Intro
Explore pre diabetic medication options, including metformin and lifestyle changes, to manage blood sugar levels and prevent type 2 diabetes, improving insulin sensitivity and overall health.
Pre-diabetes is a condition where blood sugar levels are higher than normal, but not high enough to be classified as diabetes. It is a warning sign that an individual is at risk of developing type 2 diabetes, and it is essential to take action to prevent or delay the onset of the disease. One of the ways to manage pre-diabetes is through medication. In this article, we will explore the various pre-diabetic medication options available, their benefits, and potential side effects.
Pre-diabetes is a significant health concern, affecting millions of people worldwide. If left untreated, it can lead to the development of type 2 diabetes, which increases the risk of heart disease, stroke, kidney damage, and other complications. The good news is that pre-diabetes can be managed, and medication can play a crucial role in preventing or delaying the onset of type 2 diabetes. With the right treatment and lifestyle changes, individuals with pre-diabetes can reduce their risk of developing the disease and improve their overall health.
The importance of managing pre-diabetes cannot be overstated. It is a critical step in preventing the development of type 2 diabetes and its associated complications. By understanding the various pre-diabetic medication options available, individuals can make informed decisions about their treatment and work with their healthcare providers to develop a personalized plan. This plan may include medication, lifestyle changes, or a combination of both. With the right approach, individuals with pre-diabetes can take control of their health and reduce their risk of developing type 2 diabetes.
Understanding Pre-Diabetic Medication Options
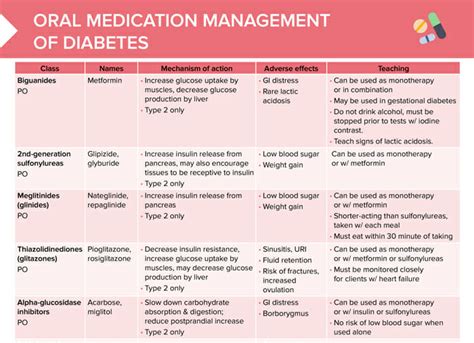
Pre-diabetic medication options are designed to help individuals manage their blood sugar levels and prevent or delay the onset of type 2 diabetes. These medications work in different ways, such as improving insulin sensitivity, reducing glucose production in the liver, or slowing the absorption of glucose from the gut. Some of the most commonly prescribed pre-diabetic medications include metformin, sulfonylureas, meglitinides, thiazolidinediones, and alpha-glucosidase inhibitors.
Metformin: The First-Line Treatment
Metformin is often the first-line treatment for pre-diabetes, as it has been shown to be effective in improving insulin sensitivity and reducing glucose production in the liver. It is also relatively inexpensive and has a long history of safe use. Metformin works by decreasing the amount of glucose produced by the liver and increasing the body's sensitivity to insulin. This helps to lower blood sugar levels and reduce the risk of developing type 2 diabetes.Benefits and Side Effects of Pre-Diabetic Medications

While pre-diabetic medications can be effective in managing blood sugar levels, they can also have potential side effects. For example, metformin can cause gastrointestinal side effects such as diarrhea, nausea, and abdominal pain. Sulfonylureas can cause hypoglycemia (low blood sugar), while meglitinides can cause weight gain and hypoglycemia. Thiazolidinediones can cause weight gain, fluid retention, and an increased risk of heart failure. Alpha-glucosidase inhibitors can cause gastrointestinal side effects such as bloating, gas, and diarrhea.
Lifestyle Changes: A Crucial Component of Pre-Diabetes Management
In addition to medication, lifestyle changes play a crucial role in managing pre-diabetes. These changes include eating a healthy diet, exercising regularly, losing weight, and quitting smoking. A healthy diet should focus on whole, unprocessed foods such as vegetables, fruits, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats. Regular exercise, such as brisk walking, cycling, or swimming, can help improve insulin sensitivity and reduce blood sugar levels. Losing weight, particularly around the abdominal area, can also help improve insulin sensitivity and reduce the risk of developing type 2 diabetes.Alternative Therapies for Pre-Diabetes
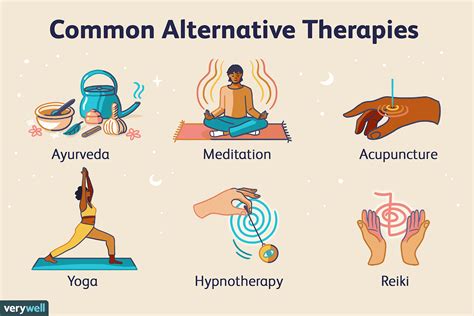
In addition to conventional medications and lifestyle changes, alternative therapies may also be effective in managing pre-diabetes. These therapies include acupuncture, herbal supplements, and mind-body therapies such as yoga and meditation. Acupuncture has been shown to improve insulin sensitivity and reduce blood sugar levels, while herbal supplements such as berberine and chromium may also have a beneficial effect. Mind-body therapies such as yoga and meditation can help reduce stress and improve overall well-being, which can also help manage blood sugar levels.
