Intro
Discover Raynauds Disease causes, symptoms, and treatment options. Learn about vasospasm, blood flow, and triggers, and how to manage this circulatory condition effectively.
Raynaud's disease is a condition that affects blood flow to the fingers and toes, and sometimes the ears, nose, and lips. It is characterized by a sudden and temporary narrowing of the blood vessels in response to cold temperatures or stress, resulting in a lack of blood flow to the affected areas. This can cause the skin to turn white or blue, and can be painful. Raynaud's disease is a common condition that affects millions of people worldwide, and it is more common in women than men. The exact cause of Raynaud's disease is not known, but it is thought to be related to a problem with the blood vessels and the nervous system.
Raynaud's disease can have a significant impact on a person's quality of life, as it can cause pain, discomfort, and difficulty performing daily activities. In severe cases, it can also lead to complications such as skin ulcers, gangrene, and scarring. Therefore, it is essential to understand the symptoms, causes, and treatment options for Raynaud's disease. By learning more about this condition, individuals can take steps to manage their symptoms, prevent complications, and improve their overall health and well-being.
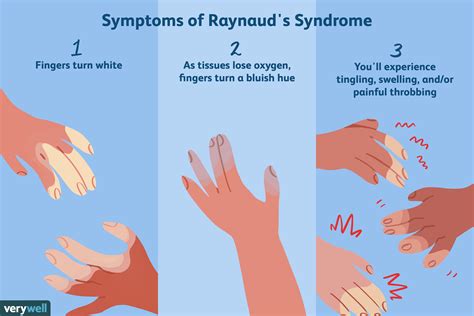
The symptoms of Raynaud's disease can vary from person to person, but they typically include a sudden and temporary change in skin color, pain, numbness, and tingling in the affected areas. The skin may turn white or blue due to a lack of blood flow, and it may feel cold to the touch. In some cases, the skin may also turn red or purple as the blood vessels dilate and blood flow returns to the area. Raynaud's disease can be triggered by a variety of factors, including cold temperatures, stress, smoking, and certain medications.
What is Raynaud's Disease?
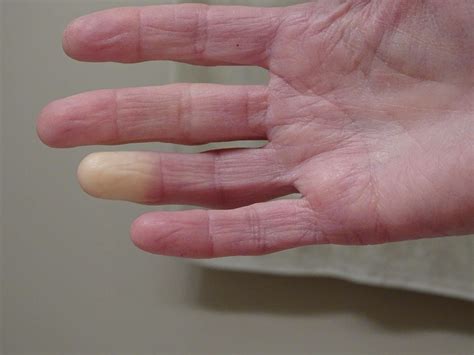
Types of Raynaud's Disease
There are two main types of Raynaud's disease: primary and secondary. Primary Raynaud's disease is the most common type and is characterized by a sudden and temporary narrowing of the blood vessels in response to cold temperatures or stress. Secondary Raynaud's disease is less common and is caused by an underlying medical condition, such as lupus, rheumatoid arthritis, or scleroderma. Secondary Raynaud's disease can be more severe and may require treatment for the underlying condition.Symptoms of Raynaud's Disease
- Pain or discomfort in the affected areas
- Numbness or tingling in the fingers or toes
- Weakness or fatigue in the hands or feet
- Difficulty performing daily activities, such as buttoning a shirt or tying shoelaces
- Skin ulcers or sores on the fingers or toes
Causes of Raynaud's Disease
The exact cause of Raynaud's disease is not known, but it is thought to be related to a problem with the blood vessels and the nervous system. The blood vessels in people with Raynaud's disease may be more sensitive to cold temperatures or stress, which can cause them to narrow or constrict. This can lead to a lack of blood flow to the affected areas, resulting in a range of symptoms. Other factors that may contribute to the development of Raynaud's disease include:- Genetics: Raynaud's disease can run in families, suggesting a genetic component
- Hormonal changes: Hormonal changes, such as those that occur during pregnancy or menopause, may contribute to the development of Raynaud's disease
- Smoking: Smoking can damage the blood vessels and increase the risk of developing Raynaud's disease
- Certain medications: Certain medications, such as beta blockers and some antidepressants, may trigger or worsen Raynaud's disease
Treatment Options for Raynaud's Disease

Lifestyle Changes for Raynaud's Disease
Making lifestyle changes can help to reduce the frequency and severity of symptoms. Some lifestyle changes that may be helpful include:- Avoiding cold temperatures: Avoid exposure to cold temperatures, such as cold water or air conditioning
