Intro
Understand normal Protime INR levels, International Normalized Ratio, and blood clotting factors to manage anticoagulation therapy, prevent thrombosis, and maintain optimal coagulation balance.
The importance of understanding normal Protime INR levels cannot be overstated, especially for individuals who are taking anticoagulant medications such as warfarin. Protime, also known as prothrombin time, is a test used to evaluate the blood's ability to clot, and the international normalized ratio (INR) is a calculation based on the results of this test. The INR is a standardized measurement that allows for the comparison of results from different laboratories. For individuals taking warfarin, maintaining a therapeutic INR range is crucial to prevent both thrombotic and bleeding complications.
The Protime INR test is a vital tool for healthcare providers to monitor the effectiveness of anticoagulation therapy and to adjust medication doses as needed. It is also used to diagnose and monitor coagulation disorders, such as liver disease or vitamin K deficiency. Understanding normal Protime INR levels is essential for individuals to take an active role in their healthcare, ensuring they are within a safe and effective therapeutic range. This knowledge can empower patients to ask informed questions, recognize potential issues, and adhere to their treatment plans more effectively.
For many individuals, particularly those with conditions like atrial fibrillation, deep vein thrombosis, or pulmonary embolism, managing anticoagulation therapy is a long-term commitment. The goal of this therapy is to prevent the formation of blood clots that could lead to serious health issues, such as stroke or heart attack. However, anticoagulants also increase the risk of bleeding, making it crucial to find a balance. The Protime INR test provides valuable insights into how well the blood is clotting, guiding healthcare providers in making informed decisions about patient care.
Understanding Protime INR Levels
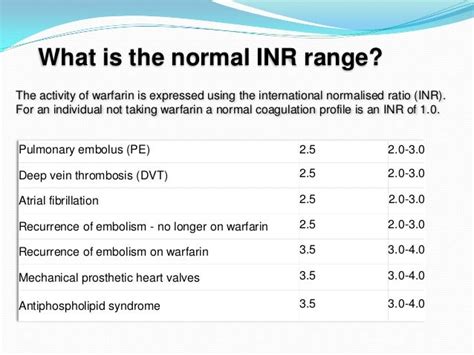
Protime INR levels are categorized based on their therapeutic range, which varies depending on the individual's health condition and the reason for taking anticoagulant medication. Generally, a normal INR range for someone not taking anticoagulants is between 0.9 and 1.1. For patients on warfarin, the target INR range is typically between 2.0 and 3.0, although this can vary. For example, individuals with mechanical heart valves may require a higher INR range, often between 2.5 and 3.5, to prevent valve thrombosis and embolism.
Interpreting INR Results
Interpreting INR results requires consideration of several factors, including the patient's medical history, current health status, and any potential drug interactions. An INR result below the therapeutic range indicates that the blood is clotting too quickly, suggesting an increased risk of thrombosis. Conversely, an INR above the therapeutic range indicates that the blood is clotting too slowly, suggesting an increased risk of bleeding. Healthcare providers use these results to adjust medication doses, ensuring that patients remain within a safe and effective therapeutic range.Factors Influencing Protime INR Levels