Monitoring and Adjusting Treatment
Monitoring and adjusting treatment is a critical component of pre-diabetes management. Regular blood sugar monitoring can help track progress and identify any potential issues. Adjusting medication or lifestyle changes as needed can help ensure that blood sugar levels remain under control. Working with a healthcare provider to develop a personalized treatment plan can also help ensure that individuals with pre-diabetes receive the best possible care.Pre-Diabetic Medication Options: A Summary

In summary, pre-diabetic medication options are designed to help individuals manage their blood sugar levels and prevent or delay the onset of type 2 diabetes. These medications work in different ways, such as improving insulin sensitivity, reducing glucose production in the liver, or slowing the absorption of glucose from the gut. Lifestyle changes, such as eating a healthy diet, exercising regularly, losing weight, and quitting smoking, also play a crucial role in managing pre-diabetes. Alternative therapies, such as acupuncture, herbal supplements, and mind-body therapies, may also be effective in managing pre-diabetes.
Future Directions in Pre-Diabetes Management
Future directions in pre-diabetes management may include the development of new medications or therapies that can help prevent or delay the onset of type 2 diabetes. Researchers are currently exploring new treatments, such as GLP-1 receptor agonists and SGLT-2 inhibitors, which have shown promise in improving insulin sensitivity and reducing blood sugar levels. Additionally, advances in technology, such as continuous glucose monitoring systems, may also help individuals with pre-diabetes better manage their blood sugar levels and reduce their risk of developing type 2 diabetes.Conclusion and Next Steps
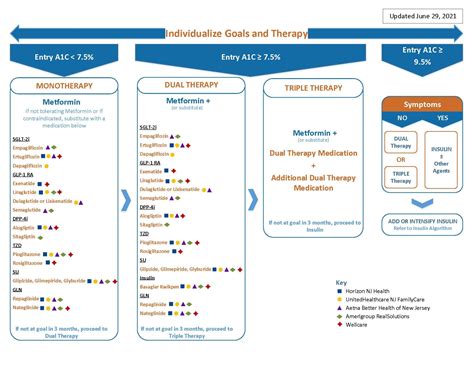
In conclusion, pre-diabetic medication options are a crucial component of pre-diabetes management. By understanding the various medications available, individuals can work with their healthcare providers to develop a personalized treatment plan that meets their unique needs. Lifestyle changes, such as eating a healthy diet, exercising regularly, losing weight, and quitting smoking, also play a critical role in managing pre-diabetes. Alternative therapies, such as acupuncture, herbal supplements, and mind-body therapies, may also be effective in managing pre-diabetes. By taking a comprehensive approach to pre-diabetes management, individuals can reduce their risk of developing type 2 diabetes and improve their overall health.
We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences with pre-diabetic medication options in the comments below. Have you been diagnosed with pre-diabetes? What treatment options have you explored? What lifestyle changes have you made to manage your condition? Your insights and feedback can help others who are navigating the complexities of pre-diabetes management.
What is pre-diabetes, and how is it diagnosed?
+Pre-diabetes is a condition where blood sugar levels are higher than normal, but not high enough to be classified as diabetes. It is diagnosed through a blood test, such as a fasting plasma glucose test or an oral glucose tolerance test.
What are the benefits of taking pre-diabetic medication?
+The benefits of taking pre-diabetic medication include improving insulin sensitivity, reducing glucose production in the liver, and slowing the absorption of glucose from the gut. This can help prevent or delay the onset of type 2 diabetes.
What lifestyle changes can help manage pre-diabetes?
+Lifestyle changes that can help manage pre-diabetes include eating a healthy diet, exercising regularly, losing weight, and quitting smoking. These changes can help improve insulin sensitivity and reduce blood sugar levels.
Are there any alternative therapies that can help manage pre-diabetes?
+Yes, alternative therapies such as acupuncture, herbal supplements, and mind-body therapies may also be effective in managing pre-diabetes. These therapies can help improve insulin sensitivity and reduce blood sugar levels.
How can I work with my healthcare provider to develop a personalized treatment plan?
+You can work with your healthcare provider to develop a personalized treatment plan by discussing your medical history, lifestyle, and treatment goals. Your healthcare provider can help you determine the best course of treatment, including medication, lifestyle changes, and alternative therapies.
