Intro
Boost vitamin B12 levels naturally with 5 proven methods, addressing deficiency symptoms, energy enhancement, and nutritional benefits, using supplements, diet, and lifestyle changes to optimize overall health and wellbeing.
Vitamin B12 is an essential nutrient that plays a crucial role in various bodily functions, including the production of red blood cells, nerve function, and DNA synthesis. A deficiency in vitamin B12 can lead to a range of health problems, including fatigue, weakness, and neurological disorders. Fortunately, there are several ways to boost vitamin B12 levels, and understanding these methods can help individuals maintain optimal health. In this article, we will explore the importance of vitamin B12, its benefits, and provide practical tips on how to increase its levels in the body.
The human body relies on vitamin B12 to function properly, and a deficiency can have severe consequences. Vitamin B12 deficiency is common, especially among older adults, vegetarians, and individuals with certain medical conditions. The symptoms of a vitamin B12 deficiency can be subtle, making it essential to be aware of the signs and take proactive steps to maintain adequate levels. By incorporating vitamin B12-rich foods into their diet, individuals can reduce their risk of deficiency and ensure they are getting enough of this vital nutrient.
Vitamin B12 is found in animal products, such as meat, fish, and dairy products, making it challenging for vegetarians and vegans to get enough of this nutrient. However, there are several plant-based sources of vitamin B12, including fortified foods and supplements. Understanding the different sources of vitamin B12 and how to incorporate them into a balanced diet can help individuals maintain optimal levels. Additionally, there are several other factors that can affect vitamin B12 levels, including age, medical conditions, and lifestyle choices.
Understanding Vitamin B12

Benefits of Vitamin B12
The benefits of vitamin B12 are numerous, and it is essential to understand its role in maintaining optimal health. Some of the key benefits of vitamin B12 include: * Production of red blood cells: Vitamin B12 is necessary for the production of red blood cells, which carry oxygen throughout the body. * Nerve function: Vitamin B12 is involved in the maintenance of healthy nerves, and a deficiency can lead to neurological problems. * DNA synthesis: Vitamin B12 is necessary for DNA synthesis, which is essential for cell growth and development. * Energy production: Vitamin B12 is involved in the production of energy, and a deficiency can lead to fatigue and weakness.Food Sources of Vitamin B12

Plant-Based Sources of Vitamin B12
While animal products are the richest sources of vitamin B12, there are several plant-based sources of this nutrient. Some of the best plant-based sources of vitamin B12 include: * Fortified foods: Some plant-based milk and cereals are fortified with vitamin B12. * Nutritional yeast: Nutritional yeast is a popular vegan ingredient that is rich in vitamin B12. * Seaweed: Some types of seaweed, such as nori and wakame, are rich in vitamin B12. * Mushrooms: Some types of mushrooms, such as shiitake and portobello, are rich in vitamin B12.Supplements and Vitamin B12

Types of Vitamin B12 Supplements
There are several types of vitamin B12 supplements available, each with its own unique characteristics. Some of the most common types of vitamin B12 supplements include: * Methylcobalamin: Methylcobalamin is a form of vitamin B12 that is easily absorbed by the body. * Cyanocobalamin: Cyanocobalamin is a synthetic form of vitamin B12 that is commonly used in supplements. * Adenosylcobalamin: Adenosylcobalamin is a form of vitamin B12 that is involved in the production of energy.Boosting Vitamin B12 Levels
Practical Tips for Boosting Vitamin B12
In addition to dietary changes and supplements, there are several practical tips that can help boost vitamin B12 levels. Some of the most effective tips include: * Eating smaller, more frequent meals: Eating smaller meals throughout the day can help increase vitamin B12 absorption. * Avoiding foods that interfere with absorption: Certain foods, such as coffee and tea, can interfere with vitamin B12 absorption. * Staying hydrated: Adequate hydration is necessary for the absorption of vitamin B12. * Managing medical conditions: Certain medical conditions, such as celiac disease and Crohn's disease, can increase the risk of vitamin B12 deficiency.Vitamin B12 Deficiency and Health Risks
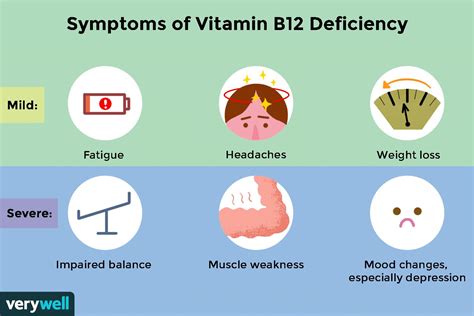
Risk Factors for Vitamin B12 Deficiency
Certain individuals are at a higher risk of vitamin B12 deficiency, including: * Vegetarians and vegans: Vegetarians and vegans are at a higher risk of vitamin B12 deficiency due to the limited availability of vitamin B12 in plant-based foods. * Older adults: Older adults are at a higher risk of vitamin B12 deficiency due to decreased absorption and increased excretion. * Individuals with medical conditions: Certain medical conditions, such as celiac disease and Crohn's disease, can increase the risk of vitamin B12 deficiency. * Pregnant and breastfeeding women: Pregnant and breastfeeding women have a higher demand for vitamin B12 and are at a higher risk of deficiency.Diagnosing and Treating Vitamin B12 Deficiency

Treatment Options for Vitamin B12 Deficiency
Treatment for vitamin B12 deficiency depends on the underlying cause and severity of the deficiency. Some of the most effective treatment options include: * Supplements: Vitamin B12 supplements can be used to treat deficiency and maintain adequate levels. * Dietary changes: Incorporating vitamin B12-rich foods into the diet can help maintain adequate levels. * Injections: Vitamin B12 injections can be used to treat deficiency, especially in individuals with severe deficiency or absorption problems.What are the symptoms of vitamin B12 deficiency?
+The symptoms of vitamin B12 deficiency can include fatigue, weakness, shortness of breath, numbness, tingling, and weakness. If left untreated, vitamin B12 deficiency can lead to anemia, neurological problems, and cardiovascular disease.
How can I boost my vitamin B12 levels?
+Boosting vitamin B12 levels can be achieved through a combination of dietary changes, supplements, and lifestyle modifications. Eating vitamin B12-rich foods, taking supplements, managing stress, and getting enough sleep can all help maintain adequate levels.
What are the risk factors for vitamin B12 deficiency?
+Certain individuals are at a higher risk of vitamin B12 deficiency, including vegetarians and vegans, older adults, individuals with medical conditions, and pregnant and breastfeeding women. Understanding these risk factors can help individuals take proactive steps to maintain adequate levels.
In conclusion, vitamin B12 is an essential nutrient that plays a critical role in various bodily functions. Understanding the benefits, food sources, and supplements of vitamin B12 can help individuals maintain optimal health. By incorporating vitamin B12-rich foods into their diet, taking supplements, managing stress, and getting enough sleep, individuals can reduce their risk of deficiency and ensure they are getting enough of this vital nutrient. If you have any questions or concerns about vitamin B12, please do not hesitate to comment below. Share this article with your friends and family to help them understand the importance of vitamin B12 and take proactive steps to maintain optimal health.
