Intro
Discover key facts about Pregabalin, including its uses, side effects, and interactions, to understand this medications role in treating epilepsy, anxiety, and nerve pain, and learn about its dosage, benefits, and risks.
Pregabalin, a medication primarily used to treat epilepsy, fibromyalgia, and neuropathic pain, has been a subject of interest for many due to its efficacy and potential side effects. Understanding pregabalin is crucial for patients who are prescribed this medication, as well as for those interested in pharmacology and pain management. The importance of pregabalin lies in its ability to provide relief to individuals suffering from chronic pain conditions that are often difficult to manage. As research and clinical experiences with pregabalin continue to grow, so does the body of knowledge surrounding its use, benefits, and limitations.
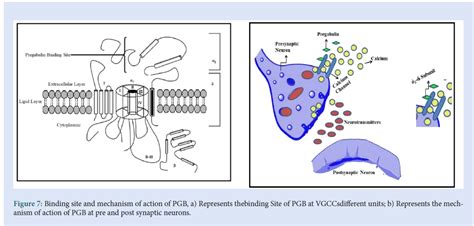
The mechanism of action of pregabalin, though not fully understood, is believed to involve the binding to the alpha2-delta subunit of voltage-gated calcium channels in the central nervous system, which reduces the release of several neurotransmitters, including glutamate, norepinephrine, and substance P. This reduction in neurotransmitter release is thought to account for its therapeutic effects, including the alleviation of pain and the reduction of seizure frequency. The unique mechanism of pregabalin sets it apart from other medications used for similar conditions, making it a valuable option for patients who may not respond well to other treatments.
As with any medication, pregabalin comes with its own set of potential side effects and considerations. Common side effects include dizziness, drowsiness, and dry mouth, among others. However, for many patients, the benefits of pregabalin in managing their condition outweigh the risks associated with its use. The efficacy of pregabalin has been demonstrated in various clinical trials, showcasing its potential to significantly improve the quality of life for individuals with conditions such as diabetic neuropathy, postherpetic neuralgia, and fibromyalgia. This makes pregabalin a critical component in the treatment arsenal against these often debilitating conditions.
Pregabalin Mechanism of Action
Benefits of Pregabalin
The benefits of pregabalin are multifaceted, ranging from its efficacy in reducing neuropathic pain to its role in managing epilepsy and fibromyalgia. Some key benefits include: - Efficacy in managing neuropathic pain conditions, such as diabetic neuropathy and postherpetic neuralgia. - Reduction in seizure frequency for patients with epilepsy. - Improvement in sleep quality for patients with fibromyalgia. - Rapid onset of action compared to some other medications used for similar conditions.Pregabalin Uses
Pregabalin Side Effects
While pregabalin is generally well-tolerated, it can cause a range of side effects. Common side effects include: - Dizziness. - Drowsiness. - Dry mouth. - Edema (swelling). - Weight gain. - Blurred vision. It's essential for patients to discuss any side effects with their healthcare provider, as adjustments in dosage or alternative treatments may be necessary.Pregabalin Dosage
Pregabalin Interactions
Pregabalin can interact with other medications, including: - Other central nervous system depressants, which can increase the risk of sedation and respiratory depression. - Certain antiepileptic drugs, which may require dosage adjustments. - Medications that affect renal function, as pregabalin is excreted primarily by the kidneys.Pregabalin and Pregnancy

Pregabalin and Breastfeeding
Pregabalin is excreted in breast milk, but the effect on the nursing infant is unknown. Women should discuss the risks and benefits of breastfeeding while taking pregabalin with their healthcare provider.Pregabalin Abuse Potential

Pregabalin Withdrawal
Withdrawal symptoms can occur when pregabalin is discontinued, especially after prolonged use or at high dosages. These symptoms may include insomnia, nausea, headache, and diarrhea. To minimize the risk of withdrawal symptoms, pregabalin should be tapered off gradually under the supervision of a healthcare provider.Pregabalin FAQs

What is pregabalin used for?
+Pregabalin is used to treat conditions such as epilepsy, fibromyalgia, and neuropathic pain, including diabetic neuropathy and postherpetic neuralgia.
How does pregabalin work?
+Pregabalin works by binding to the alpha2-delta subunit of voltage-gated calcium channels in the central nervous system, reducing the release of excitatory neurotransmitters.
What are common side effects of pregabalin?
+Common side effects of pregabalin include dizziness, drowsiness, dry mouth, and weight gain.
In conclusion, pregabalin is a valuable medication for the management of various pain conditions and epilepsy. Its unique mechanism of action and efficacy in reducing neuropathic pain and seizure frequency make it a critical component in the treatment of these conditions. However, like all medications, it comes with potential side effects and considerations, such as the risk of abuse and withdrawal symptoms. Patients and healthcare providers must work together to ensure that pregabalin is used safely and effectively, balancing its benefits against its potential risks.
We invite readers to share their experiences or ask questions about pregabalin in the comments section. For those seeking more information or support regarding conditions treated by pregabalin, we encourage exploring reputable resources and consulting with healthcare professionals. By engaging in open discussions and seeking knowledge, we can better understand the role of pregabalin in managing pain and epilepsy, ultimately improving the lives of individuals affected by these conditions.
