Intro
Discover how Fluconazole treats fungal infections, including candidiasis, thrush, and ringworm, with its antifungal properties, dosage, and side effects, for effective management of yeast and fungal diseases.
The world of medicine has seen significant advancements in recent years, with various treatments being developed to combat a wide range of diseases. One such treatment is fluconazole, an antifungal medication used to treat various fungal infections. Fungal infections can be debilitating and even life-threatening if left untreated, making it essential to understand the importance of fluconazole in the medical world. In this article, we will delve into the world of fluconazole, exploring its uses, benefits, and working mechanisms.
Fungal infections are a common occurrence, affecting millions of people worldwide. These infections can range from mild to severe, causing a significant impact on a person's quality of life. Fluconazole is a triazole antifungal agent that has been widely used to treat various fungal infections, including vaginal yeast infections, oral thrush, and fungal meningitis. The medication works by inhibiting the growth of fungi, ultimately leading to their death. This makes fluconazole an essential treatment option for individuals suffering from fungal infections.
The importance of fluconazole cannot be overstated, as it has revolutionized the treatment of fungal infections. Prior to its development, fungal infections were often difficult to treat, with limited treatment options available. Fluconazole has changed this landscape, providing a safe and effective treatment option for individuals suffering from these infections. In addition to its effectiveness, fluconazole is also relatively safe, with minimal side effects reported. This makes it an attractive treatment option for individuals who may be susceptible to the adverse effects of other medications.
What is Fluconazole?

How Does Fluconazole Work?
Fluconazole works by interfering with the synthesis of ergosterol, a critical component of the fungal cell membrane. Ergosterol is essential for the growth and survival of fungi, and its inhibition leads to the death of the fungal cells. Fluconazole achieves this by binding to the enzyme lanosterol 14-alpha-demethylase, which is responsible for the conversion of lanosterol to ergosterol. This binding inhibits the enzyme, leading to a decrease in ergosterol synthesis and ultimately causing the death of the fungal cells.Uses of Fluconazole
Benefits of Fluconazole
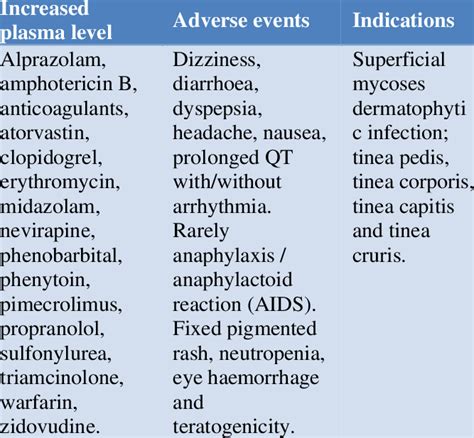
The benefits of fluconazole are numerous, making it a popular treatment option for fungal infections. Some of the benefits include: * Effective treatment of fungal infections * Relatively safe, with minimal side effects * Easy to administer, with various forms available * Can be used to prevent fungal infections in high-risk individuals * Has a broad spectrum of activity, making it effective against a wide range of fungiSide Effects of Fluconazole

Precautions and Contraindications
Fluconazole is contraindicated in individuals who are allergic to the medication or have a history of allergic reactions to other triazole antifungal agents. The medication should also be used with caution in individuals with liver or kidney disease, as it can exacerbate these conditions. Pregnant and breastfeeding women should also use fluconazole with caution, as it can pass into breast milk and affect the fetus.Interactions with Other Medications
Dosage and Administration
The dosage and administration of fluconazole vary depending on the type and severity of the fungal infection being treated. The medication is usually taken orally, with doses ranging from 50 to 400 mg per day. The duration of treatment also varies, ranging from a few days to several weeks or even months. Individuals should follow the dosage and administration instructions provided by their healthcare provider to ensure effective treatment and minimize the risk of side effects.Conclusion and Final Thoughts

We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences with fluconazole in the comments section below. Have you or someone you know used fluconazole to treat a fungal infection? What were your experiences with the medication? Share your story and help others understand the importance of fluconazole in the treatment of fungal infections.
What is fluconazole used for?
+Fluconazole is used to treat a wide range of fungal infections, including vaginal yeast infections, oral thrush, and fungal meningitis.
How does fluconazole work?
+Fluconazole works by inhibiting the synthesis of ergosterol, a critical component of the fungal cell membrane, ultimately leading to the death of the fungal cells.
What are the side effects of fluconazole?
+The side effects of fluconazole include nausea and vomiting, diarrhea, abdominal pain, headache, dizziness, and rash. These side effects are usually mild and temporary, resolving on their own once the medication is discontinued.
Can fluconazole interact with other medications?
+Yes, fluconazole can interact with other medications, including warfarin, phenyltoin, cyclosporine, rifampin, and hydrochlorothiazide. These interactions can lead to increased levels of fluconazole in the body, increasing the risk of side effects.
How should fluconazole be taken?
+Fluconazole should be taken orally, with doses ranging from 50 to 400 mg per day. The duration of treatment varies depending on the type and severity of the fungal infection being treated. Individuals should follow the dosage and administration instructions provided by their healthcare provider to ensure effective treatment and minimize the risk of side effects.