Intro
Dysuria, or painful urination, is a symptom of urinary tract issues, including UTIs, kidney stones, and prostate problems, characterized by burning sensations, frequent urination, and discomfort.
Painful urination, also known as dysuria, is a common symptom that affects millions of people worldwide. It is characterized by a burning sensation or discomfort while urinating, which can be a sign of an underlying medical condition. Dysuria can be caused by a variety of factors, including infections, inflammation, and obstruction of the urinary tract. In this article, we will delve into the world of painful urination, exploring its causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options.
The importance of addressing dysuria cannot be overstated. If left untreated, it can lead to more severe complications, such as kidney damage, sepsis, and even infertility. Furthermore, dysuria can significantly impact a person's quality of life, causing discomfort, anxiety, and embarrassment. Therefore, it is essential to seek medical attention if you are experiencing painful urination, as early diagnosis and treatment can make a significant difference in preventing long-term damage and promoting overall well-being.
Dysuria can affect anyone, regardless of age or sex. However, some individuals are more prone to experiencing painful urination due to various factors, such as genetics, lifestyle, and underlying medical conditions. For instance, women are more likely to experience dysuria due to urinary tract infections (UTIs), while men may be more susceptible to prostate-related issues. Understanding the risk factors and causes of dysuria is crucial in preventing and managing this condition.
Causes of Dysuria

Dysuria can be caused by a variety of factors, including:
- Urinary tract infections (UTIs): Bacterial, viral, or fungal infections that affect the urinary tract, including the kidneys, bladder, and urethra.
- Kidney stones: Small, hard mineral deposits that can cause obstruction and inflammation in the urinary tract.
- Prostate issues: Enlargement, infection, or cancer of the prostate gland can cause dysuria in men.
- Interstitial cystitis: A chronic condition characterized by inflammation and irritation of the bladder wall.
- Urethral stricture: A narrowing of the urethra, which can cause obstructed urine flow and pain.
Types of Dysuria
Dysuria can be classified into different types, including: * Internal dysuria: Pain or discomfort felt inside the body, often in the pelvic area or abdomen. * External dysuria: Pain or discomfort felt outside the body, often in the genital area or perineum. * Terminal dysuria: Pain or discomfort felt at the end of urination. * Initial dysuria: Pain or discomfort felt at the beginning of urination.Symptoms of Dysuria
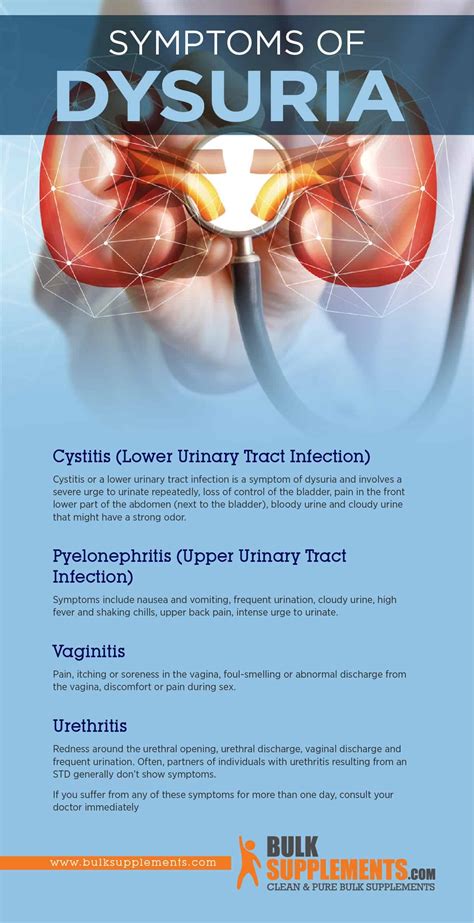
The symptoms of dysuria can vary depending on the underlying cause. Common symptoms include:
- Burning sensation or pain while urinating
- Discomfort or pain in the pelvic area, abdomen, or genital area
- Frequent or urgent need to urinate
- Cloudy, dark, or foul-smelling urine
- Blood in the urine
- Fever, chills, or flank pain
Diagnosis of Dysuria
Diagnosing dysuria typically involves a combination of physical examination, medical history, and diagnostic tests. These may include: * Urinalysis: A test to analyze the urine for signs of infection, blood, or other abnormalities. * Urine culture: A test to identify the presence of bacteria or other microorganisms in the urine. * Imaging studies: Such as X-rays, ultrasound, or CT scans to visualize the urinary tract and detect any obstructions or abnormalities. * Cystoscopy: A procedure to visually examine the inside of the bladder and urethra.Treatment Options for Dysuria

Treatment for dysuria depends on the underlying cause. Common treatment options include:
- Antibiotics: To treat bacterial infections, such as UTIs.
- Pain relief medications: To manage pain and discomfort.
- Anti-inflammatory medications: To reduce inflammation and swelling.
- Surgical intervention: To remove kidney stones, repair urethral strictures, or treat other underlying conditions.
- Lifestyle modifications: Such as increasing fluid intake, practicing good hygiene, and avoiding irritants.
Prevention of Dysuria
Preventing dysuria involves practicing good hygiene, staying hydrated, and avoiding irritants. Some tips include: * Drinking plenty of water to help flush out bacteria and other microorganisms. * Wiping correctly after using the bathroom to prevent bacterial spread. * Avoiding tight clothing and irritants, such as scented soaps or bubble baths. * Practicing safe sex to reduce the risk of sexually transmitted infections. * Getting regular check-ups to monitor urinary tract health.Complications of Dysuria
If left untreated, dysuria can lead to more severe complications, such as:
- Kidney damage: Bacterial infections or other conditions can cause permanent damage to the kidneys.
- Sepsis: A life-threatening condition that occurs when bacteria enter the bloodstream.
- Infertility: Untreated infections or conditions can affect fertility in both men and women.
- Chronic pain: Dysuria can lead to chronic pain and discomfort, affecting quality of life.
Living with Dysuria
Living with dysuria requires managing symptoms, preventing complications, and maintaining overall urinary tract health. Some tips include: * Keeping a symptom journal to track pain and discomfort. * Practicing stress-reducing techniques, such as meditation or deep breathing. * Staying hydrated and avoiding irritants. * Seeking support from healthcare providers, support groups, or online resources.What is the most common cause of dysuria?
+Urinary tract infections (UTIs) are the most common cause of dysuria, accounting for approximately 80-90% of cases.
Can dysuria be a sign of a more serious condition?
+Yes, dysuria can be a sign of a more serious condition, such as kidney stones, prostate issues, or interstitial cystitis. It is essential to seek medical attention if symptoms persist or worsen over time.
How can I prevent dysuria?
+Preventing dysuria involves practicing good hygiene, staying hydrated, and avoiding irritants. Drinking plenty of water, wiping correctly after using the bathroom, and avoiding tight clothing can help reduce the risk of developing dysuria.
In conclusion, dysuria is a common symptom that can significantly impact a person's quality of life. Understanding the causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options is essential in preventing and managing this condition. By seeking medical attention, practicing good hygiene, and maintaining overall urinary tract health, individuals can reduce the risk of developing dysuria and its complications. We invite you to share your experiences, ask questions, or seek support in the comments below. Together, we can promote awareness and education about dysuria, empowering individuals to take control of their urinary tract health.
