Intro
Discover key facts about Omeprazole, a proton pump inhibitor, including its uses, side effects, and interactions, to better manage heartburn, acid reflux, and GERD symptoms effectively.
Omeprazole, a medication commonly used to treat heartburn, gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), and other stomach acid-related conditions, has been a staple in many households for decades. Despite its widespread use, many people are not aware of the intricacies of this medication. Understanding how omeprazole works, its benefits, and potential side effects can help individuals make informed decisions about their health. In this article, we will delve into the world of omeprazole, exploring its mechanism of action, advantages, and considerations for use.
The importance of omeprazole lies in its ability to alleviate symptoms of acid reflux and related disorders, significantly improving the quality of life for those affected. By reducing stomach acid production, omeprazole helps heal the esophagus and prevents further damage. This medication has become a first-line treatment for many gastrointestinal issues due to its efficacy and relatively low risk of severe side effects. However, like all medications, omeprazole should be used under the guidance of a healthcare provider to maximize its benefits while minimizing potential drawbacks.
As we explore the realm of omeprazole, it's essential to consider the broader context of gastrointestinal health. The prevalence of acid reflux and GERD has been increasing, partly due to dietary habits, obesity, and lifestyle factors. Understanding the role of omeprazole within this context can provide insights into preventive measures and holistic approaches to managing these conditions. By combining medication with lifestyle changes, individuals can better manage their symptoms and reduce their reliance on medication over time.
Omeprazole Mechanism of Action
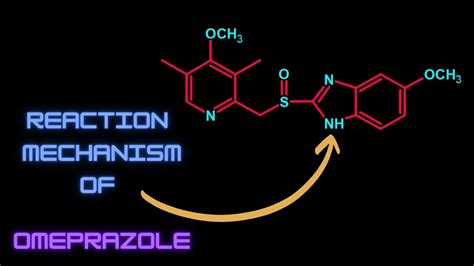
How Omeprazole Reduces Stomach Acid
The reduction of stomach acid by omeprazole is not immediate. It takes about one to four days for the medication to reach its full effect, as it needs time to bind to all the proton pumps in the stomach lining. Once the proton pumps are inhibited, they cannot produce acid until new pumps are produced, which can take several days. This delayed onset of action is why it's essential to take omeprazole as directed by a healthcare provider, typically in the morning before eating, to ensure optimal effectiveness throughout the day.Benefits of Omeprazole

Common Uses of Omeprazole
Omeprazole is indicated for the treatment of several conditions, including: - Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) - Erosive esophagitis - Zollinger-Ellison syndrome, a rare condition characterized by excessive acid production - Duodenal and gastric ulcers - Helicobacter pylori infection, often in combination with antibioticsPotential Side Effects of Omeprazole
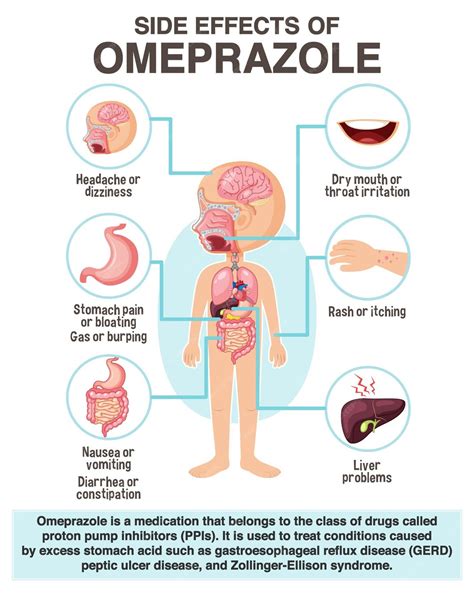
Precautions and Interactions
It's crucial to inform your healthcare provider about all medications, vitamins, and supplements you're taking, as omeprazole can interact with several substances, including: - Antifungals - Antiplatelet agents - Diazepam - Phenytoin - Warfarin Pregnant or breastfeeding women should consult their healthcare provider before taking omeprazole, as there is limited data on its safety during these periods.Lifestyle Changes to Enhance Omeprazole Effectiveness

Dietary Recommendations
A diet low in trigger foods and high in alkaline foods can help manage acid reflux symptoms. Alkaline foods include: - Leafy greens - Almonds - Fatty fish - Sweet potatoes - Ginger - Aloe vera juiceAlternatives to Omeprazole
Future Directions in Acid Reflux Treatment
Research into new treatments for acid reflux and GERD is ongoing. Some promising areas include: - Novel PPIs with improved safety profiles - Drugs that enhance the barrier function of the esophagus - Endoscopic and surgical procedures to tighten the lower esophageal sphincter - Personalized medicine approaches based on genetic predispositions and individual responses to treatmentConclusion and Next Steps
We encourage readers to share their experiences with omeprazole and acid reflux management in the comments below. Your insights can help others navigate their treatment journeys. If you found this article informative, please consider sharing it with friends and family who may benefit from this information. Together, we can promote better health and well-being.
What is the primary mechanism of action of omeprazole?
+Omeprazole works by inhibiting the proton pump in the gastric parietal cells, thereby reducing stomach acid production.
Can omeprazole be used during pregnancy?
+Pregnant women should consult their healthcare provider before taking omeprazole, as there is limited data on its safety during pregnancy.
What lifestyle changes can enhance the effectiveness of omeprazole?
+Lifestyle changes such as maintaining a healthy weight, eating smaller meals, avoiding trigger foods, and elevating the head of the bed can help manage acid reflux symptoms and enhance the effectiveness of omeprazole.
