Intro
Learn about Pericardial Effusion symptoms, causes, and treatment. Discover signs like chest pain, fatigue, and shortness of breath, and understand diagnostic tests for this heart condition, including echocardiogram and cardiac MRI.
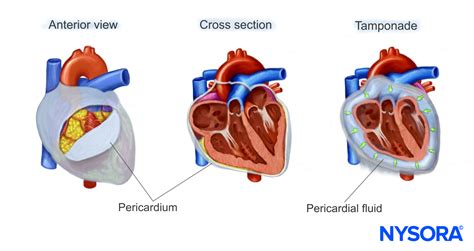
The human body is a complex and fascinating system, with various organs and structures working together to maintain overall health. One such structure is the pericardium, a sac that surrounds the heart and plays a crucial role in its functioning. However, certain conditions can affect the pericardium, leading to issues such as pericardial effusion. This condition occurs when an abnormal amount of fluid accumulates in the pericardial space, which can lead to various symptoms and complications. Understanding these symptoms is essential for early diagnosis and treatment.
Pericardial effusion can be caused by a range of factors, including infections, inflammation, trauma, and certain medical conditions. The symptoms of pericardial effusion can vary depending on the underlying cause and the severity of the condition. Some people may experience mild symptoms, while others may have more severe and life-threatening complications. It is essential to recognize the symptoms of pericardial effusion and seek medical attention promptly if they occur. Early diagnosis and treatment can help prevent long-term damage to the heart and improve outcomes.
The importance of understanding pericardial effusion symptoms cannot be overstated. Pericardial effusion can lead to serious complications, such as cardiac tamponade, which can be life-threatening if left untreated. Cardiac tamponade occurs when the fluid in the pericardial space compresses the heart, preventing it from functioning properly. This can lead to a range of symptoms, including chest pain, shortness of breath, and fatigue. By recognizing the symptoms of pericardial effusion and seeking medical attention promptly, individuals can reduce their risk of developing complications and improve their overall health outcomes.
Introduction to Pericardial Effusion
Causes of Pericardial Effusion
Pericardial effusion can be caused by a range of factors, including: * Infections, such as bacterial, viral, or fungal infections * Inflammation, such as pericarditis * Trauma, such as a blow to the chest * Certain medical conditions, such as cancer, kidney disease, or autoimmune disorders * Surgery or other medical procedures * Certain medications, such as diuretics or anticoagulantsSymptoms of Pericardial Effusion

Diagnosis of Pericardial Effusion
Diagnosing pericardial effusion involves a range of tests and procedures, including: * Chest X-ray or computed tomography (CT) scan to visualize the heart and pericardium * Electrocardiogram (ECG) to assess heart function * Echocardiogram to evaluate heart function and detect fluid accumulation * Blood tests to check for signs of infection or inflammation * Pericardiocentesis, which involves removing fluid from the pericardial space using a needleTreatment of Pericardial Effusion
Complications of Pericardial Effusion
Pericardial effusion can lead to serious complications, including: * Cardiac tamponade, which can be life-threatening if left untreated * Constrictive pericarditis, which can lead to chronic inflammation and scarring of the pericardium * Recurrent pericardial effusion, which can occur if the underlying cause is not treatedPrevention of Pericardial Effusion
Living with Pericardial Effusion
Living with pericardial effusion requires ongoing management and monitoring to prevent complications and improve outcomes. Individuals with pericardial effusion should: * Work closely with their healthcare provider to manage underlying conditions and prevent complications * Attend regular follow-up appointments to monitor heart function and fluid accumulation * Take medications as directed to reduce inflammation or treat underlying conditions * Avoid strenuous activities or heavy lifting to reduce the risk of trauma to the chestWhat is pericardial effusion?
+Pericardial effusion is a condition characterized by the accumulation of excess fluid in the pericardial space, which is the area between the pericardium and the heart.
What are the symptoms of pericardial effusion?
+The symptoms of pericardial effusion can include chest pain or discomfort, shortness of breath or difficulty breathing, fatigue or weakness, palpitations or irregular heartbeat, and swelling in the legs or ankles.
How is pericardial effusion diagnosed?
+Diagnosing pericardial effusion involves a range of tests and procedures, including chest X-ray or computed tomography (CT) scan, electrocardiogram (ECG), echocardiogram, blood tests, and pericardiocentesis.
What are the complications of pericardial effusion?
+Pericardial effusion can lead to serious complications, including cardiac tamponade, constrictive pericarditis, and recurrent pericardial effusion.
How can pericardial effusion be prevented?
+Preventing pericardial effusion involves managing underlying medical conditions, such as infections or inflammation, and avoiding trauma to the chest. Individuals can also take steps to reduce their risk of developing pericardial effusion, such as practicing good hygiene and getting vaccinated against infections.
In conclusion, pericardial effusion is a serious medical condition that requires prompt attention and treatment. By understanding the symptoms, causes, and complications of pericardial effusion, individuals can take steps to reduce their risk of developing the condition and improve their overall health outcomes. If you or someone you know is experiencing symptoms of pericardial effusion, it is essential to seek medical attention promptly. We encourage you to share this article with others, and we invite you to comment below with any questions or concerns you may have. Together, we can work to raise awareness and promote education about pericardial effusion and other important health topics.
