Intro
Discover the normal sugar glucose range and learn about blood glucose levels, glucose monitoring, and healthy glucose targets to manage diabetes and maintain optimal glucose control.
Maintaining a healthy blood sugar level is crucial for overall well-being, and understanding the normal sugar glucose range is essential for individuals to take control of their health. Blood sugar levels, also known as blood glucose levels, refer to the amount of glucose present in the blood. Glucose is a type of sugar that serves as the primary source of energy for the body's cells. The normal sugar glucose range varies throughout the day, depending on factors such as diet, physical activity, and the time of day.
The importance of monitoring blood sugar levels cannot be overstated, as abnormal levels can lead to serious health complications. For instance, high blood sugar levels can cause damage to organs and tissues over time, increasing the risk of developing conditions such as diabetes, heart disease, and kidney disease. On the other hand, low blood sugar levels can cause symptoms such as dizziness, confusion, and even loss of consciousness. Therefore, it is essential to understand the normal sugar glucose range and take steps to maintain healthy blood sugar levels.
The normal sugar glucose range is typically measured in milligrams per deciliter (mg/dL) or millimoles per liter (mmol/L). In individuals without diabetes, the normal blood sugar range is usually between 70 and 140 mg/dL (3.9 and 7.8 mmol/L). However, these values can vary depending on the time of day, the type of test used, and other factors. For example, blood sugar levels tend to be higher after eating and lower after fasting. Understanding these variations is crucial for interpreting blood sugar test results and making informed decisions about health.
Understanding Blood Sugar Levels

Blood sugar levels are regulated by the body's natural mechanisms, including the release of insulin and glucagon. Insulin is a hormone produced by the pancreas that helps to lower blood sugar levels by facilitating the uptake of glucose by cells. Glucagon, on the other hand, is a hormone that raises blood sugar levels by stimulating the release of glucose from stored energy sources. In individuals with diabetes, the body's ability to regulate blood sugar levels is impaired, leading to high blood sugar levels that can cause a range of symptoms and complications.
Factors Affecting Blood Sugar Levels
Several factors can affect blood sugar levels, including diet, physical activity, stress, and certain medications. For example, consuming high-carbohydrate foods can cause a rapid increase in blood sugar levels, while regular physical activity can help to lower blood sugar levels by increasing insulin sensitivity. Stress can also affect blood sugar levels, as the body's "fight or flight" response causes the release of stress hormones such as cortisol and adrenaline, which can raise blood sugar levels.Normal Sugar Glucose Range in Different Situations
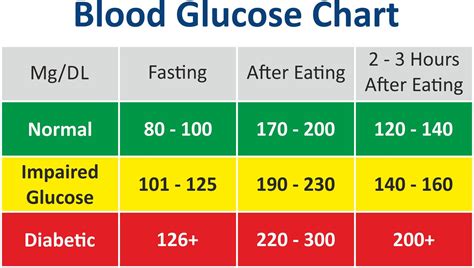
The normal sugar glucose range can vary depending on the situation. For example, in individuals without diabetes, the normal blood sugar range after fasting is typically between 70 and 100 mg/dL (3.9 and 5.6 mmol/L). After eating, blood sugar levels can rise to between 120 and 140 mg/dL (6.7 and 7.8 mmol/L). In individuals with diabetes, the target blood sugar range may be slightly higher, typically between 80 and 180 mg/dL (4.4 and 10 mmol/L).
Target Blood Sugar Ranges for Individuals with Diabetes
Individuals with diabetes need to monitor their blood sugar levels regularly to ensure that they are within the target range. The target blood sugar range for individuals with diabetes varies depending on the type of diabetes, the individual's age, and other factors. For example, the American Diabetes Association recommends the following target blood sugar ranges for individuals with diabetes: * Before meals: 70-130 mg/dL (3.9-7.2 mmol/L) * After meals: Less than 180 mg/dL (10 mmol/L) * At bedtime: 100-140 mg/dL (5.6-7.8 mmol/L)Monitoring Blood Sugar Levels
Monitoring blood sugar levels is essential for individuals with diabetes, as well as those who are at risk of developing diabetes. There are several ways to monitor blood sugar levels, including:
- Fasting blood sugar test: This test measures blood sugar levels after an overnight fast.
- Postprandial blood sugar test: This test measures blood sugar levels after eating.
- Random blood sugar test: This test measures blood sugar levels at any time of day.
- Continuous glucose monitoring (CGM): This involves wearing a small device that measures blood sugar levels continuously throughout the day.
Interpreting Blood Sugar Test Results
Interpreting blood sugar test results requires an understanding of the normal sugar glucose range and the factors that can affect blood sugar levels. For example, a blood sugar level of 120 mg/dL (6.7 mmol/L) after eating may be considered normal, while a level of 200 mg/dL (11.1 mmol/L) may indicate high blood sugar. It is essential to consult with a healthcare provider to determine the best course of action based on individual test results.Maintaining Healthy Blood Sugar Levels

Maintaining healthy blood sugar levels requires a combination of healthy lifestyle habits, including:
- Eating a balanced diet that is low in sugar and refined carbohydrates
- Engaging in regular physical activity, such as walking or other aerobic exercises
- Managing stress through techniques such as meditation or deep breathing
- Getting enough sleep each night
- Monitoring blood sugar levels regularly and adjusting treatment as needed
Benefits of Maintaining Healthy Blood Sugar Levels
Maintaining healthy blood sugar levels has numerous benefits, including: * Reducing the risk of developing diabetes and other health complications * Improving energy levels and overall well-being * Supporting weight management and reducing the risk of obesity * Improving heart health and reducing the risk of heart disease * Supporting healthy digestion and reducing the risk of digestive disordersConclusion and Next Steps

In conclusion, understanding the normal sugar glucose range is essential for maintaining healthy blood sugar levels and reducing the risk of developing diabetes and other health complications. By monitoring blood sugar levels regularly, making healthy lifestyle choices, and seeking medical attention when necessary, individuals can take control of their health and well-being. If you have concerns about your blood sugar levels or would like to learn more about maintaining healthy blood sugar levels, consult with a healthcare provider or registered dietitian for personalized guidance and support.
What is the normal sugar glucose range for individuals without diabetes?
+The normal sugar glucose range for individuals without diabetes is typically between 70 and 140 mg/dL (3.9 and 7.8 mmol/L).
How can I maintain healthy blood sugar levels?
+Maintaining healthy blood sugar levels requires a combination of healthy lifestyle habits, including eating a balanced diet, engaging in regular physical activity, managing stress, and getting enough sleep each night.
What are the benefits of maintaining healthy blood sugar levels?
+Maintaining healthy blood sugar levels has numerous benefits, including reducing the risk of developing diabetes and other health complications, improving energy levels and overall well-being, and supporting weight management and heart health.
We hope this article has provided you with a comprehensive understanding of the normal sugar glucose range and the importance of maintaining healthy blood sugar levels. If you have any further questions or concerns, please do not hesitate to reach out to a healthcare provider or registered dietitian for personalized guidance and support. Additionally, we invite you to share this article with others who may benefit from this information, and to leave a comment below with any thoughts or questions you may have.
