Intro
Discover Scopolamine Patch Side Effects, including drowsiness, dry mouth, and blurred vision. Learn about transdermal patch risks, overdose symptoms, and interactions, to ensure safe motion sickness treatment and minimize adverse reactions.
Scopolamine, also known as hyoscine, is a medication used to prevent nausea and vomiting caused by motion sickness and for the drying of oral, pharyngeal, and tracheal secretions before surgery. The scopolamine patch is a transdermal patch that releases a controlled amount of scopolamine into the bloodstream over a prolonged period. While the scopolamine patch can be effective in managing motion sickness and preoperative secretions, it can also cause several side effects. Understanding these side effects is crucial for patients who are considering using the scopolamine patch or are already using it.
The importance of being aware of the potential side effects of the scopolamine patch cannot be overstated. Side effects can range from mild and temporary to severe and long-lasting. In some cases, side effects may be so bothersome that they outweigh the benefits of using the medication, leading patients to seek alternative treatments. Furthermore, recognizing side effects early on can help prevent more serious complications from developing. As with any medication, it is essential to weigh the potential benefits against the potential risks and to discuss any concerns with a healthcare provider.
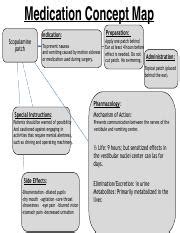
The scopolamine patch works by releasing scopolamine, an anticholinergic medication, into the bloodstream. Scopolamine blocks the action of acetylcholine, a neurotransmitter in the brain that is involved in many functions, including muscle contraction, heart rate, digestion, saliva production, and the regulation of mood and sleep. By blocking acetylcholine, scopolamine can prevent nausea and vomiting, reduce saliva and mucus production, and cause drowsiness, among other effects. However, this mechanism of action can also lead to a variety of side effects, some of which may be uncomfortable or disruptive to daily life.
Common Side Effects of the Scopolamine Patch
Less Common but More Serious Side Effects
In addition to the common side effects, the scopolamine patch can cause less common but more serious side effects. These include hallucinations, disorientation, and delirium, particularly in elderly patients. The patch can also cause urinary retention, which can lead to discomfort and increase the risk of urinary tract infections. Furthermore, the scopolamine patch can exacerbate glaucoma, a condition characterized by increased pressure in the eye that can lead to vision loss if left untreated.Rare but Potentially Life-Threatening Side Effects
Factors That Increase the Risk of Side Effects
Certain factors can increase the risk of experiencing side effects from the scopolamine patch. Older adults, for example, may be more susceptible to the anticholinergic effects of scopolamine due to age-related changes in drug metabolism and excretion. Patients with certain medical conditions, such as glaucoma, urinary retention, or gastrointestinal obstruction, may also be at higher risk for side effects. Additionally, taking other medications that have anticholinergic properties can increase the risk of side effects when used in combination with the scopolamine patch.Managing Side Effects of the Scopolamine Patch
When to Seek Medical Attention
In some cases, side effects of the scopolamine patch can be severe enough to require medical attention. Patients should seek immediate medical help if they experience symptoms such as difficulty breathing, rapid heartbeat, or a drop in blood pressure, which can indicate anaphylaxis. They should also seek medical attention if they experience severe hallucinations, disorientation, or delirium, or if they have symptoms of anticholinergic toxicity, such as fever, agitation, and hallucinations.Alternatives to the Scopolamine Patch

Preventing Side Effects with Proper Use
Proper use of the scopolamine patch can help to minimize the risk of side effects. Patients should follow the instructions provided by their healthcare provider carefully and apply the patch to a clean, dry area of skin behind the ear. They should avoid touching the patch or handling it excessively, as this can cause the scopolamine to be absorbed through the skin and increase the risk of side effects. Patients should also avoid using the patch for longer than recommended or using multiple patches at the same time, as this can increase the risk of overdose and severe side effects.Conclusion and Future Directions
Final Thoughts
The scopolamine patch is a valuable treatment option for patients who need to manage nausea and vomiting or preoperative secretions. However, it is crucial for patients to be aware of the potential side effects and to discuss any concerns with their healthcare provider. By working together, patients and healthcare providers can ensure that the benefits of treatment outweigh the risks and that patients receive the best possible care.What are the most common side effects of the scopolamine patch?
+The most common side effects of the scopolamine patch include dry mouth, drowsiness, dizziness, blurred vision, and confusion.
Can the scopolamine patch cause serious side effects?
+Yes, the scopolamine patch can cause serious side effects, including anaphylaxis, anticholinergic toxicity, and hallucinations, particularly in elderly patients.
How can I manage side effects of the scopolamine patch?
+Patients can manage side effects of the scopolamine patch by staying hydrated, using sugar-free candy or gum to stimulate saliva production, avoiding driving or operating heavy machinery, and taking regular breaks to rest.
Are there alternative treatments to the scopolamine patch?
+Yes, alternative treatments to the scopolamine patch include other medications, such as ondansetron or metoclopramide, and non-pharmacological approaches, such as acupressure or ginger.
How can I prevent side effects of the scopolamine patch?
+Patients can prevent side effects of the scopolamine patch by following the instructions provided by their healthcare provider carefully, applying the patch to a clean, dry area of skin behind the ear, and avoiding touching the patch or handling it excessively.
