Intro
Discover 5 uses of Pregabalin, a versatile medication for epilepsy, anxiety, and nerve pain management, also treating fibromyalgia, and neuropathic pain, offering relief and improved quality of life.
Pregabalin, commonly known by its brand name Lyrica, is a medication that has been widely used for various neurological and psychiatric conditions. Its primary mechanism of action involves the modulation of calcium channels in the central nervous system, which helps in reducing the excitability of nerve cells. This unique mechanism of action makes pregabalin a versatile drug with a range of applications. Here, we delve into the 5 main uses of pregabalin, exploring its benefits, working mechanisms, and practical examples or statistical data where applicable.
Pregabalin has become an essential component in the management of several conditions, primarily due to its efficacy in reducing symptoms and improving the quality of life for patients. The importance of understanding pregabalin's uses cannot be overstated, given its potential to address a broad spectrum of neurological and psychiatric disorders. As we explore the various applications of pregabalin, it becomes clear that this medication offers significant hope for individuals suffering from conditions that were previously challenging to manage.
The versatility of pregabalin is a testament to the advancements in pharmacology and the ongoing quest to develop treatments that can effectively target complex neurological pathways. By modulating these pathways, pregabalin can provide relief from symptoms that significantly impact an individual's daily life. Whether it's managing chronic pain, reducing anxiety, or treating seizures, pregabalin's role in modern medicine is multifaceted. As research continues to uncover the full potential of this medication, its importance in clinical practice is likely to grow, offering new avenues for the treatment of a variety of conditions.
Overview of Pregabalin
Pregabalin is known for its rapid absorption and high bioavailability, which contributes to its effectiveness. It is primarily used for the treatment of epilepsy, fibromyalgia, and neuropathic pain. The drug's ability to bind to the alpha2-delta subunit of voltage-gated calcium channels reduces the release of several neurotransmitters, including glutamate, norepinephrine, and substance P, which are involved in pain transmission and other neurological processes.
Treatment of Neuropathic Pain
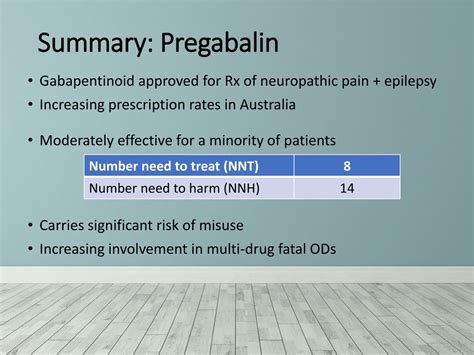
One of the primary uses of pregabalin is in the treatment of neuropathic pain, which is caused by damage to the nervous system. Conditions such as diabetic neuropathy, postherpetic neuralgia (a complication of shingles), and spinal cord injury can lead to neuropathic pain. Pregabalin has been shown to significantly reduce pain in these conditions, improving sleep and quality of life for patients. Its efficacy in managing neuropathic pain is attributed to its unique mechanism of action, which involves reducing the abnormal electrical activity in damaged nerves.
Benefits and Working Mechanism
The benefits of pregabalin in treating neuropathic pain include:
- Reduced pain intensity
- Improved sleep quality
- Enhanced overall well-being Its working mechanism involves the modulation of calcium channels, which in turn reduces the release of excitatory neurotransmitters, thereby decreasing the transmission of pain signals to the brain.
Management of Epilepsy
Pregabalin is also used as an adjunctive therapy for the treatment of partial onset seizures in adults with epilepsy. It has been found to be effective in reducing the frequency of seizures when used in combination with other antiepileptic drugs. The exact mechanism by which pregabalin exerts its antiseizure effects is not fully understood but is believed to involve its ability to reduce the excitability of neurons.
Steps for Effective Management
For effective management of epilepsy with pregabalin:
- Initial Dosing: Starting with a low dose and gradually increasing it based on efficacy and tolerability.
- Combination Therapy: Using pregabalin in conjunction with other antiepileptic medications.
- Regular Monitoring: Regular follow-up with a healthcare provider to adjust the treatment plan as necessary.
Treatment of Fibromyalgia
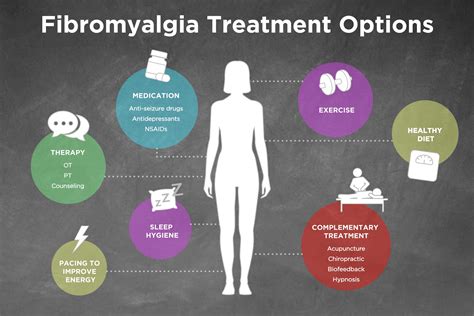
Fibromyalgia is a chronic condition characterized by widespread musculoskeletal pain, fatigue, and tenderness in localized areas. Pregabalin has been approved for the treatment of fibromyalgia, offering relief from pain and improving sleep quality. Its use in fibromyalgia is based on its ability to reduce the levels of neurotransmitters that transmit pain signals.
Practical Examples
Practical examples of pregabalin's efficacy in fibromyalgia include:
- Reduced pain scores in clinical trials
- Improved sleep quality
- Enhanced ability to perform daily activities
Management of Anxiety Disorders
Pregabalin has also been studied for its potential in treating anxiety disorders, including generalized anxiety disorder (GAD). It has shown efficacy in reducing symptoms of anxiety, although its use for this indication may vary by region and is not universally approved.
Statistical Data
Statistical data supporting the use of pregabalin in anxiety disorders includes:
- Significant reduction in Hamilton Anxiety Rating Scale (HAM-A) scores
- Improvement in sleep quality
- Reduction in the severity of anxiety symptoms
Off-Label Uses

Beyond its approved indications, pregabalin has been explored for several off-label uses, including the treatment of restless legs syndrome, hot flashes, and certain psychiatric conditions. However, the efficacy and safety of pregabalin for these conditions can vary, and its use should be guided by clinical judgment and patient response.
As we conclude our exploration of the 5 main uses of pregabalin, it's clear that this medication has revolutionized the treatment of various neurological and psychiatric conditions. Its unique mechanism of action, efficacy, and relatively favorable side effect profile make it a valuable addition to the therapeutic arsenal against conditions that were once difficult to manage. Whether you're a healthcare professional seeking to understand the latest in pharmacological treatments or an individual looking for information on managing chronic conditions, pregabalin stands out as a medication with significant potential.
We invite you to share your thoughts, experiences, or questions regarding pregabalin and its uses. Your input can help foster a community of support and knowledge, contributing to a better understanding of how medications like pregabalin can improve lives. Feel free to comment below, share this article with others who might find it informative, or explore further resources on the topic.
What is the primary mechanism of action of pregabalin?
+Pregabalin works by binding to the alpha2-delta subunit of voltage-gated calcium channels, reducing the release of several neurotransmitters involved in pain transmission and other neurological processes.
Is pregabalin effective for treating neuropathic pain?
+Yes, pregabalin has been shown to significantly reduce pain in conditions such as diabetic neuropathy, postherpetic neuralgia, and spinal cord injury, improving sleep and quality of life for patients.
Can pregabalin be used for the treatment of epilepsy?
+Pregabalin is used as an adjunctive therapy for the treatment of partial onset seizures in adults with epilepsy, reducing the frequency of seizures when used in combination with other antiepileptic drugs.
