Intro
Discover the risks of high Prothrombin Time, including bleeding disorders, blood clotting issues, and cardiovascular disease, and learn how to manage and prevent complications with proper diagnosis and treatment.
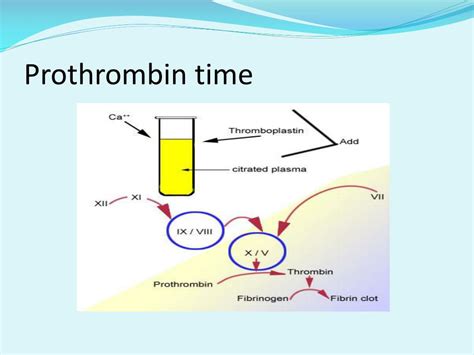
Prothrombin time, also known as PT, is a test used to evaluate the blood's ability to clot. It measures the time it takes for blood to clot and is often used to monitor patients who are taking anticoagulant medications, such as warfarin. A high prothrombin time indicates that the blood is taking longer than normal to clot, which can increase the risk of bleeding. In this article, we will delve into the world of prothrombin time high risks, exploring the causes, symptoms, and consequences of elevated PT levels.
The importance of prothrombin time cannot be overstated. It is a crucial indicator of the blood's clotting ability, and abnormal results can have significant implications for patient health. A high prothrombin time can be a sign of an underlying condition, such as liver disease or vitamin K deficiency, which requires prompt medical attention. Moreover, patients with elevated PT levels are at a higher risk of bleeding complications, which can be life-threatening if left untreated. As we explore the topic of prothrombin time high risks, it is essential to understand the underlying mechanisms and factors that contribute to this condition.
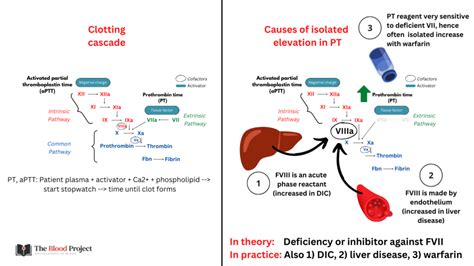
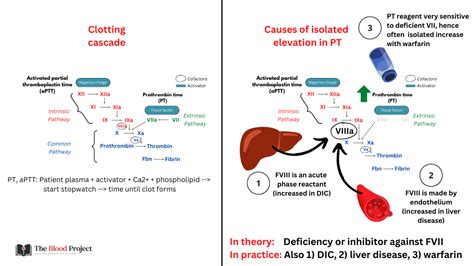
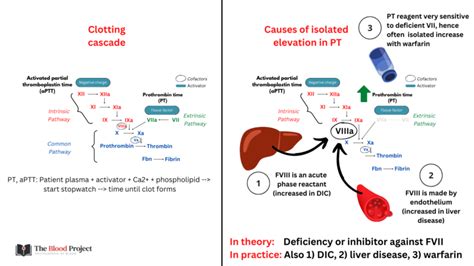
The prothrombin time test is a widely used diagnostic tool in clinical practice. It is often used in conjunction with other tests, such as the partial thromboplastin time (PTT) and the international normalized ratio (INR), to evaluate the blood's clotting ability. A high prothrombin time can be caused by a variety of factors, including anticoagulant medications, liver disease, and vitamin K deficiency. Patients with elevated PT levels may experience symptoms such as easy bruising, nosebleeds, and heavy menstrual bleeding. In severe cases, a high prothrombin time can increase the risk of life-threatening bleeding complications, such as intracranial hemorrhage and gastrointestinal bleeding.
