Intro
Discover how PFO affects health in 5 significant ways, including stroke risk, migraine links, and oxygenation issues, impacting overall well-being and cardiovascular health.
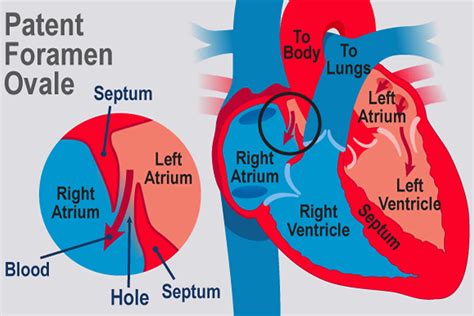
The importance of understanding the impact of PFO (Patent Foramen Ovale) on health cannot be overstated. PFO is a hole in the heart that didn't close the way it should after birth, and it can have significant effects on a person's overall well-being. While some people may not experience any symptoms, others may be at risk of serious health complications. In this article, we will delve into the world of PFO and explore how it can affect health in various ways.
PFO is a relatively common condition, affecting approximately 25% of the population. However, many people are unaware that they have a PFO, as it often doesn't produce any noticeable symptoms. Nevertheless, it's crucial to understand the potential risks associated with PFO, as it can increase the likelihood of certain health issues. From stroke and migraine to decompression sickness and platypnea orthodeoxia, the effects of PFO on health are diverse and multifaceted.
As we navigate the complexities of PFO, it's essential to recognize the various ways it can impact health. By understanding the benefits and risks of PFO closure, as well as the symptoms and treatment options available, individuals can take proactive steps to manage their condition and reduce their risk of complications. Whether you're someone who has been diagnosed with PFO or simply wants to learn more about this condition, this article aims to provide a comprehensive overview of the ways PFO can affect health.
Introduction to PFO
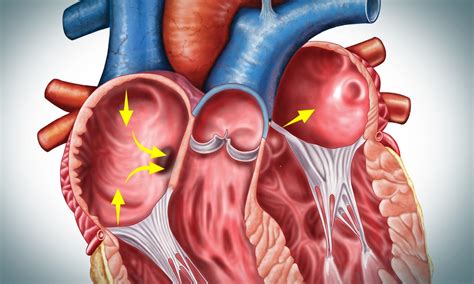
Types of PFO
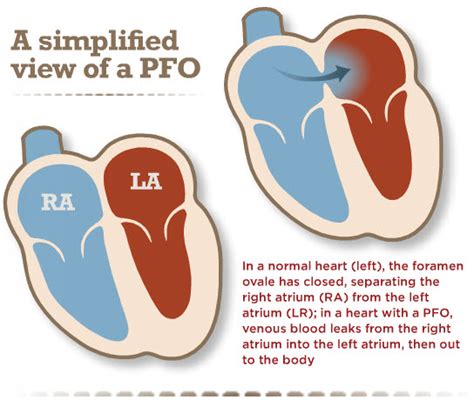
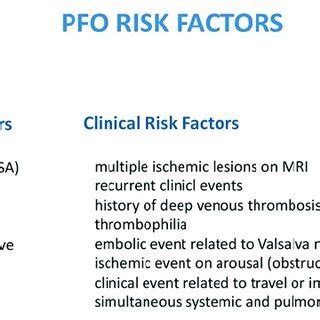
Causes and Risk Factors of PFO
Symptoms of PFO
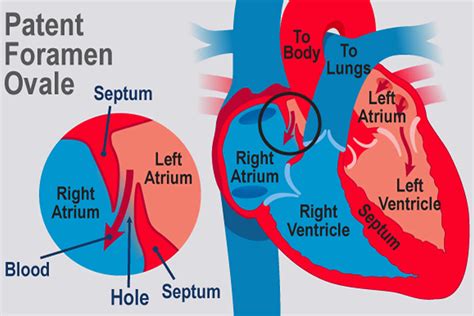
Diagnosis and Treatment of PFO
PFO Closure Devices
PFO closure devices are small, implantable devices that are used to close the PFO. These devices are typically made of metal or fabric and are implanted through a minimally invasive procedure. The most common types of PFO closure devices include: * Amplatzer PFO Occluder * Gore HELEX Septal Occluder * STARFlex Septal Closure SystemPFO Closure Surgery
PFO closure surgery is a more invasive procedure that involves closing the PFO using sutures or a patch. This procedure is typically performed under general anesthesia and requires a longer recovery time than PFO closure device implantation.Benefits and Risks of PFO Closure

Living with PFO
As we conclude our exploration of the ways PFO can affect health, we invite you to share your thoughts and experiences with us. Whether you're someone who has been diagnosed with PFO or simply wants to learn more about this condition, we encourage you to comment below or share this article with others. By working together, we can raise awareness about PFO and promote a better understanding of this complex and multifaceted condition.
What is PFO, and how is it diagnosed?
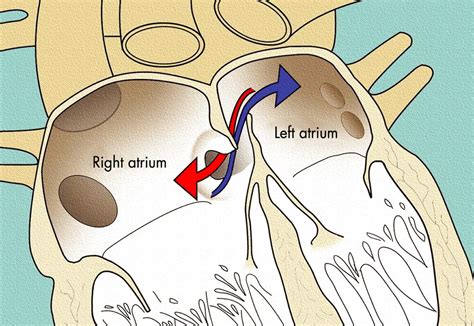
+PFO is a congenital heart defect that occurs when the foramen ovale, a natural opening between the upper chambers of the heart, fails to close after birth. It can be diagnosed using various tests, including echocardiography, transesophageal echocardiography, and cardiac catheterization.
What are the symptoms of PFO, and how are they treated?
+The symptoms of PFO can vary, but may include stroke or TIA, migraine with aura, decompression sickness, and platypnea orthodeoxia. Treatment options depend on the size and location of the defect, as well as the individual's overall health, and may include watchful waiting, medications, or PFO closure.
What are the benefits and risks of PFO closure, and is it right for me?
+PFO closure can offer several benefits, including reduced risk of stroke and TIA, improved symptoms of migraine and decompression sickness, and reduced risk of platypnea orthodeoxia. However, it also carries certain risks, including bleeding or hematoma at the implantation site, infection or endocarditis, and device malfunction or failure. Whether PFO closure is right for you depends on your individual circumstances and should be discussed with a healthcare provider.
