Intro
Learn about Heart Ablation Procedure, a minimally invasive catheter ablation treatment for arrhythmia, including benefits, risks, and recovery, to restore normal heart rhythm and improve cardiovascular health.
The heart is a vital organ that pumps blood throughout the body, and any irregularities in its rhythm can lead to serious health complications. One of the most effective treatments for irregular heartbeats, also known as arrhythmias, is a procedure called heart ablation. In this article, we will delve into the world of heart ablation, exploring its benefits, working mechanisms, and steps involved in the procedure.
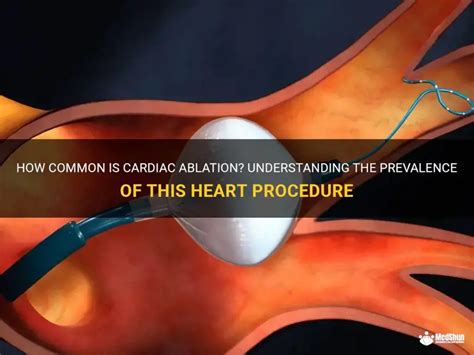
Heart ablation is a minimally invasive procedure that aims to destroy or scar the abnormal electrical pathways in the heart that cause arrhythmias. This procedure has become a popular treatment option for patients with arrhythmias, as it can significantly improve their quality of life. With the advancement of medical technology, heart ablation has become a highly effective and safe procedure, with a high success rate in treating various types of arrhythmias.
The importance of heart ablation cannot be overstated, as it has revolutionized the treatment of arrhythmias. Before the advent of heart ablation, patients with arrhythmias had limited treatment options, and their conditions were often managed with medications or implantable devices. However, with the development of heart ablation, patients can now undergo a procedure that can potentially cure their arrhythmia, eliminating the need for long-term medication or device therapy. This has significantly improved the quality of life for patients with arrhythmias, allowing them to return to their normal activities and enjoy a healthier lifestyle.
What is Heart Ablation?
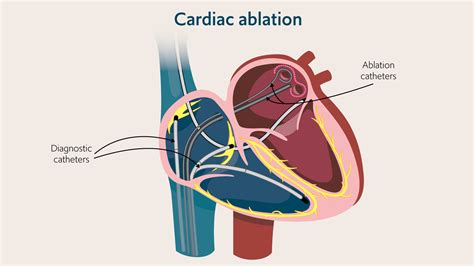
There are several types of heart ablation procedures, including radiofrequency ablation, cryoablation, and laser ablation. Radiofrequency ablation is the most common type of heart ablation, which uses high-frequency energy to heat and destroy the abnormal electrical pathways. Cryoablation, on the other hand, uses extreme cold to freeze and scar the abnormal electrical pathways. Laser ablation is a newer type of heart ablation that uses a laser to destroy the abnormal electrical pathways.
Benefits of Heart Ablation
The benefits of heart ablation are numerous, and the procedure has revolutionized the treatment of arrhythmias. Some of the benefits of heart ablation include: * Improved quality of life: Heart ablation can significantly improve the quality of life for patients with arrhythmias, allowing them to return to their normal activities and enjoy a healthier lifestyle. * Reduced symptoms: Heart ablation can reduce or eliminate the symptoms of arrhythmias, such as palpitations, shortness of breath, and fatigue. * Reduced risk of complications: Heart ablation can reduce the risk of complications associated with arrhythmias, such as stroke and heart failure. * Minimally invasive: Heart ablation is a minimally invasive procedure, which means that it does not require open-heart surgery.How Does Heart Ablation Work?
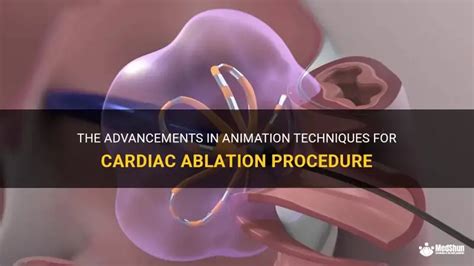
The steps involved in heart ablation include:
- Preparation: The patient is prepared for the procedure by removing any clothing or jewelry that may interfere with the procedure.