Several factors can influence Protime INR levels, including diet, other medications, and underlying health conditions. Foods high in vitamin K, such as leafy green vegetables, can decrease INR levels because vitamin K is essential for the production of clotting factors in the liver. Certain medications, including antibiotics and anti-inflammatory drugs, can also affect INR levels by interacting with warfarin. Additionally, health conditions like liver disease or kidney disease can impact the metabolism of warfarin, leading to fluctuations in INR levels.
Dietary Considerations
Dietary considerations play a significant role in managing Protime INR levels. Individuals taking warfarin are often advised to maintain a consistent intake of vitamin K-rich foods to minimize fluctuations in their INR. This does not mean avoiding these foods altogether but rather consuming them in a consistent manner. Other dietary factors, such as alcohol consumption and cranberry juice intake, can also affect warfarin's efficacy and should be discussed with a healthcare provider.Monitoring and Adjusting Protime INR Levels
Regular monitoring of Protime INR levels is essential for individuals on anticoagulation therapy. The frequency of testing depends on the stability of the patient's INR, their adherence to medication, and any changes in their health status or medications. Healthcare providers may adjust the dose of warfarin based on INR results to maintain a therapeutic range. It's crucial for patients to keep a record of their INR results and any dose adjustments to track their progress over time.
Importance of Patient Education
Patient education is paramount in the management of anticoagulation therapy. Understanding the importance of regular INR monitoring, the implications of dietary factors, and the potential for drug interactions can empower patients to take an active role in their care. Healthcare providers should ensure that patients are well-informed about their treatment, including how to recognize signs of bleeding or thrombosis, the importance of adherence to their medication regimen, and when to seek medical attention.Complications of Abnormal Protime INR Levels

Abnormal Protime INR levels can lead to serious complications. An INR that is too low increases the risk of thrombotic events, such as stroke or heart attack, due to the formation of blood clots. Conversely, an INR that is too high increases the risk of bleeding complications, ranging from minor bruising to life-threatening hemorrhages. Recognizing the signs of these complications, such as sudden severe headache, difficulty speaking, or uncontrolled bleeding, and seeking immediate medical attention is critical.
Prevention Strategies
Prevention strategies are key to minimizing the risk of complications associated with abnormal Protime INR levels. These include regular INR monitoring, adherence to the prescribed medication regimen, maintaining a consistent diet, avoiding unnecessary medications that could interact with warfarin, and being vigilant for signs of bleeding or thrombosis. By taking these proactive steps, individuals can significantly reduce their risk of complications and ensure the effectiveness of their anticoagulation therapy.Future Directions in Anticoagulation Therapy

The field of anticoagulation therapy is evolving, with new medications and technologies being developed to improve the management of blood clotting disorders. Direct oral anticoagulants (DOACs), such as dabigatran, rivaroxaban, and apixaban, offer alternatives to warfarin with potentially fewer dietary restrictions and less need for regular blood monitoring. However, these medications also come with their own set of considerations and potential risks, emphasizing the need for ongoing patient education and healthcare provider vigilance.
Personalized Medicine
The concept of personalized medicine is becoming increasingly relevant in the context of anticoagulation therapy. Genetic testing can help identify individuals who may be more susceptible to the effects of certain anticoagulants, allowing for tailored treatment approaches. Additionally, the development of point-of-care INR testing devices enables more frequent monitoring in various settings, potentially improving the management of anticoagulation therapy.Conclusion and Next Steps

In conclusion, understanding normal Protime INR levels is crucial for the effective management of anticoagulation therapy. By recognizing the factors that influence INR, adhering to treatment plans, and being proactive about monitoring and adjusting therapy as needed, individuals can minimize their risk of complications and improve their overall health outcomes. As the field of anticoagulation therapy continues to evolve, staying informed about the latest developments and advancements will be essential for both patients and healthcare providers.
Encouraging Engagement
We invite readers to share their experiences and questions about managing Protime INR levels in the comments section below. Your insights can help others navigate the complexities of anticoagulation therapy and foster a community of support and understanding. Additionally, consider sharing this article with friends and family who may benefit from this information, and explore other resources on this topic to deepen your knowledge and stay up-to-date on the latest research and guidelines.What is a normal Protime INR level?
+A normal Protime INR level for someone not taking anticoagulants is between 0.9 and 1.1. For patients on warfarin, the target INR range is typically between 2.0 and 3.0, although this can vary depending on the individual's health condition.
How often should I get my INR levels checked?
+The frequency of INR testing depends on the stability of your INR, your adherence to medication, and any changes in your health status or medications. Your healthcare provider will determine the best schedule for your specific situation.
