Intro
The sedimentation rate test, also known as the erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) test, is a blood test that measures how quickly erythrocytes (red blood cells) settle at the bottom of a test tube containing a blood sample. It indirectly measures how much inflammation is in the body. The sedimentation rate test has been a crucial diagnostic tool in the medical field for many years, helping doctors diagnose and monitor various conditions, including inflammatory diseases, infections, and cancers. In this article, we will delve into the world of sedimentation rate tests, exploring how they work, their benefits, and what the results mean.
The sedimentation rate test is a simple, yet effective way to assess the level of inflammation in the body. When a person has an inflammatory condition, their blood contains more proteins that cause red blood cells to clump together, making them heavier and more likely to settle quickly. By measuring the rate at which these cells settle, doctors can determine the level of inflammation and make informed decisions about the best course of treatment. The test is particularly useful for monitoring conditions such as rheumatoid arthritis, lupus, and other autoimmune diseases, where inflammation can cause significant damage to the body.
Inflammation is a natural response of the body's immune system, designed to protect against infection and injury. However, chronic inflammation can lead to a range of health problems, including tissue damage, organ dysfunction, and increased risk of diseases such as heart disease and cancer. The sedimentation rate test provides a valuable tool for doctors to assess the level of inflammation and make adjustments to treatment plans as needed. With its ability to detect even slight changes in inflammation levels, the test has become an essential component of medical diagnosis and monitoring.
How Sedimentation Rate Test Works
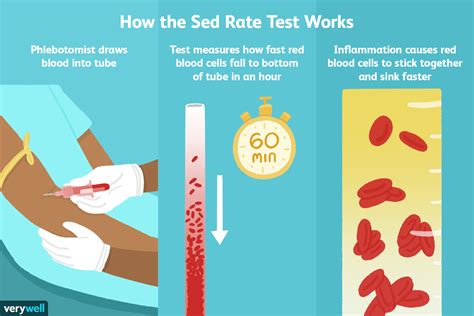
Steps Involved in Sedimentation Rate Test
The steps involved in the sedimentation rate test are relatively straightforward. They include: * Collecting a blood sample from the patient * Adding an anticoagulant to the sample to prevent clotting * Placing the sample in a test tube * Leaving the tube to stand for a specified period * Measuring and recording the distance the red blood cells have settled * Interpreting the results to determine the level of inflammationBenefits of Sedimentation Rate Test
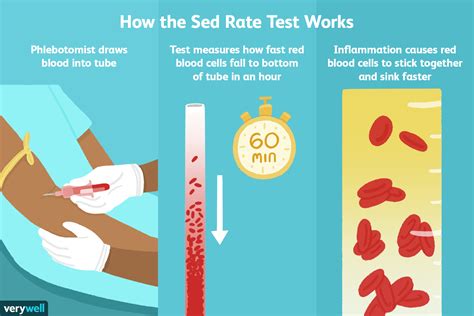
What the Results Mean
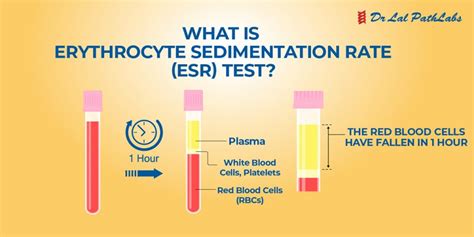
The results of the sedimentation rate test are measured in millimeters per hour (mm/h). A normal result typically ranges from 0-20 mm/h, although this can vary depending on the laboratory and the individual's age and sex. A high result indicates a higher level of inflammation, while a low result suggests a lower level of inflammation. The results are often used in conjunction with other diagnostic tests to confirm a diagnosis and develop an effective treatment plan.Interpreting Sedimentation Rate Test Results

Factors that Can Affect Sedimentation Rate Test Results
Several factors can affect the results of the sedimentation rate test, including age, sex, pregnancy, and certain medications. For example, women tend to have higher sedimentation rates than men, while older adults may have higher rates due to age-related changes. Pregnancy can also affect the results, as the body's inflammatory response changes during pregnancy. Certain medications, such as corticosteroids and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), can also impact the results.Common Conditions Diagnosed with Sedimentation Rate Test
Limitations of Sedimentation Rate Test
While the sedimentation rate test is a valuable diagnostic tool, it has several limitations. The test is not specific, meaning that a high result can indicate a range of conditions, rather than a single diagnosis. The test is also not sensitive, meaning that a low result does not necessarily rule out the presence of an inflammatory condition. Additionally, the test can be affected by several factors, including age, sex, and certain medications.Future Directions for Sedimentation Rate Test

Conclusion and Final Thoughts
In conclusion, the sedimentation rate test is a valuable diagnostic tool that has been used for many years to detect and monitor inflammation in the body. While the test has several limitations, its benefits make it a crucial component of medical diagnosis and monitoring. As research and technology continue to evolve, it is likely that the sedimentation rate test will remain an essential tool for doctors and healthcare professionals. By understanding how the test works, its benefits, and its limitations, individuals can better appreciate the importance of this diagnostic tool and make informed decisions about their health.What is the sedimentation rate test used for?
+The sedimentation rate test is used to detect and monitor inflammation in the body, and to diagnose and monitor conditions such as inflammatory diseases, infections, and cancers.
How is the sedimentation rate test performed?
+The sedimentation rate test involves collecting a blood sample, adding an anticoagulant, and placing the sample in a test tube. The tube is then left to stand for a specified period, allowing the red blood cells to settle. The distance the cells have settled is then measured and recorded.
What do the results of the sedimentation rate test mean?
+The results of the sedimentation rate test are measured in millimeters per hour (mm/h). A normal result typically ranges from 0-20 mm/h, although this can vary depending on the laboratory and the individual's age and sex. A high result indicates a higher level of inflammation, while a low result suggests a lower level of inflammation.
