Intro
Discover the 5 common staph infection causes, including poor hygiene, contaminated food, and skin conditions, to understand the risks of MRSA, boils, and cellulitis, and learn prevention methods to reduce bacterial transmission.
Staph infections, caused by the bacterium Staphylococcus, are a common and sometimes serious health issue affecting millions of people worldwide. These infections can range from mild to severe and are known for their rapid onset and potential to spread quickly. Understanding the causes of staph infections is crucial for prevention and treatment. Staph bacteria are typically found on the skin and in the noses of healthy individuals, but they can become harmful when they enter the body through cuts or other openings. The bacteria can also be spread through contact with contaminated surfaces, food, or other people.
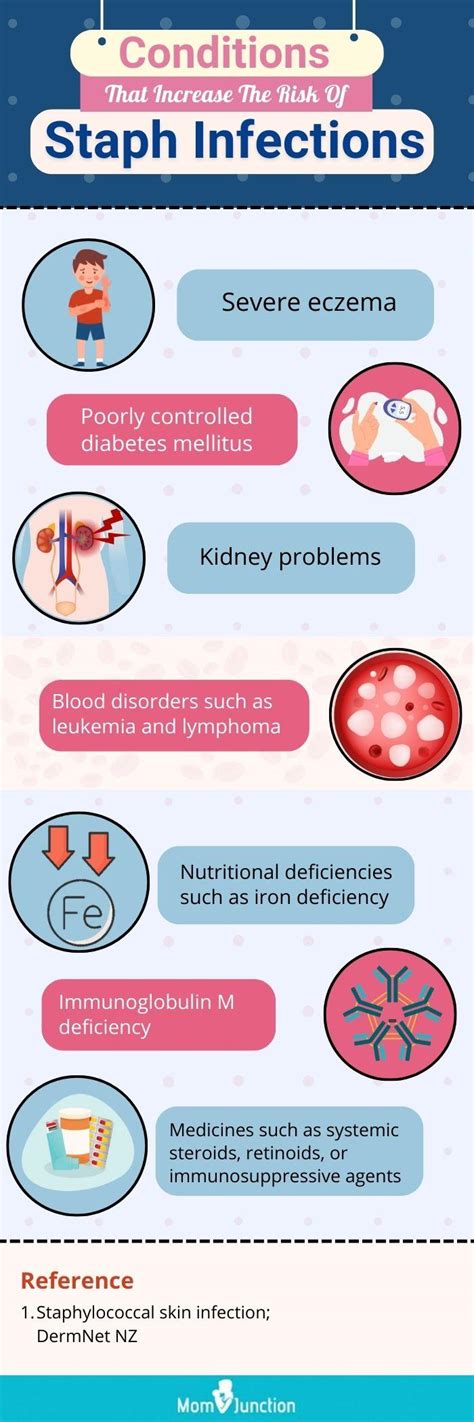
Staph infections can manifest in various forms, including skin infections like boils, impetigo, and cellulitis, as well as more severe conditions such as pneumonia, meningitis, and sepsis. The severity of the infection often depends on the location of the infection, the depth of the infection, and the overall health of the individual. People with weakened immune systems, such as those with chronic illnesses or taking immunosuppressive drugs, are at a higher risk of developing severe staph infections.
The importance of recognizing the causes of staph infections cannot be overstated. By understanding how these infections occur, individuals can take proactive steps to prevent them. This includes practicing good hygiene, such as washing hands regularly, keeping wounds clean and covered, and avoiding close contact with someone who has a staph infection. Furthermore, being aware of the common causes of staph infections can help in early diagnosis and treatment, which is critical for preventing the infection from becoming severe.
Introduction to Staph Infections
Types of Staph Infections
Staph infections can be classified based on the location and severity of the infection. Skin infections are the most common type and include conditions such as boils, impetigo, and cellulitis. More severe infections can affect the lungs (pneumonia), the brain and spinal cord (meningitis), the blood (sepsis), and other parts of the body. The type of infection and its severity often dictate the treatment approach, which can range from oral antibiotics for mild skin infections to intravenous antibiotics and hospitalization for more severe conditions.Cause 1: Skin-to-Skin Contact

