Intro
Understand your Calcium Level Test Results, including normal ranges, high and low calcium levels, and related health implications like osteoporosis, hypercalcemia, and hypocalcemia, to maintain optimal bone health and prevent related diseases.
Calcium plays a crucial role in the human body, and its level in the blood is a vital indicator of overall health. The calcium level test is a common diagnostic tool used to measure the amount of calcium in the blood. Abnormal calcium levels can indicate various health issues, such as bone disorders, kidney problems, or hormonal imbalances. Understanding the importance of calcium level test results is essential for individuals to take control of their health and make informed decisions.
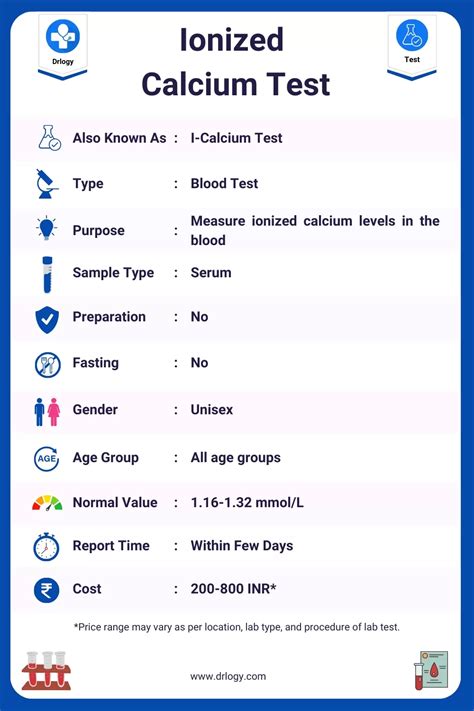
The calcium level test is typically performed as part of a routine health checkup or when symptoms such as muscle cramps, weakness, or bone pain are present. The test measures the total calcium level in the blood, which includes both free and bound calcium. Free calcium is the active form of calcium that is not attached to proteins, while bound calcium is attached to proteins such as albumin. The test results are usually reported in milligrams per deciliter (mg/dL) or millimoles per liter (mmol/L).
The normal range for calcium levels in the blood is between 8.6 and 10.3 mg/dL. However, this range may vary slightly depending on the laboratory or testing method used. It is essential to consult with a healthcare professional to understand the test results and determine the best course of action. Abnormal calcium levels can be caused by various factors, such as dietary deficiencies, certain medications, or underlying medical conditions.
Understanding Calcium Level Test Results
Understanding calcium level test results requires a comprehensive approach, taking into account the individual's medical history, symptoms, and lifestyle. A healthcare professional will interpret the test results and provide guidance on the necessary steps to take. In some cases, additional testing may be required to determine the underlying cause of abnormal calcium levels.
Normal Calcium Levels
Normal calcium levels are typically between 8.6 and 10.3 mg/dL. However, this range may vary slightly depending on the laboratory or testing method used. It is essential to consult with a healthcare professional to understand the test results and determine the best course of action. Individuals with normal calcium levels are generally considered healthy and do not require any specific treatment.Abnormal Calcium Levels
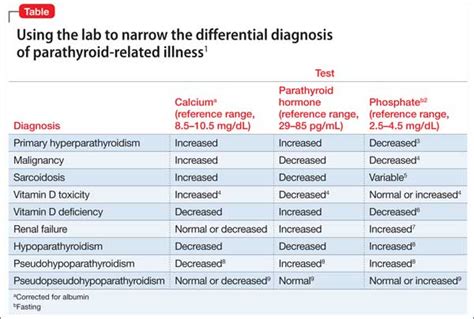
Abnormal calcium levels can be caused by various factors, such as dietary deficiencies, certain medications, or underlying medical conditions. Hypercalcemia, or elevated calcium levels, can be caused by conditions such as hyperparathyroidism, vitamin D toxicity, or certain types of cancer. Hypocalcemia, or low calcium levels, can be caused by conditions such as vitamin D deficiency, kidney disease, or certain medications.
Hypocalcemia
Hypocalcemia is a condition characterized by low calcium levels in the blood. Symptoms of hypocalcemia may include muscle cramps, weakness, and numbness or tingling in the fingers and toes. Treatment for hypocalcemia typically involves addressing the underlying cause of the condition, such as vitamin D deficiency or kidney disease. In some cases, calcium supplements may be prescribed to help raise calcium levels.Causes of Abnormal Calcium Levels
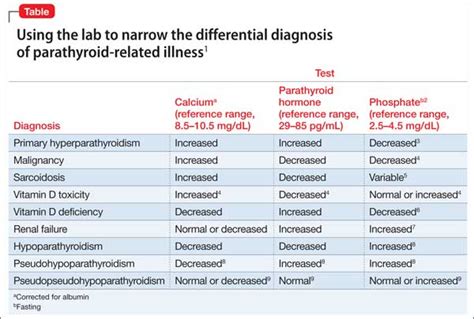
Abnormal calcium levels can be caused by various factors, including dietary deficiencies, certain medications, or underlying medical conditions. Some common causes of abnormal calcium levels include:
- Dietary deficiencies: A diet that is low in calcium or vitamin D can lead to abnormal calcium levels.
- Certain medications: Certain medications, such as diuretics or antacids, can affect calcium levels.
- Underlying medical conditions: Conditions such as hyperparathyroidism, kidney disease, or certain types of cancer can cause abnormal calcium levels.
Treatment Options
Treatment options for abnormal calcium levels depend on the underlying cause of the condition. In some cases, lifestyle changes such as dietary modifications or increased physical activity may be recommended. In other cases, medication or surgery may be necessary to address the underlying cause of the condition.Prevention and Management

Prevention and management of abnormal calcium levels require a comprehensive approach, taking into account the individual's medical history, symptoms, and lifestyle. Some tips for preventing and managing abnormal calcium levels include:
- Maintaining a balanced diet that is rich in calcium and vitamin D
- Engaging in regular physical activity to support bone health
- Avoiding certain medications that can affect calcium levels
- Managing underlying medical conditions that can cause abnormal calcium levels
Lifestyle Modifications
Lifestyle modifications can play an essential role in preventing and managing abnormal calcium levels. Maintaining a balanced diet that is rich in calcium and vitamin D is crucial for supporting bone health. Engaging in regular physical activity, such as weight-bearing exercises, can also help to support bone health.Conclusion and Next Steps

In conclusion, understanding calcium level test results is essential for individuals to take control of their health and make informed decisions. Abnormal calcium levels can be caused by various factors, and treatment options depend on the underlying cause of the condition. By maintaining a balanced diet, engaging in regular physical activity, and managing underlying medical conditions, individuals can help to prevent and manage abnormal calcium levels.
Final Thoughts
Final thoughts on calcium level test results emphasize the importance of a comprehensive approach to healthcare. By working with a healthcare professional and making informed decisions, individuals can take control of their health and reduce the risk of complications associated with abnormal calcium levels.What is the normal range for calcium levels in the blood?
+The normal range for calcium levels in the blood is between 8.6 and 10.3 mg/dL.
What are the symptoms of hypocalcemia?
+Symptoms of hypocalcemia may include muscle cramps, weakness, and numbness or tingling in the fingers and toes.
How can I prevent and manage abnormal calcium levels?
+Prevention and management of abnormal calcium levels require a comprehensive approach, including maintaining a balanced diet, engaging in regular physical activity, and managing underlying medical conditions.
We encourage readers to share their thoughts and experiences with calcium level test results in the comments below. If you have any questions or concerns, please do not hesitate to reach out to a healthcare professional. Share this article with friends and family to help raise awareness about the importance of calcium level test results and overall health.
