Intro
Learn the normal Prothrombin Ratio value and understand its significance in blood clotting tests, including INR, coagulation, and thrombosis diagnosis.
The prothrombin time (PT) test is a crucial diagnostic tool used to evaluate the blood's clotting ability, and the prothrombin ratio is an essential component of this test. Understanding the normal value of the prothrombin ratio is vital for healthcare professionals to accurately diagnose and manage bleeding disorders. In this article, we will delve into the importance of the prothrombin ratio, its normal value, and the implications of abnormal results.
The prothrombin time test measures the time it takes for blood to clot, and the prothrombin ratio is calculated by comparing the patient's PT result to a normal control sample. This ratio helps to standardize the results and account for any variations in the testing process. A normal prothrombin ratio indicates that the blood is clotting properly, while an abnormal ratio may suggest a bleeding disorder or other underlying condition.
The normal value of the prothrombin ratio typically ranges from 0.9 to 1.1, although this can vary slightly depending on the laboratory and the specific testing method used. It is essential to note that the prothrombin ratio is often expressed as a percentage, with a normal range of 90% to 110%. This means that if the patient's PT result is within 10% of the normal control sample, the prothrombin ratio is considered normal.
Introduction to Prothrombin Time Test

The prothrombin time test is a widely used diagnostic tool that measures the blood's clotting ability by evaluating the extrinsic and common coagulation pathways. The test involves adding a substance called tissue factor to a blood sample, which triggers the clotting process. The time it takes for the blood to clot is then measured, and this result is compared to a normal control sample to calculate the prothrombin ratio.
How Prothrombin Time Test Works
The prothrombin time test works by evaluating the blood's ability to form a clot in response to tissue factor. The test is typically performed on a blood sample that has been treated with an anticoagulant to prevent clotting. The tissue factor is then added to the sample, and the time it takes for the blood to clot is measured using a coagulometer or other specialized equipment.Normal Value of Prothrombin Ratio
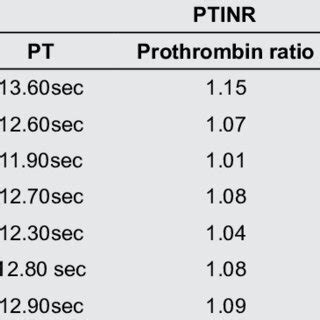
The normal value of the prothrombin ratio is typically considered to be between 0.9 and 1.1, although this can vary slightly depending on the laboratory and the specific testing method used. It is essential to note that the prothrombin ratio is often expressed as a percentage, with a normal range of 90% to 110%. This means that if the patient's PT result is within 10% of the normal control sample, the prothrombin ratio is considered normal.
Interpretation of Prothrombin Ratio Results
Interpreting the results of the prothrombin ratio test requires careful consideration of the patient's medical history, symptoms, and other laboratory results. A normal prothrombin ratio suggests that the blood is clotting properly, while an abnormal ratio may indicate a bleeding disorder or other underlying condition. The following are some possible interpretations of prothrombin ratio results:- A prothrombin ratio of 0.9 to 1.1 (or 90% to 110%) is considered normal.
- A prothrombin ratio of 1.2 to 1.5 (or 80% to 90%) may indicate mild coagulopathy.
- A prothrombin ratio of 1.6 to 2.0 (or 60% to 80%) may indicate moderate coagulopathy.
- A prothrombin ratio of 2.1 or higher (or less than 60%) may indicate severe coagulopathy.
Factors Affecting Prothrombin Ratio
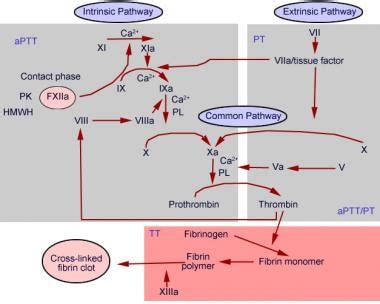
Several factors can affect the prothrombin ratio, including:
- Medications: Certain medications, such as warfarin and heparin, can affect the prothrombin ratio by altering the blood's clotting ability.
- Liver disease: Liver disease can affect the production of clotting factors, leading to an abnormal prothrombin ratio.
- Vitamin K deficiency: Vitamin K is essential for the production of clotting factors, and a deficiency can lead to an abnormal prothrombin ratio.
