Intro
The importance of understanding the normal range for various health metrics cannot be overstated. In the medical field, a normal range refers to the typical values for a particular measurement or test result that are considered healthy or average for a given population. This range is usually determined by conducting studies on large groups of people and analyzing the data to establish a baseline for what is considered normal. For instance, the normal range for blood pressure is typically considered to be around 120/80 mmHg, while the normal range for blood glucose levels is usually between 70 and 110 mg/dL.
Understanding the normal range for different health metrics is crucial for diagnosing and treating various medical conditions. Healthcare professionals rely on these ranges to determine whether a patient's test results are within a healthy range or if they indicate a potential health issue. For example, if a patient's blood pressure is consistently above the normal range, it may indicate hypertension, which can increase the risk of heart disease, stroke, and other cardiovascular conditions. Similarly, blood glucose levels that are outside the normal range can indicate diabetes or pre-diabetes, which require prompt medical attention.
The concept of a normal range is not limited to physical health metrics; it also applies to mental health and cognitive function. For instance, the normal range for cognitive abilities such as memory, attention, and processing speed can vary depending on age, education level, and other factors. Understanding these ranges is essential for diagnosing and treating conditions such as dementia, attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), and other cognitive disorders.
Understanding Normal Ranges
Normal ranges are typically established through statistical analysis of data from large populations. This involves collecting data on a particular health metric, such as blood pressure or blood glucose levels, from a representative sample of people. The data is then analyzed to determine the average value and the range of values that are considered normal. This range is usually expressed as a mean value plus or minus one or two standard deviations, which represents the typical variation in the population.
Factors that Influence Normal Ranges
Several factors can influence normal ranges, including age, sex, ethnicity, and lifestyle. For example, the normal range for blood pressure tends to increase with age, while the normal range for blood glucose levels may be lower in people who are physically active or have a healthy diet. Understanding these factors is essential for interpreting test results and making accurate diagnoses.Common Normal Ranges
There are several common normal ranges that are used in medical practice, including:
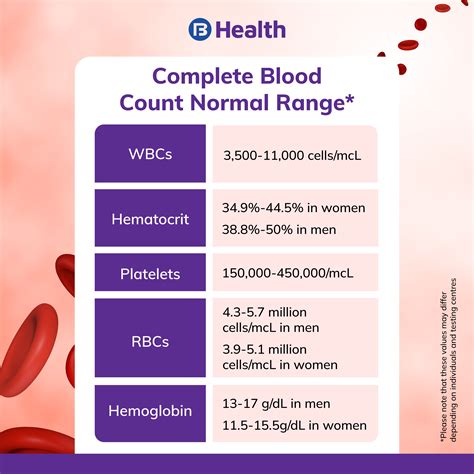
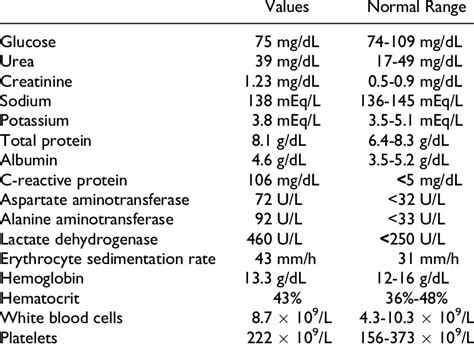
- Blood pressure: 90/60 mmHg to 120/80 mmHg
- Blood glucose levels: 70 mg/dL to 110 mg/dL
- Cholesterol levels: less than 200 mg/dL
- Body mass index (BMI): 18.5 to 24.9
- White blood cell count: 4,500 to 11,000 cells per microliter
These ranges are not absolute and can vary depending on the individual and the specific test or measurement being used.
Interpreting Test Results
Interpreting test results requires a thorough understanding of normal ranges and the factors that can influence them. Healthcare professionals must consider the individual's medical history, lifestyle, and other relevant factors when interpreting test results. For example, a patient with a blood pressure reading of 140/90 mmHg may be considered hypertensive, but if they are physically active and have a healthy diet, their blood pressure may be considered normal.Importance of Normal Ranges in Medicine

Normal ranges play a crucial role in medicine, as they provide a framework for diagnosing and treating various medical conditions. By understanding what is considered normal, healthcare professionals can identify potential health issues early on and provide targeted interventions to prevent or manage disease. Normal ranges also help to reduce unnecessary testing and treatment, which can improve patient outcomes and reduce healthcare costs.
Limitations of Normal Ranges
While normal ranges are essential in medicine, they have several limitations. For example, normal ranges can vary depending on the population being studied, and they may not account for individual differences in health status or lifestyle. Additionally, normal ranges can be influenced by various factors, such as laboratory error or instrument calibration, which can affect the accuracy of test results.Future Directions

The concept of normal ranges is continually evolving, as new research and technologies become available. For example, advances in genomics and precision medicine are enabling healthcare professionals to tailor treatments to an individual's unique genetic profile, which can improve patient outcomes and reduce healthcare costs. Additionally, the development of new diagnostic tests and biomarkers is expanding our understanding of normal ranges and enabling earlier detection and treatment of various medical conditions.
Personalized Medicine
Personalized medicine is an emerging field that involves tailoring medical treatment to an individual's unique genetic profile, lifestyle, and health status. This approach has the potential to improve patient outcomes and reduce healthcare costs, as it enables healthcare professionals to target specific underlying mechanisms of disease. By understanding an individual's normal ranges and how they vary over time, healthcare professionals can provide more effective and targeted interventions.Conclusion and Next Steps

In conclusion, understanding normal ranges is essential for diagnosing and treating various medical conditions. By recognizing the factors that influence normal ranges and interpreting test results in the context of an individual's unique health profile, healthcare professionals can provide more effective and targeted interventions. As the field of medicine continues to evolve, it is likely that our understanding of normal ranges will become even more refined, enabling more personalized and effective care.
We invite you to share your thoughts and questions about normal ranges in the comments section below. How do you think normal ranges can be used to improve patient outcomes and reduce healthcare costs? What are some potential limitations or challenges associated with using normal ranges in medical practice?
What is a normal range in medicine?
+A normal range in medicine refers to the typical values for a particular measurement or test result that are considered healthy or average for a given population.
How are normal ranges established?
+Normal ranges are typically established through statistical analysis of data from large populations, which involves collecting data on a particular health metric and analyzing it to determine the average value and range of values that are considered normal.
What factors can influence normal ranges?
+Several factors can influence normal ranges, including age, sex, ethnicity, lifestyle, and laboratory error or instrument calibration.
