Intro
Discover 5 ways sunspots appear, exploring solar activity, magnetic storms, and sunspot cycles, revealing astronomys role in understanding space weather and celestial phenomena.
The sun is a massive ball of hot, glowing gas, and its surface is constantly changing. One of the most fascinating features of the sun is the appearance of sunspots, which are dark regions that appear on the surface of the sun due to intense magnetic activity. Sunspots have been observed for centuries, and they continue to be a topic of interest for scientists and astronomers. In this article, we will explore the different ways that sunspots appear, and what they can tell us about the sun's behavior.
Sunspots are an important area of study in the field of solar physics, as they can provide valuable insights into the sun's internal dynamics and its impact on the solar system. By studying sunspots, scientists can gain a better understanding of the sun's magnetic field, its rotation, and its energy output. This knowledge can also help us to better understand the effects of solar activity on the Earth's climate and magnetic field.
The study of sunspots is also important for understanding the sun's impact on space weather. Space weather refers to the dynamic and variable conditions in the space environment, which can affect the performance and reliability of spacecraft and satellites. Sunspots are a key driver of space weather, as they can produce intense magnetic storms and solar flares that can interact with the Earth's magnetic field and cause disruptions to communication and navigation systems.
Introduction to Sunspots
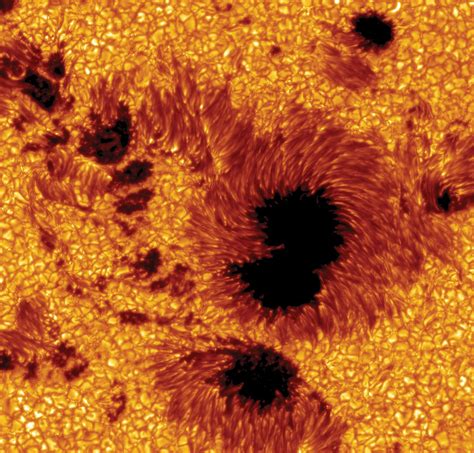
Types of Sunspots
There are several types of sunspots, each with its own unique characteristics. The most common type of sunspot is the umbral sunspot, which is a dark region with a well-defined boundary. Umbral sunspots are typically surrounded by a lighter region known as the penumbra, which is a area of partial shadowing. There are also more complex sunspots, such as the bipolar sunspot, which has two distinct regions of opposite magnetic polarity.The Life Cycle of Sunspots
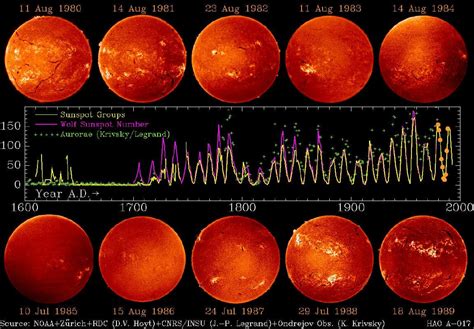
Sunspot Activity and the Solar Cycle
Sunspot activity is closely tied to the solar cycle, which is the periodic variation in the sun's energy output and magnetic field. The solar cycle is typically 11 years long, and it is characterized by periods of high and low sunspot activity. During periods of high activity, the sun's magnetic field is strong, and sunspots are more frequent and intense. During periods of low activity, the sun's magnetic field is weak, and sunspots are less frequent and less intense.The Effects of Sunspots on Space Weather
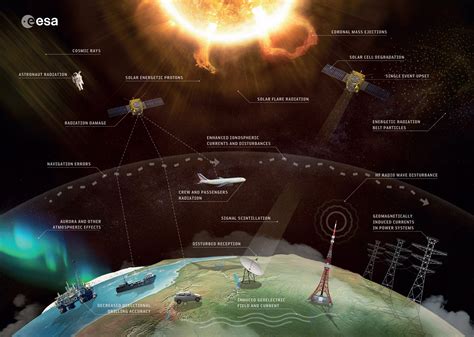
The Impact of Sunspots on the Earth's Climate
There is ongoing debate about the impact of sunspots on the Earth's climate. Some scientists argue that changes in sunspot activity can affect the Earth's climate by altering the amount of solar energy that reaches the planet. Others argue that the impact of sunspots on the Earth's climate is minimal, and that other factors such as volcanic eruptions and human activities are more important. While the exact impact of sunspots on the Earth's climate is still unclear, it is clear that sunspots can have a significant impact on space weather and the performance of spacecraft and satellites.Observing Sunspots
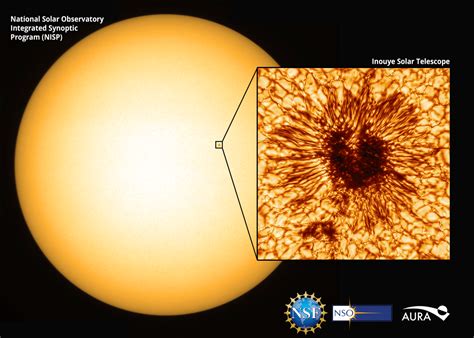
The Future of Sunspot Research
The study of sunspots is an ongoing area of research, with new missions and telescopes being developed to study the sun and its behavior. The Solar Dynamics Observatory (SDO) is a NASA mission that has been studying the sun since 2010, providing high-resolution images and data on the sun's magnetic field and energy output. The Parker Solar Probe is a NASA mission that was launched in 2018, which will study the sun's corona and the solar wind. These and other missions will help us to better understand the sun and its behavior, and to improve our predictions of space weather events.Conclusion and Future Directions

Final Thoughts
The study of sunspots is a rich and rewarding area of research, with many opportunities for new discoveries and insights. By continuing to study the sun and its behavior, we can gain a deeper understanding of the solar system and our place within it. We can also improve our predictions of space weather events, which can help to protect spacecraft and satellites from the effects of solar activity. Whether you are a scientist, an astronomer, or simply someone who is interested in the sun and its behavior, there is no denying the fascination and importance of sunspots.What are sunspots?
+Sunspots are dark regions that appear on the surface of the sun due to intense magnetic activity.
How are sunspots formed?
+Sunspots are formed when concentrations of magnetic field lines inhibit the flow of hot, ionized gas from the sun's interior to its surface.
What is the life cycle of a sunspot?
+The life cycle of a sunspot begins with its emergence, grows as it develops a complex structure, and eventually decays and disappears.
We hope that this article has provided you with a comprehensive overview of sunspots and their importance in the field of solar physics. Whether you are a scientist, an astronomer, or simply someone who is interested in the sun and its behavior, we encourage you to continue learning about sunspots and their role in the solar system. Share your thoughts and questions in the comments below, and don't forget to share this article with others who may be interested in the fascinating world of sunspots.