- Quitting smoking: Smoking can damage the blood vessels and increase the risk of developing Raynaud's disease
- Managing stress: Stress can trigger or worsen Raynaud's disease, so finding ways to manage stress, such as through exercise or meditation, can be helpful
- Avoiding certain medications: Certain medications, such as beta blockers and some antidepressants, may trigger or worsen Raynaud's disease
- Getting regular exercise: Regular exercise can help to improve blood flow and reduce the risk of developing Raynaud's disease
Complications of Raynaud's Disease
Managing Complications of Raynaud's Disease
Managing complications of Raynaud's disease requires prompt medical attention. Treatment may include medications to improve blood flow, wound care to promote healing, and surgery to remove damaged tissue. In some cases, hospitalization may be necessary to manage complications. It is essential to work with a healthcare provider to develop a treatment plan and to manage complications effectively.Prevention of Raynaud's Disease
Risk Factors for Raynaud's Disease
Several risk factors can increase the likelihood of developing Raynaud's disease, including:- Family history: Raynaud's disease can run in families, suggesting a genetic component
- Age: Raynaud's disease is more common in people under the age of 30
- Sex: Raynaud's disease is more common in women than men
- Smoking: Smoking can damage the blood vessels and increase the risk of developing Raynaud's disease
- Certain medications: Certain medications, such as beta blockers and some antidepressants, may trigger or worsen Raynaud's disease
Diagnosis of Raynaud's Disease
Diagnostic Tests for Raynaud's Disease
Several diagnostic tests can help to diagnose Raynaud's disease, including:- Blood tests: Blood tests can help to rule out other conditions that may be causing symptoms, such as anemia or infection
- Imaging studies: Imaging studies, such as angiography or Doppler ultrasound, can help to visualize the blood vessels and check for signs of poor circulation
- Cold stimulation test: A cold stimulation test can help to trigger symptoms and confirm the diagnosis of Raynaud's disease
What is Raynaud's disease?
+Raynaud's disease is a medical condition that affects the blood vessels and causes them to narrow or constrict in response to certain stimuli, resulting in a lack of blood flow to the affected areas.
What are the symptoms of Raynaud's disease?
+The symptoms of Raynaud's disease include a sudden and temporary change in skin color, pain, numbness, and tingling in the affected areas, as well as skin ulcers or sores on the fingers or toes.
How is Raynaud's disease diagnosed?
+Diagnosing Raynaud's disease requires a combination of medical history, physical examination, and diagnostic tests, such as blood tests, imaging studies, and cold stimulation tests.
What are the treatment options for Raynaud's disease?
+Treatment options for Raynaud's disease include lifestyle changes, such as avoiding cold temperatures and quitting smoking, as well as medications, such as calcium channel blockers and alpha blockers, and alternative therapies, such as acupuncture and biofeedback.
Can Raynaud's disease be prevented?
+Preventing Raynaud's disease requires a combination of lifestyle changes and medical treatment, including avoiding cold temperatures, quitting smoking, and managing stress, as well as medications to improve blood flow.
In conclusion, Raynaud's disease is a complex medical condition that requires a comprehensive approach to diagnosis and treatment. By understanding the symptoms, causes, and treatment options for Raynaud's disease, individuals can take steps to manage their symptoms, prevent complications, and improve their overall health and well-being. If you or someone you know is experiencing symptoms of Raynaud's disease, it is essential to seek medical attention to develop a treatment plan and prevent complications. We invite you to share your experiences and questions about Raynaud's disease in the comments below, and to share this article with others who may be affected by this condition.
