Intro
Discover the 7 signs of Vitamin B12 deficiency, including fatigue, weakness, and neurological symptoms, and learn how to boost energy and overall health with B12 rich foods and supplements, addressing anemia, nerve damage, and brain function.
Vitamin B12 is a crucial nutrient that plays a significant role in various bodily functions, including the production of red blood cells, nerve function, and DNA synthesis. A deficiency in vitamin B12 can lead to a range of health problems, from mild fatigue to severe neurological damage. It is essential to recognize the signs of vitamin B12 deficiency to take prompt action and prevent long-term damage. In this article, we will delve into the importance of vitamin B12, its functions, and the 7 signs that may indicate a deficiency.
The human body cannot produce vitamin B12 on its own, and it is primarily obtained through animal-based food sources, such as meat, fish, and dairy products. Vegans and vegetarians are at a higher risk of developing a vitamin B12 deficiency due to their limited dietary intake. Additionally, certain medical conditions, such as celiac disease, Crohn's disease, and gastric bypass surgery, can impair the body's ability to absorb vitamin B12.
Vitamin B12 deficiency can be a silent condition, and many people may not experience any noticeable symptoms in the early stages. However, as the deficiency progresses, it can lead to a range of health problems, including anemia, nerve damage, and increased risk of infections. It is crucial to recognize the signs of vitamin B12 deficiency to seek medical attention and prevent long-term damage.
Vitamin B12 Deficiency: An Overview
Causes of Vitamin B12 Deficiency
The causes of vitamin B12 deficiency can be broadly classified into three categories: dietary, malabsorptive, and miscellaneous. Dietary causes include a limited intake of animal-based food sources, while malabsorptive causes include conditions that impair the body's ability to absorb vitamin B12. Miscellaneous causes include certain medications, such as proton pump inhibitors, and gastric bypass surgery.7 Signs of Vitamin B12 Deficiency

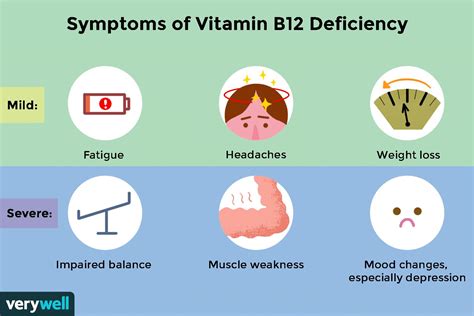
- Fatigue and Weakness: Vitamin B12 plays a crucial role in the production of red blood cells, which carry oxygen to the body's tissues. A deficiency in vitamin B12 can lead to anemia, causing fatigue, weakness, and shortness of breath.
- Numbness and Tingling: Vitamin B12 is essential for the health of the nervous system. A deficiency can cause numbness, tingling, and pain in the hands and feet, as well as balance problems and difficulty walking.
- Mood Changes: Vitamin B12 deficiency has been linked to depression, anxiety, and mood changes. The deficiency can cause a range of emotional symptoms, from mild irritability to severe depression.
- Digestive Problems: Vitamin B12 deficiency can cause digestive problems, such as diarrhea, constipation, and abdominal pain. The deficiency can also lead to a range of gastrointestinal symptoms, including bloating and gas.
- Skin Problems: Vitamin B12 deficiency can cause skin problems, such as acne, rosacea, and dermatitis. The deficiency can also lead to hair loss, brittle nails, and skin lesions.
- Eye Problems: Vitamin B12 deficiency can cause eye problems, such as blurred vision, double vision, and sensitivity to light. The deficiency can also lead to a range of eye symptoms, including dry eyes and eye pain.
- Cognitive Impairment: Vitamin B12 deficiency can cause cognitive impairment, including memory loss, confusion, and difficulty concentrating. The deficiency can also lead to a range of neurological symptoms, including dementia and Parkinson's disease.
Treatment and Prevention
Treatment for vitamin B12 deficiency typically involves supplements or injections to restore normal levels of the vitamin. Dietary changes, such as increasing intake of animal-based food sources, can also help to prevent deficiency. It is essential to seek medical attention if you experience any of the signs of vitamin B12 deficiency, as prompt treatment can help to prevent long-term damage.Diagnosis and Testing

Risk Factors
Certain groups of people are at a higher risk of developing vitamin B12 deficiency, including:- Vegans and vegetarians
- Older adults
- People with certain medical conditions, such as celiac disease and Crohn's disease
- People who have undergone gastric bypass surgery
- People taking certain medications, such as proton pump inhibitors
Conclusion and Next Steps

We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences with vitamin B12 deficiency in the comments section below. If you have any questions or concerns, please do not hesitate to reach out to us. We are committed to providing you with accurate and reliable information to help you make informed decisions about your health.
What are the common causes of vitamin B12 deficiency?
+Vitamin B12 deficiency can be caused by dietary limitations, malabsorption, and certain medical conditions. Dietary causes include a limited intake of animal-based food sources, while malabsorptive causes include conditions that impair the body's ability to absorb vitamin B12.
What are the symptoms of vitamin B12 deficiency?
+The symptoms of vitamin B12 deficiency can include fatigue, weakness, numbness, tingling, mood changes, digestive problems, skin problems, eye problems, and cognitive impairment.
How is vitamin B12 deficiency diagnosed?
+Diagnosis of vitamin B12 deficiency typically involves a combination of physical examination, medical history, and laboratory tests, including the serum vitamin B12 test, the methylmalonic acid test, and the homocysteine test.
What is the treatment for vitamin B12 deficiency?
+Treatment for vitamin B12 deficiency typically involves supplements or injections to restore normal levels of the vitamin. Dietary changes, such as increasing intake of animal-based food sources, can also help to prevent deficiency.
Can vitamin B12 deficiency be prevented?
+Yes, vitamin B12 deficiency can be prevented by maintaining a balanced diet that includes animal-based food sources, avoiding certain medications, and managing underlying medical conditions.
