Intro
Learn about normal blood sugar levels, glucose targets, and healthy range management to prevent diabetes and hypoglycemia, maintaining optimal blood glucose control.
Maintaining normal blood sugar levels is crucial for overall health and well-being. Blood sugar, also known as glucose, is the primary source of energy for the body's cells. When blood sugar levels are within a normal range, the body functions properly, and the risk of developing chronic diseases is reduced. On the other hand, abnormal blood sugar levels can lead to various health problems, including diabetes, heart disease, and nerve damage. In this article, we will delve into the importance of normal blood sugar levels, the factors that influence them, and provide tips on how to maintain a healthy blood sugar range.
The human body has a complex system for regulating blood sugar levels. After consuming a meal, the digestive system breaks down carbohydrates into glucose, which is then absorbed into the bloodstream. The pancreas, an organ located behind the stomach, releases insulin, a hormone that helps cells absorb glucose from the blood. As glucose enters the cells, blood sugar levels decrease. Conversely, when blood sugar levels drop, the pancreas releases glucagon, a hormone that stimulates the liver to release stored glucose into the bloodstream. This delicate balance ensures that blood sugar levels remain within a normal range.
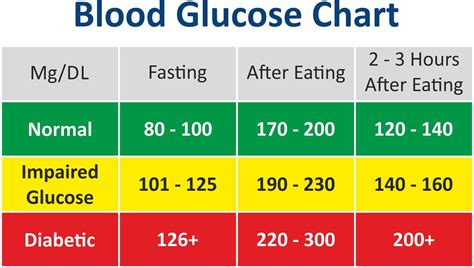
Understanding normal blood sugar levels is essential for individuals with diabetes or those who are at risk of developing the condition. Normal blood sugar levels vary throughout the day, depending on factors such as meal times, physical activity, and sleep patterns. For individuals without diabetes, normal blood sugar levels are typically between 70 and 140 milligrams per deciliter (mg/dL). After eating, blood sugar levels may rise to 180 mg/dL or higher, but they should return to normal within a few hours. For individuals with diabetes, the American Diabetes Association recommends the following blood sugar targets: before meals, 80-130 mg/dL; after meals, less than 180 mg/dL; and at bedtime, 100-140 mg/dL.
Factors That Influence Blood Sugar Levels
Several factors can influence blood sugar levels, including diet, physical activity, stress, and certain medications. A diet high in sugary foods and drinks can cause blood sugar levels to spike, while a diet rich in fiber and protein can help regulate blood sugar levels. Regular physical activity, such as walking or jogging, can also help lower blood sugar levels by increasing insulin sensitivity. Stress, on the other hand, can raise blood sugar levels by stimulating the release of stress hormones, such as cortisol and adrenaline. Certain medications, such as steroids and certain psychiatric medications, can also affect blood sugar levels.
Diet and Blood Sugar Levels
Diet plays a crucial role in maintaining normal blood sugar levels. Foods that are high in sugar, salt, and unhealthy fats can cause blood sugar levels to rise, while foods that are rich in fiber, protein, and healthy fats can help regulate blood sugar levels. The glycemic index (GI) is a measure of how quickly a food raises blood sugar levels. Foods with a high GI, such as white bread and sugary snacks, can cause blood sugar levels to spike, while foods with a low GI, such as whole grains and non-starchy vegetables, can help regulate blood sugar levels.
Benefits of Maintaining Normal Blood Sugar Levels
Maintaining normal blood sugar levels has numerous benefits, including reducing the risk of chronic diseases, such as heart disease, kidney disease, and nerve damage. Normal blood sugar levels can also improve cognitive function, reduce the risk of depression and anxiety, and promote healthy weight management. Additionally, maintaining normal blood sugar levels can improve sleep quality, increase energy levels, and enhance overall well-being.
Steps to Maintain Normal Blood Sugar Levels
Maintaining normal blood sugar levels requires a combination of healthy lifestyle habits, including a balanced diet, regular physical activity, stress management, and adequate sleep. Here are some steps to help maintain normal blood sugar levels:
- Eat a balanced diet that is rich in whole grains, fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and healthy fats.
- Engage in regular physical activity, such as walking, jogging, or yoga, for at least 30 minutes per day.
- Practice stress-reducing techniques, such as meditation or deep breathing exercises, to manage stress levels.
- Get adequate sleep, aiming for 7-8 hours per night, to help regulate blood sugar levels.
- Monitor blood sugar levels regularly, using a glucose meter or continuous glucose monitor, to track progress and make adjustments as needed.
Monitoring Blood Sugar Levels
Monitoring blood sugar levels is essential for individuals with diabetes or those who are at risk of developing the condition. There are several ways to monitor blood sugar levels, including:
- Fasting blood sugar test: This test measures blood sugar levels after an overnight fast.
- Postprandial blood sugar test: This test measures blood sugar levels after eating a meal.
- Continuous glucose monitoring: This involves wearing a small device that tracks blood sugar levels throughout the day.
- Urine tests: These tests measure the presence of ketones or glucose in the urine.
Tips for Monitoring Blood Sugar Levels
Here are some tips for monitoring blood sugar levels:
- Test blood sugar levels at the same time every day to track progress and make adjustments as needed.
- Use a glucose meter or continuous glucose monitor to track blood sugar levels.
- Keep a log of blood sugar levels, including the time of day, food consumed, and any medications taken.
- Adjust diet and physical activity habits based on blood sugar level readings.
- Consult with a healthcare provider to determine the best monitoring schedule and to discuss any concerns or questions.
Managing Blood Sugar Levels with Medication

