Intro
Discover the 7 DKA symptoms, including hyperglycemia, ketoacidosis, and dehydration, to recognize diabetic ketoacidosis warning signs and seek timely medical help, managing blood sugar levels and preventing complications.
Diabetic ketoacidosis, commonly referred to as DKA, is a serious complication of diabetes that occurs when the body produces high levels of blood acids called ketones. This condition arises when the body cannot produce enough insulin, a hormone that regulates blood sugar levels. Without sufficient insulin, the body starts breaking down fat for energy, resulting in the production of ketones. If left untreated, DKA can lead to severe illness or even death. Recognizing the symptoms of DKA is crucial for timely medical intervention.
The importance of understanding DKA symptoms cannot be overstated. Early detection and treatment can significantly improve outcomes for individuals with diabetes. Moreover, being aware of the risk factors and taking preventive measures can reduce the likelihood of developing DKA. This knowledge is not only essential for individuals living with diabetes but also for their families and caregivers, who play a vital role in monitoring their health and providing support.
DKA can affect anyone with diabetes, although it is more common in people with type 1 diabetes. However, individuals with type 2 diabetes can also develop DKA, especially if they are taking certain medications or have underlying health conditions. The condition can arise suddenly, even in people who have been managing their diabetes well. Therefore, it is critical to be familiar with the warning signs of DKA and to seek medical help immediately if these symptoms occur.
Understanding DKA

Causes of DKA
The causes of DKA can be multifaceted and include a range of factors. Some of the most common causes include: - Inadequate insulin therapy - Infection or illness - Certain medications - Poor dietary habits - Underlying health conditionsDKA Symptoms

Early Warning Signs
In some cases, individuals may experience early warning signs that indicate the onset of DKA. These can include: - High blood sugar levels - Presence of ketones in the urine - Increased heart rate - Dry mouth - HeadacheRisk Factors for DKA
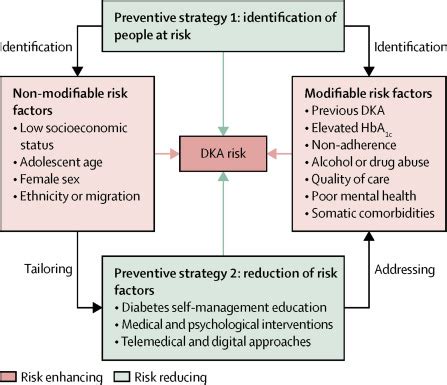
Prevention Strategies
Preventing DKA involves a combination of proper diabetes management and being aware of the risk factors. Some strategies for prevention include: - Adhering to insulin therapy as prescribed - Monitoring blood glucose levels regularly - Maintaining a healthy diet and lifestyle - Avoiding certain medications that can increase the risk of DKA - Managing stress and underlying health conditionsTreatment and Management
Emergency Intervention
In cases where DKA is severe, emergency intervention may be necessary. This can include hospitalization for intensive treatment and monitoring. The goals of emergency intervention are to stabilize the individual, correct dehydration and electrolyte imbalances, and manage blood glucose levels.Long-Term Management

Education and Support
Education and support are critical components of long-term management. Individuals with diabetes and their caregivers should be educated about the signs and symptoms of DKA, the importance of adherence to treatment plans, and how to manage risk factors. Support from healthcare providers, family, and friends can also play a significant role in preventing DKA and managing diabetes effectively.Conclusion and Next Steps

We invite you to share your experiences or questions about DKA in the comments below. Your insights can help others understand this condition better and encourage a community of support for those living with diabetes. Additionally, consider sharing this article with anyone who might benefit from this information, as knowledge and awareness are key to managing diabetes and preventing complications like DKA.
What are the most common symptoms of DKA?
+The most common symptoms of DKA include increased thirst and urination, nausea and vomiting, abdominal pain, fatigue, and a fruity odor on the breath.
How can DKA be prevented?
+DKA can be prevented by adhering to insulin therapy, monitoring blood glucose levels regularly, maintaining a healthy diet and lifestyle, and managing stress and underlying health conditions.
What is the treatment for DKA?
+The treatment for DKA typically involves fluid replacement, insulin therapy, electrolyte replacement, and treatment of underlying conditions, along with close monitoring of blood glucose and ketone levels.
