if I am pregnant or breastfeeding?
+Pregnant women should not receive the MMR vaccine, but breastfeeding women can receive the vaccine. It's essential to discuss any concerns with a healthcare provider before receiving the vaccine.
What are the common side effects of the MMR vaccine?
+Common side effects of the MMR vaccine include pain, redness, or swelling at the injection site, fever, headache, fatigue, and muscle or joint pain.
How does the MMR vaccine boost immunity against measles, mumps, and rubella?
+The MMR vaccine boosts immunity by stimulating the production of antibodies against measles, mumps, and rubella, activating immune cells, and providing long-term protection against these diseases.
Why is herd immunity important for preventing the spread of measles, mumps, and rubella?
+Herd immunity is crucial for preventing outbreaks and spread of disease in communities, protecting vulnerable populations, and reducing the risk of serious illness or complications from these diseases.