For individuals with diabetes, medication may be necessary to manage blood sugar levels. There are several types of medications available, including:
- Metformin: This medication helps reduce glucose production in the liver and increase insulin sensitivity.
- Sulfonylureas: These medications stimulate the pancreas to release more insulin.
- Meglitinides: These medications stimulate the pancreas to release more insulin and reduce glucose production in the liver.
- Thiazolidinediones: These medications increase insulin sensitivity and reduce glucose production in the liver.
- GLP-1 receptor agonists: These medications increase insulin release and reduce glucose production in the liver.
Tips for Taking Medication
Here are some tips for taking medication to manage blood sugar levels:
- Take medication as directed by a healthcare provider.
- Monitor blood sugar levels regularly to track progress and make adjustments as needed.
- Keep a log of medication taken, including the time of day and any side effects experienced.
- Consult with a healthcare provider to discuss any concerns or questions.
- Do not stop taking medication without consulting with a healthcare provider.
Complications of Abnormal Blood Sugar Levels

Abnormal blood sugar levels can lead to various complications, including:
- Heart disease: High blood sugar levels can damage blood vessels and increase the risk of heart disease.
- Kidney disease: High blood sugar levels can damage the kidneys and increase the risk of kidney disease.
- Nerve damage: High blood sugar levels can damage nerves and increase the risk of nerve damage.
- Blindness: High blood sugar levels can damage the eyes and increase the risk of blindness.
- Amputations: High blood sugar levels can damage the feet and increase the risk of amputations.
Preventing Complications
Here are some tips for preventing complications of abnormal blood sugar levels:
- Maintain normal blood sugar levels through a combination of healthy lifestyle habits and medication.
- Monitor blood sugar levels regularly to track progress and make adjustments as needed.
- Keep a log of blood sugar levels, including the time of day, food consumed, and any medications taken.
- Consult with a healthcare provider to discuss any concerns or questions.
- Do not smoke, as smoking can increase the risk of complications.
Conclusion and Next Steps

In conclusion, maintaining normal blood sugar levels is crucial for overall health and well-being. By understanding the factors that influence blood sugar levels, following a balanced diet, engaging in regular physical activity, and monitoring blood sugar levels regularly, individuals can reduce the risk of chronic diseases and promote healthy weight management. If you have concerns about your blood sugar levels or are at risk of developing diabetes, consult with a healthcare provider to discuss the best course of action.
We encourage you to share your thoughts and questions about maintaining normal blood sugar levels in the comments section below. If you found this article helpful, please share it with your friends and family to help spread awareness about the importance of blood sugar management. Additionally, if you have any personal experiences or tips for managing blood sugar levels, we would love to hear about them.
What is the normal range for blood sugar levels?
+Normal blood sugar levels are typically between 70 and 140 milligrams per deciliter (mg/dL) for individuals without diabetes.
What factors can influence blood sugar levels?
+Several factors can influence blood sugar levels, including diet, physical activity, stress, and certain medications.
How can I monitor my blood sugar levels?
+There are several ways to monitor blood sugar levels, including fasting blood sugar tests, postprandial blood sugar tests, continuous glucose monitoring, and urine tests.
What are the complications of abnormal blood sugar levels?
+Abnormal blood sugar levels can lead to various complications, including heart disease, kidney disease, nerve damage, blindness, and amputations.
How can I prevent complications of abnormal blood sugar levels?
+By maintaining normal blood sugar levels through a combination of healthy lifestyle habits and medication, monitoring blood sugar levels regularly, and consulting with a healthcare provider, individuals can reduce the risk of complications.