Causes of High Prothrombin Time
Anticoagulant Medications
Anticoagulant medications are a common cause of high prothrombin time. These medications work by inhibiting the production of clotting factors, which can increase the risk of bleeding. Patients taking anticoagulant medications, such as warfarin, require regular monitoring of their prothrombin time to ensure that their blood is not too thin. The benefits of anticoagulant medications include the prevention of blood clots and stroke, but the risks include an increased risk of bleeding complications.Liver Disease
Liver disease is another common cause of high prothrombin time. The liver plays a crucial role in the production of clotting factors, and liver disease can impair this process. Patients with liver disease, such as cirrhosis and hepatitis, may experience elevated PT levels due to a deficiency of clotting factors. The symptoms of liver disease can vary depending on the underlying condition, but common symptoms include easy bruising, nosebleeds, and heavy menstrual bleeding.Symptoms of High Prothrombin Time
Bleeding Symptoms
Bleeding symptoms are a common manifestation of high prothrombin time. Patients with elevated PT levels may experience easy bruising, nosebleeds, and heavy menstrual bleeding. These symptoms can be mild or severe, depending on the underlying cause. In some cases, bleeding symptoms can be life-threatening, such as intracranial hemorrhage and gastrointestinal bleeding.Clotting Symptoms
Clotting symptoms are less common than bleeding symptoms but can still occur in patients with high prothrombin time. Patients with elevated PT levels may experience blood clots in the legs, lungs, or brain. These clots can be life-threatening if left untreated, and patients require prompt medical attention if they experience symptoms such as chest pain, shortness of breath, or difficulty speaking.Consequences of High Prothrombin Time
Bleeding Complications
Bleeding complications are a common consequence of high prothrombin time. Patients with elevated PT levels are at a higher risk of bleeding, which can be life-threatening if left untreated. Bleeding complications can include intracranial hemorrhage, gastrointestinal bleeding, and bleeding into the joints or muscles.Clotting Complications
Clotting complications are less common than bleeding complications but can still occur in patients with high prothrombin time. Patients with elevated PT levels may experience blood clots in the legs, lungs, or brain, which can be life-threatening if left untreated.Treatment Options for High Prothrombin Time

Medication Adjustment
Medication adjustment is a common treatment option for high prothrombin time. Patients taking anticoagulant medications, such as warfarin, may require a dose adjustment to reduce the risk of bleeding. The goal of medication adjustment is to achieve a balance between preventing blood clots and minimizing the risk of bleeding.Liver Disease Treatment
Liver disease treatment is essential for patients with high prothrombin time due to liver disease. Patients with liver disease, such as cirrhosis and hepatitis, may require treatment for the underlying condition, such as medication or liver transplantation. The goal of liver disease treatment is to improve liver function and reduce the risk of bleeding.Prevention Strategies for High Prothrombin Time
Avoiding Injuries
Avoiding injuries is a crucial prevention strategy for high prothrombin time. Patients with elevated PT levels should avoid activities that may increase the risk of injury, such as contact sports or heavy lifting. Patients should also wear protective gear, such as helmets and knee pads, to reduce the risk of injury.Taking Medications as Directed
Taking medications as directed is essential for patients with high prothrombin time. Patients taking anticoagulant medications, such as warfarin, should take their medications exactly as directed to minimize the risk of bleeding. Patients should also attend regular follow-up appointments to monitor their prothrombin time and adjust their medication as needed.What is prothrombin time?
+Prothrombin time is a test used to evaluate the blood's ability to clot. It measures the time it takes for blood to clot and is often used to monitor patients who are taking anticoagulant medications.
What are the causes of high prothrombin time?
+The causes of high prothrombin time include anticoagulant medications, liver disease, and vitamin K deficiency. Patients with elevated PT levels may experience easy bruising, nosebleeds, and heavy menstrual bleeding.
How is high prothrombin time treated?
+The treatment options for high prothrombin time depend on the underlying cause. Patients with anticoagulant medications may require a dose adjustment or a change in medication. Patients with liver disease may require treatment for the underlying condition, such as medication or liver transplantation.
In conclusion, high prothrombin time is a serious condition that requires prompt medical attention. Patients with elevated PT levels are at a higher risk of bleeding complications, which can be life-threatening if left untreated. By understanding the causes, symptoms, and consequences of high prothrombin time, patients can take steps to prevent bleeding and reduce the risk of complications. We encourage readers to share their experiences and ask questions in the comments section below. If you found this article informative, please share it with others who may benefit from this information.
