Intro
Discover Oxybutynin 10mg Tablet Uses for overactive bladder treatment, managing urinary incontinence, and relieving symptoms of spasmodic bladder conditions, including frequency and urgency.
Oxybutynin 10mg tablets are a type of medication that belongs to the class of anticholinergics, also known as antimuscarinics. These medications work by relaxing the muscles in the bladder and urinary tract, helping to alleviate symptoms associated with overactive bladder and other urinary disorders. The importance of oxybutynin 10mg tablets lies in their ability to provide relief from symptoms such as frequent urination, urgent need to urinate, and leakage of urine. This makes them a crucial treatment option for individuals suffering from these conditions, significantly improving their quality of life.
The use of oxybutynin 10mg tablets is not limited to overactive bladder; they can also be prescribed for other conditions such as neurogenic bladder, which is caused by a brain, spinal cord, or nerve problem. Understanding how these tablets work and their benefits can help individuals manage their symptoms more effectively. Moreover, knowing the potential side effects and how to mitigate them is crucial for maximizing the therapeutic benefits of oxybutynin while minimizing its drawbacks.
Oxybutynin 10mg tablets have been extensively studied, and their efficacy in treating overactive bladder symptoms has been well-documented. The mechanism of action involves the selective inhibition of muscarinic receptors, which are responsible for the contraction of bladder muscles. By blocking these receptors, oxybutynin reduces the frequency of bladder contractions, thereby decreasing the urgent need to urinate and the incidence of incontinence episodes. This pharmacological action makes oxybutynin a valuable asset in the management of urinary disorders, offering patients a chance to regain control over their bladder function and reduce the emotional and social distress associated with these conditions.
Oxybutynin Mechanism of Action
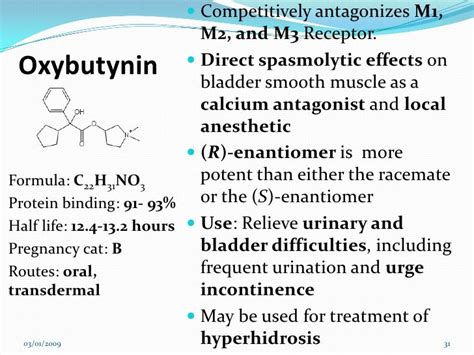
The mechanism of action of oxybutynin involves its ability to act as an antagonist to muscarinic acetylcholine receptors. These receptors are found in the bladder and other smooth muscles, and their activation leads to muscle contraction. By blocking these receptors, oxybutynin decreases the muscle spasms of the bladder and the urinary tract, which in turn reduces the symptoms of overactive bladder. This antimuscarinic effect is the primary therapeutic action of oxybutynin, making it an effective treatment for managing urinary frequency, urgency, and incontinence.
Benefits of Oxybutynin
The benefits of oxybutynin 10mg tablets are multifaceted, offering patients significant relief from the symptoms of overactive bladder and other urinary disorders. Some of the key benefits include: - Reduced frequency of urination: By decreasing the number of times a patient needs to urinate, oxybutynin improves the quality of life, allowing for more uninterrupted sleep and less disruption during daily activities. - Decreased urgency: The urgent need to urinate can be distressing and disrupt daily life. Oxybutynin helps in reducing this urgency, giving patients more time to reach the bathroom. - Increased bladder capacity: Oxybutynin helps in increasing the bladder's capacity to hold urine, which reduces the frequency of urination and leakage.Oxybutynin Side Effects