- Inherited bleeding disorders: Certain inherited bleeding disorders, such as hemophilia, can affect the prothrombin ratio.
Common Causes of Abnormal Prothrombin Ratio
The following are some common causes of an abnormal prothrombin ratio:- Bleeding disorders: Inherited bleeding disorders, such as hemophilia, can affect the prothrombin ratio.
- Liver disease: Liver disease can affect the production of clotting factors, leading to an abnormal prothrombin ratio.
- Vitamin K deficiency: Vitamin K is essential for the production of clotting factors, and a deficiency can lead to an abnormal prothrombin ratio.
- Medications: Certain medications, such as warfarin and heparin, can affect the prothrombin ratio by altering the blood's clotting ability.
Prothrombin Time Test Procedure

The prothrombin time test procedure typically involves the following steps:
- Blood sample collection: A blood sample is collected from the patient's vein using a needle and syringe.
- Anticoagulant treatment: The blood sample is treated with an anticoagulant to prevent clotting.
- Tissue factor addition: Tissue factor is added to the blood sample to trigger the clotting process.
- Clotting time measurement: The time it takes for the blood to clot is measured using a coagulometer or other specialized equipment.
- Prothrombin ratio calculation: The prothrombin ratio is calculated by comparing the patient's PT result to a normal control sample.
Precautions and Contraindications
The following are some precautions and contraindications to consider when performing the prothrombin time test:- Patients with bleeding disorders or other conditions that affect blood clotting should be carefully evaluated before undergoing the test.
- Patients taking medications that affect blood clotting, such as warfarin and heparin, should be carefully monitored during the test.
- The test should not be performed on patients with severe bleeding or other conditions that may affect the accuracy of the results.
Prothrombin Ratio in Clinical Practice
The prothrombin ratio is a valuable tool in clinical practice, particularly in the diagnosis and management of bleeding disorders. The following are some examples of how the prothrombin ratio is used in clinical practice:
- Diagnosing bleeding disorders: The prothrombin ratio is used to diagnose bleeding disorders, such as hemophilia, and to monitor the effectiveness of treatment.
- Monitoring anticoagulant therapy: The prothrombin ratio is used to monitor the effectiveness of anticoagulant therapy, such as warfarin, and to adjust the dosage as needed.
- Evaluating liver function: The prothrombin ratio is used to evaluate liver function and to diagnose liver disease.
Clinical Significance of Prothrombin Ratio
The clinical significance of the prothrombin ratio depends on the patient's medical history, symptoms, and other laboratory results. A normal prothrombin ratio suggests that the blood is clotting properly, while an abnormal ratio may indicate a bleeding disorder or other underlying condition. The following are some examples of the clinical significance of the prothrombin ratio:- A normal prothrombin ratio suggests that the blood is clotting properly and that there is no significant bleeding disorder or other underlying condition.
- An abnormal prothrombin ratio may indicate a bleeding disorder, such as hemophilia, or other underlying condition, such as liver disease.
- The prothrombin ratio is used to monitor the effectiveness of anticoagulant therapy and to adjust the dosage as needed.
What is the normal value of the prothrombin ratio?
+The normal value of the prothrombin ratio is typically considered to be between 0.9 and 1.1, although this can vary slightly depending on the laboratory and the specific testing method used.
What are the factors that affect the prothrombin ratio?
+Several factors can affect the prothrombin ratio, including medications, liver disease, vitamin K deficiency, and inherited bleeding disorders.
What is the clinical significance of the prothrombin ratio?
+The clinical significance of the prothrombin ratio depends on the patient's medical history, symptoms, and other laboratory results. A normal prothrombin ratio suggests that the blood is clotting properly, while an abnormal ratio may indicate a bleeding disorder or other underlying condition.
In conclusion, understanding the normal value of the prothrombin ratio is essential for healthcare professionals to accurately diagnose and manage bleeding disorders. The prothrombin ratio is a valuable tool in clinical practice, particularly in the diagnosis and management of bleeding disorders. By considering the factors that affect the prothrombin ratio and the clinical significance of the results, healthcare professionals can provide optimal care for patients with bleeding disorders. We encourage readers to share their thoughts and experiences with the prothrombin ratio in the comments section below. Additionally, we invite readers to share this article with others who may benefit from this information.