- Sedation: The patient is given sedation to help them relax during the procedure.
- Catheter insertion: The catheter is inserted through a vein in the leg and guided to the heart using X-ray imaging.
- Mapping: The catheter is used to map the electrical pathways in the heart, identifying the abnormal pathways that cause the arrhythmia.
- Ablation: The catheter uses energy to destroy or scar the abnormal electrical pathways, restoring a normal heart rhythm.
- Monitoring: The patient is monitored during and after the procedure to ensure that the arrhythmia has been successfully treated.
Risks and Complications of Heart Ablation
While heart ablation is a highly effective and safe procedure, there are some risks and complications associated with it. Some of the risks and complications of heart ablation include: * Bleeding or hemorrhage: There is a risk of bleeding or hemorrhage at the site where the catheter is inserted. * Infection: There is a risk of infection with any medical procedure, including heart ablation. * Damage to the heart: There is a risk of damage to the heart or its electrical pathways during the procedure. * Recurrence of arrhythmia: There is a risk that the arrhythmia may recur after the procedure.Types of Heart Ablation
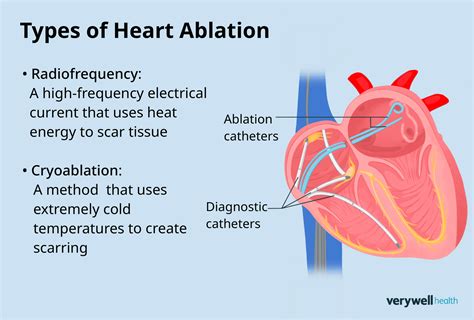
Who is a Candidate for Heart Ablation?
Heart ablation is a highly effective treatment option for patients with arrhythmias, but it is not suitable for everyone. Some of the factors that determine whether a patient is a candidate for heart ablation include: * Type of arrhythmia: Heart ablation is most effective for treating certain types of arrhythmias, such as supraventricular tachycardia and atrial fibrillation. * Severity of symptoms: Patients with severe symptoms, such as palpitations, shortness of breath, and fatigue, may be good candidates for heart ablation. * Medical history: Patients with a history of heart disease, high blood pressure, or other medical conditions may not be suitable candidates for heart ablation. * Age and overall health: Patients who are older or have underlying medical conditions may not be suitable candidates for heart ablation.Recovery After Heart Ablation

Long-Term Results of Heart Ablation
The long-term results of heart ablation are highly effective, with most patients experiencing a significant reduction or elimination of their arrhythmia symptoms. Some of the long-term benefits of heart ablation include: * Improved quality of life: Heart ablation can significantly improve the quality of life for patients with arrhythmias, allowing them to return to their normal activities and enjoy a healthier lifestyle. * Reduced risk of complications: Heart ablation can reduce the risk of complications associated with arrhythmias, such as stroke and heart failure. * Reduced need for medication: Heart ablation can reduce or eliminate the need for medication to manage arrhythmia symptoms.Conclusion and Next Steps
We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences with heart ablation in the comments section below. If you have any questions or concerns about heart ablation, please do not hesitate to ask. We are here to provide you with the information and support you need to make informed decisions about your health.
What is heart ablation?
+Heart ablation is a medical procedure that uses energy to destroy or scar the abnormal electrical pathways in the heart that cause arrhythmias.
What are the benefits of heart ablation?
+The benefits of heart ablation include improved quality of life, reduced symptoms, reduced risk of complications, and a minimally invasive procedure.
What are the risks and complications of heart ablation?
+The risks and complications of heart ablation include bleeding or hemorrhage, infection, damage to the heart, and recurrence of arrhythmia.
Who is a candidate for heart ablation?
+Heart ablation is a suitable treatment option for patients with certain types of arrhythmias, such as supraventricular tachycardia and atrial fibrillation, who have severe symptoms and are in good overall health.
What is the recovery like after heart ablation?
+The recovery after heart ablation is typically quick and straightforward, with most patients returning home the same day or the next day after the procedure.
