Intro
Identify 7 key bladder infection signs, including UTI symptoms, painful urination, and frequent bathroom trips, to seek timely treatment and prevent complications like kidney damage and sepsis.
Bladder infections, also known as urinary tract infections (UTIs), are a common health issue that affects millions of people worldwide. These infections occur when bacteria enter the urinary tract, causing inflammation and discomfort. Recognizing the signs of a bladder infection is crucial for seeking medical attention and preventing complications. In this article, we will delve into the importance of understanding bladder infection signs, their impact on daily life, and the measures that can be taken to prevent and treat these infections.
Bladder infections can affect anyone, regardless of age or gender, although they are more prevalent in women due to their shorter urethra, which makes it easier for bacteria to reach the bladder. Understanding the signs and symptoms of bladder infections is essential for early detection and treatment, which can help prevent the infection from spreading to the kidneys and causing more severe damage. The symptoms of a bladder infection can range from mild to severe and may include frequent urination, burning sensations while urinating, and abdominal pain.
The importance of recognizing bladder infection signs cannot be overstated. If left untreated, these infections can lead to serious complications, such as kidney damage, sepsis, and even life-threatening conditions. Furthermore, recurring bladder infections can significantly impact an individual's quality of life, causing discomfort, anxiety, and disrupting daily activities. Therefore, it is crucial to be aware of the signs and symptoms of bladder infections and to seek medical attention if any of these symptoms persist or worsen over time.
Introduction to Bladder Infections
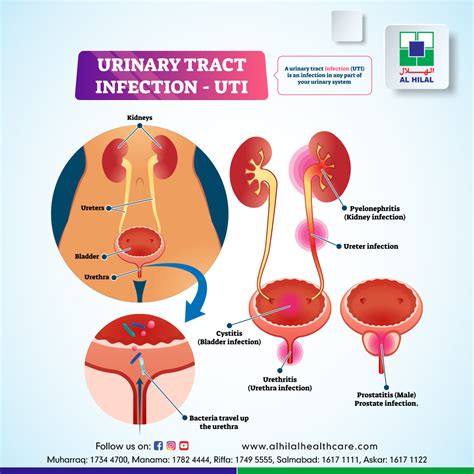
Risk Factors for Bladder Infections
Several risk factors increase the likelihood of developing bladder infections, including: * Gender: Women are more prone to bladder infections due to their shorter urethra. * Age: Older adults and young children are more susceptible to bladder infections. * Sexual activity: Sexual intercourse can increase the risk of introducing bacteria into the urinary tract. * Certain medical conditions: Individuals with diabetes, kidney stones, or spinal cord injuries are more prone to bladder infections. * Weakened immune system: People with weakened immune systems, such as those with HIV/AIDS or undergoing chemotherapy, are more susceptible to bladder infections.Signs and Symptoms of Bladder Infections
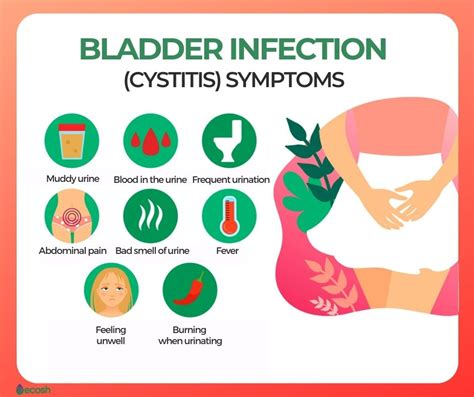
Diagnosing Bladder Infections
Diagnosing bladder infections typically involves a physical examination, medical history, and laboratory tests, such as: * Urinalysis: A test that checks the urine for bacteria, blood, or other abnormalities. * Urine culture: A test that identifies the type of bacteria causing the infection. * Imaging tests: Such as ultrasound or CT scans, which can help identify any abnormalities in the urinary tract.Treatment and Prevention of Bladder Infections

Complications of Bladder Infections
If left untreated, bladder infections can lead to serious complications, including: * Kidney damage: The infection can spread to the kidneys, causing permanent damage. * Sepsis: A life-threatening condition that occurs when the infection spreads to the bloodstream. * Recurring infections: Untreated bladder infections can increase the risk of recurring infections.Managing Bladder Infection Symptoms
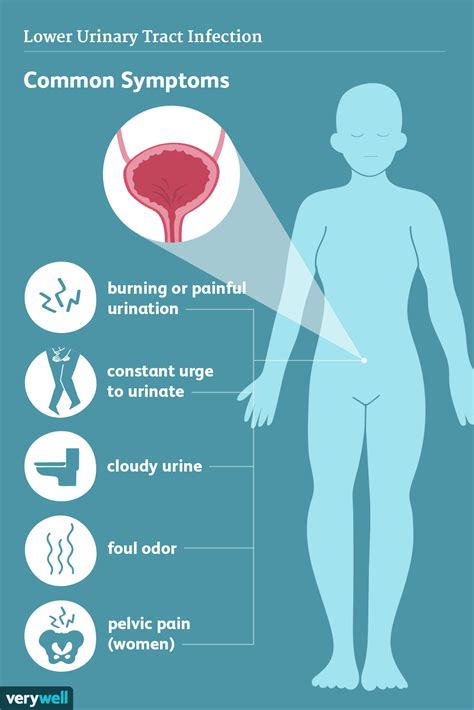
Seeking Medical Attention
It is essential to seek medical attention if any of the following occur: * Severe symptoms: Such as severe abdominal pain, vomiting, or fever. * Blood in the urine: Which can be a sign of a more severe infection. * Recurring infections: If bladder infections recur frequently, it may be necessary to consult a healthcare provider for further evaluation and treatment.Conclusion and Next Steps
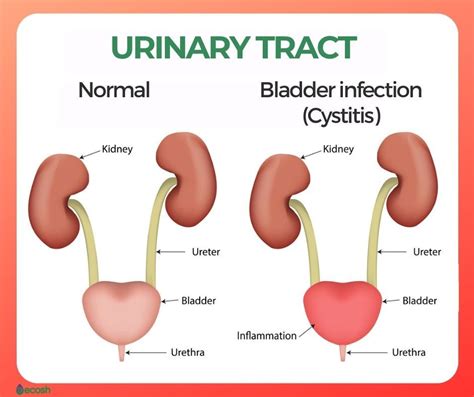
We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences with bladder infections in the comments below. If you found this article informative, please consider sharing it with others who may benefit from this information. Additionally, if you have any questions or concerns, please do not hesitate to reach out to a healthcare professional for guidance and support.
What are the most common causes of bladder infections?
+Bladder infections are typically caused by bacteria, such as Escherichia coli (E. coli), which enter the urinary tract through the urethra.
How can I prevent bladder infections?
+To prevent bladder infections, drink plenty of water, urinate when needed, wipe correctly, avoid certain foods, and practice good hygiene.
What are the complications of untreated bladder infections?
+Untreated bladder infections can lead to serious complications, including kidney damage, sepsis, and recurring infections.