While oxybutynin 10mg tablets are effective in managing overactive bladder symptoms, they can also cause side effects. The most common side effects include dry mouth, constipation, and drowsiness. These side effects are generally mild and temporary, but in some cases, they can be more severe. It's essential for patients to discuss any side effects they experience with their healthcare provider, as adjustments to the dosage or switching to a different medication may be necessary.
Managing Side Effects
Managing the side effects of oxybutynin involves a combination of lifestyle adjustments and, in some cases, medical interventions. For example, to manage dry mouth, patients can increase their fluid intake, suck on sugar-free candies, or use a saliva substitute. For constipation, a high-fiber diet, adequate fluid intake, and regular physical activity can help. If side effects persist or worsen, patients should consult their healthcare provider for guidance.Oxybutynin Dosage and Administration
The dosage and administration of oxybutynin 10mg tablets are crucial for their effectiveness and safety. The typical dosage is one 10mg tablet taken two to three times a day, but this can vary based on the patient's response to the medication and their individual health status. It's essential to follow the healthcare provider's instructions regarding dosage and not to adjust it without consultation. Oxybutynin can be taken with or without food, but taking it with food may help reduce stomach upset.
Precautions and Contraindications
Before starting oxybutynin, patients should inform their healthcare provider about any medical conditions they have, especially those related to the bladder, stomach, or intestines, as well as any medications they are currently taking. Oxybutynin is contraindicated in patients with urinary retention, gastric retention, or uncontrolled narrow-angle glaucoma. Additionally, caution should be exercised in patients with autonomic neuropathy, hepatic or renal impairment, and myasthenia gravis.Oxybutynin Interactions
Oxybutynin can interact with other medications, which may lead to increased side effects or reduced efficacy. Patients should provide their healthcare provider with a list of all medications, supplements, and vitamins they are taking. Notable interactions include other anticholinergic medications, which can increase the risk of side effects, and drugs that affect the liver enzymes, which can alter the levels of oxybutynin in the blood.
Practical Considerations
Practically, patients taking oxybutynin should be aware of the potential for interactions and side effects. Keeping a medication journal can help track any changes or concerns, which can then be discussed with the healthcare provider. Regular follow-up appointments are also crucial for monitoring the effectiveness of the treatment and adjusting the dosage as needed.Oxybutynin and Pregnancy

The use of oxybutynin during pregnancy should be approached with caution. While oxybutynin is classified as a category B medication, meaning that animal reproduction studies have failed to demonstrate a risk to the fetus and there are no adequate and well-controlled studies in pregnant women, it is generally recommended to use oxybutynin during pregnancy only if clearly needed. The potential benefits to the mother must be weighed against the potential risks to the fetus. Patients who become pregnant while taking oxybutynin should inform their healthcare provider immediately.
Breastfeeding Considerations
For breastfeeding mothers, oxybutynin is excreted in breast milk, but the levels are generally considered to be low. However, because of the potential for anticholinergic effects in the infant, oxybutynin should be used with caution in breastfeeding mothers. The decision to use oxybutynin during breastfeeding should be made after consulting a healthcare provider, considering the benefits of the medication to the mother and the potential risks to the infant.Oxybutynin Alternatives

For patients who experience significant side effects or do not respond adequately to oxybutynin, there are alternative treatments available. Other antimuscarinic medications, such as tolterodine, solifenacin, and darifenacin, can be considered. Additionally, beta-3 adrenergic agonists like mirabegron offer a different mechanism of action with potentially fewer side effects. In some cases, combination therapy may be recommended. The choice of alternative medication depends on the patient's specific condition, medical history, and response to previous treatments.
Future Directions
The future of oxybutynin and other treatments for overactive bladder involves ongoing research into new medications and therapies that can offer improved efficacy and tolerability. Advances in drug delivery systems and the development of medications with more targeted actions may provide patients with more options and better outcomes. Moreover, a greater understanding of the pathophysiology of overactive bladder will help in developing more effective treatment strategies.Oxybutynin Conclusion and Recommendations

In conclusion, oxybutynin 10mg tablets are a valuable treatment option for individuals suffering from overactive bladder and other urinary disorders. By understanding the mechanism of action, benefits, potential side effects, and precautions, patients can work closely with their healthcare providers to maximize the therapeutic benefits of oxybutynin while minimizing its drawbacks. As with any medication, it's crucial to follow the prescribed dosage and administration instructions and to attend regular follow-up appointments to monitor the treatment's effectiveness and adjust the treatment plan as necessary.
We invite readers to share their experiences or ask questions about oxybutynin and its uses in the comments below. Your input can help others better understand this medication and its role in managing urinary disorders. Additionally, feel free to share this article with anyone who might benefit from the information provided, and consider exploring other resources on our site for more detailed information on health and wellness topics.
What is oxybutynin used for?
+Oxybutynin is used to treat overactive bladder and its symptoms, including frequent urination, urgent need to urinate, and leakage of urine.
How does oxybutynin work?
+Oxybutynin works by relaxing the muscles in the bladder, which helps to increase the amount of urine the bladder can hold and reduces the need to urinate as often.
What are the common side effects of oxybutynin?
+Common side effects of oxybutynin include dry mouth, constipation, and drowsiness. These side effects are generally mild and temporary but can be more severe in some cases.
Can oxybutynin be used during pregnancy?
+Oxybutynin should be used during pregnancy only if clearly needed, as the potential benefits to the mother must be weighed against the potential risks to the fetus.
Are there alternatives to oxybutynin?
+Yes, there are alternative medications and therapies for overactive bladder, including other antimuscarinic medications and beta-3 adrenergic agonists. The choice of alternative depends on the patient's specific condition and response to previous treatments.
