Intro
Discover the normal sugar level chart and understand blood glucose ranges, including fasting, postprandial, and random levels, to manage diabetes and maintain healthy glucose levels.
Maintaining normal sugar levels is crucial for overall health and well-being. Blood sugar levels, also known as blood glucose levels, refer to the amount of glucose present in the blood. Glucose is a type of sugar that serves as the primary source of energy for the body's cells. The body regulates blood sugar levels through a complex process involving the pancreas, liver, and other organs. Understanding normal sugar levels is essential for preventing and managing conditions like diabetes, which can have severe consequences if left uncontrolled.
The importance of maintaining normal sugar levels cannot be overstated. When blood sugar levels are within the normal range, the body functions optimally, and the risk of developing complications associated with diabetes is minimized. On the other hand, consistently high or low blood sugar levels can lead to a range of health problems, including damage to organs like the kidneys, heart, and nerves. Furthermore, normal sugar levels are essential for maintaining energy levels, supporting weight management, and ensuring proper cognitive function.
Normal sugar levels are typically measured using a blood test, which provides an accurate reading of the glucose concentration in the blood. The results are usually expressed in milligrams per deciliter (mg/dL) or millimoles per liter (mmol/L). Understanding the normal sugar level chart is vital for individuals with diabetes or those who are at risk of developing the condition. By monitoring blood sugar levels regularly, individuals can make informed decisions about their diet, exercise, and medication, ultimately helping them maintain normal sugar levels and prevent complications.
Understanding Normal Sugar Levels

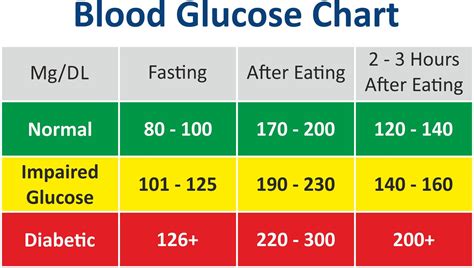
Normal sugar levels vary throughout the day, depending on factors like meal times, physical activity, and sleep. The American Diabetes Association (ADA) provides guidelines for normal blood sugar levels, which are as follows:
- Fasting blood sugar levels: Less than 100 mg/dL (5.6 mmol/L)
- Blood sugar levels after eating: Less than 140 mg/dL (7.8 mmol/L)
- Blood sugar levels before meals: 70-130 mg/dL (3.9-7.2 mmol/L) It is essential to note that these values may vary slightly depending on the individual and their specific health needs.
Factors Affecting Normal Sugar Levels
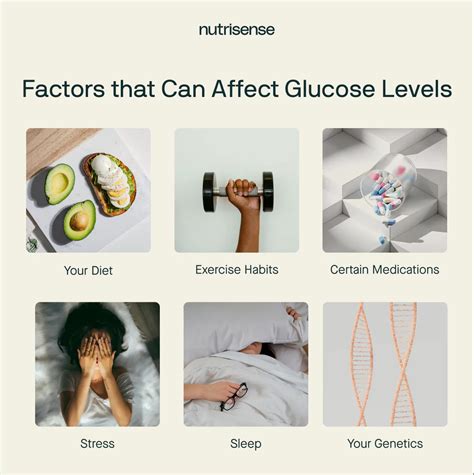
Several factors can influence normal sugar levels, including:
- Diet: Consuming high-carbohydrate or high-sugar foods can cause blood sugar levels to rise.
- Physical activity: Regular exercise can help lower blood sugar levels and improve insulin sensitivity.
- Stress: Stress can cause blood sugar levels to increase due to the release of stress hormones like cortisol.
- Sleep: Poor sleep quality or duration can disrupt blood sugar regulation and lead to increased levels.
- Medications: Certain medications, such as steroids and certain psychiatric medications, can affect blood sugar levels. Understanding these factors is crucial for maintaining normal sugar levels and preventing complications associated with diabetes.
Importance of Monitoring Blood Sugar Levels
Monitoring blood sugar levels is essential for individuals with diabetes or those who are at risk of developing the condition. Regular monitoring helps individuals:
- Understand how their body responds to different foods, physical activity, and medications
- Identify patterns and trends in their blood sugar levels
- Make informed decisions about their diet, exercise, and medication
- Prevent complications associated with diabetes, such as nerve damage, kidney disease, and vision problems There are several ways to monitor blood sugar levels, including:
- Fingertip blood glucose testing
- Continuous glucose monitoring (CGM)
- Hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c) testing
Consequences of Abnormal Sugar Levels
Abnormal sugar levels can have severe consequences, including:
- Hyperglycemia (high blood sugar): Can cause damage to organs like the kidneys, heart, and nerves
- Hypoglycemia (low blood sugar): Can cause confusion, dizziness, and even loss of consciousness
- Diabetes: Can increase the risk of heart disease, stroke, and kidney disease
- Nerve damage: Can cause numbness, tingling, and pain in the hands and feet
- Kidney damage: Can lead to kidney failure and the need for dialysis or a kidney transplant
Maintaining Normal Sugar Levels
Maintaining normal sugar levels requires a comprehensive approach that includes:
- Healthy diet: Focus on whole, unprocessed foods like vegetables, fruits, whole grains, and lean proteins
- Regular physical activity: Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise per week
- Stress management: Engage in stress-reducing activities like yoga, meditation, or deep breathing exercises
- Medication adherence: Take medications as prescribed by a healthcare provider
- Regular monitoring: Monitor blood sugar levels regularly to identify patterns and trends
Conclusion and Next Steps

In conclusion, maintaining normal sugar levels is crucial for overall health and well-being. By understanding the normal sugar level chart, factors that affect blood sugar levels, and the importance of monitoring, individuals can take control of their health and prevent complications associated with diabetes. If you have concerns about your blood sugar levels or are at risk of developing diabetes, consult with a healthcare provider to develop a personalized plan for maintaining normal sugar levels.
We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences with maintaining normal sugar levels in the comments below. If you found this article informative, please share it with others who may benefit from this information. By working together, we can promote healthy habits and prevent complications associated with diabetes.
What is the normal range for blood sugar levels?
+The normal range for blood sugar levels is less than 100 mg/dL (5.6 mmol/L) for fasting blood sugar and less than 140 mg/dL (7.8 mmol/L) for blood sugar after eating.
How often should I monitor my blood sugar levels?
+The frequency of monitoring blood sugar levels depends on individual factors, such as the type of diabetes, medication, and lifestyle. Consult with a healthcare provider to determine the best monitoring schedule for your needs.
What are the consequences of abnormal sugar levels?
+Abnormal sugar levels can lead to severe consequences, including hyperglycemia, hypoglycemia, diabetes, nerve damage, and kidney damage. It is essential to maintain normal sugar levels to prevent these complications.