Prevention Strategies
Preventing the spread of staph infections through skin-to-skin contact involves several strategies. Individuals should avoid sharing personal items such as towels, razors, and athletic equipment. Regular cleaning and disinfection of surfaces, especially in areas where people are more likely to come into contact with each other, can also reduce the risk of transmission. Furthermore, encouraging good hygiene practices, such as frequent hand washing and proper wound care, can help prevent the spread of staph infections.Cause 2: Contaminated Surfaces and Objects

Environmental Cleaning
Regular and thorough cleaning of environments, particularly in areas prone to high touch or where individuals may be more susceptible to infections, is crucial. This includes schools, hospitals, and athletic facilities. The use of appropriate disinfectants that are known to be effective against staph bacteria can significantly reduce the presence of these pathogens on surfaces. Additionally, promoting practices such as covering wounds, washing hands after touching potentially contaminated surfaces, and avoiding touching one's face can help prevent the spread of staph infections.Cause 3: Food Contamination

Safe Food Handling Practices
Safe food handling practices are key to preventing the spread of staph infections through food. This includes ensuring that food is stored at the correct temperature, cooked thoroughly, and handled by individuals who practice good hygiene. Regular hand washing, especially after touching raw foods and before handling ready-to-eat foods, can significantly reduce the risk of contamination. Additionally, avoiding leaving perishable foods at room temperature for extended periods can help prevent the growth of staph bacteria.Cause 4: Poor Hygiene Practices

Importance of Hand Hygiene
Hand hygiene is one of the most effective measures to prevent the spread of staph infections. Washing hands with soap and water for at least 20 seconds, especially after coming into contact with someone who has a staph infection, after using the bathroom, and before eating, can significantly reduce the risk of transmission. In settings where soap and water are not available, using an alcohol-based hand sanitizer is an effective alternative. Promoting a culture of hand hygiene in all settings, from households to healthcare facilities, is crucial for preventing the spread of staph infections.Cause 5: Weakened Immune System

Supporting Immune Function
Supporting immune function through a healthy lifestyle can help prevent staph infections. This includes maintaining a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains, staying hydrated, exercising regularly, and getting enough sleep. Avoiding smoking and limiting alcohol consumption can also help support immune function. For individuals with chronic conditions or taking immunosuppressive medications, following the advice of healthcare providers and taking all prescribed medications as directed is crucial for managing their condition and preventing infections.In conclusion, understanding the causes of staph infections is vital for their prevention and treatment. By recognizing the role of skin-to-skin contact, contaminated surfaces and objects, food contamination, poor hygiene practices, and weakened immune systems in the spread of these infections, individuals can take proactive steps to protect themselves and their communities. Promoting good hygiene practices, supporting immune function, and being aware of the risks associated with staph infections can significantly reduce their incidence and severity.
To further understand and address concerns about staph infections, it's essential to engage with the community and healthcare professionals. We invite readers to share their experiences, ask questions, and seek advice on how to prevent and manage staph infections. By working together, we can better combat these infections and improve public health.
What are the common symptoms of staph infections?
+Common symptoms of staph infections include redness, swelling, and pain at the site of infection, as well as fever, chills, and fatigue in more severe cases.
How are staph infections diagnosed?
+Staph infections are typically diagnosed through a combination of physical examination, medical history, and laboratory tests such as blood cultures and wound cultures.
Can staph infections be prevented?
+Yes, staph infections can be prevented through good hygiene practices such as frequent hand washing, keeping wounds clean and covered, and avoiding close contact with individuals who have staph infections.
What is the treatment for staph infections?
+Treatment for staph infections typically involves antibiotics, with the specific type and duration of treatment depending on the severity and location of the infection.
Are staph infections contagious?
+Yes, staph infections can be contagious and are spread through skin-to-skin contact with an infected person, contaminated surfaces and objects, and in some cases, through food contamination.
