Intro
Learn about Norovirus Symptoms 2025, including vomiting, diarrhea, and stomach cramps, and discover prevention methods and treatment options for this highly contagious gastrointestinal illness.
Norovirus is a highly contagious virus that affects millions of people worldwide every year. It is a leading cause of gastroenteritis, which is inflammation of the stomach and intestines. Norovirus symptoms can be severe and debilitating, causing significant discomfort and disruption to daily life. As we move into 2025, it is essential to understand the symptoms of norovirus and how to prevent and treat this illness.
Norovirus is highly infectious and can spread quickly through contaminated food, water, and surfaces. It can also be transmitted through close contact with an infected person. The virus is highly resistant to environmental stressors, making it challenging to eliminate from surfaces and objects. Norovirus symptoms typically begin within 24-48 hours of exposure to the virus and can last for several days.
The impact of norovirus on public health is significant. According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), norovirus is responsible for approximately 21 million cases of gastroenteritis in the United States each year. This results in significant economic burdens, including lost productivity, medical expenses, and other related costs. Furthermore, norovirus outbreaks can have devastating consequences, particularly in vulnerable populations such as the elderly, young children, and people with weakened immune systems.
Norovirus Symptoms

Norovirus symptoms can be similar to those of other gastrointestinal illnesses, making diagnosis challenging. A healthcare professional may perform a physical examination, take a medical history, and order laboratory tests to confirm the diagnosis. In some cases, a stool sample may be collected to test for the presence of norovirus.
Common Norovirus Symptoms
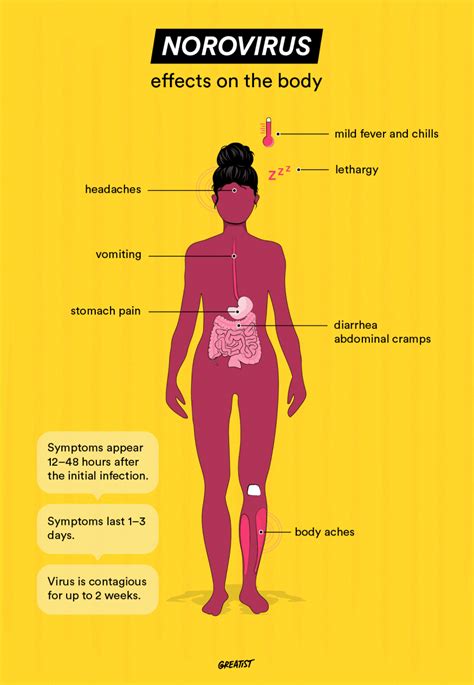
Some common norovirus symptoms include: * Diarrhea: Watery, loose stools that may be frequent and explosive * Vomiting: Forceful expulsion of stomach contents, which may be projectile * Stomach cramps: Severe abdominal pain that may be crampy or colicky * Fever: Elevated body temperature, usually below 101.5°F (38.6°C) * Headache: Pain or discomfort in the head or neck * Fatigue: Feeling weak, tired, or lacking energy * Muscle aches: Pain or discomfort in the muscles, often in the arms and legsNorovirus Transmission
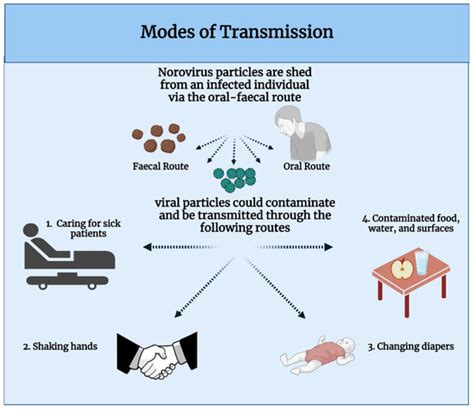
Preventing Norovirus Transmission
Preventing norovirus transmission requires attention to hygiene and sanitation. Some strategies include: * Washing hands frequently with soap and water * Avoiding close contact with infected individuals * Cleaning and disinfecting surfaces and objects * Avoiding contaminated food and water * Practicing good hygiene during food preparation and handlingNorovirus Treatment
Complications of Norovirus
Norovirus complications can be severe, particularly in vulnerable populations. Some potential complications include: * Dehydration: Severe dehydration can lead to electrolyte imbalances, kidney damage, and other complications * Malnutrition: Prolonged diarrhea and vomiting can lead to malnutrition and weight loss * Respiratory infections: Norovirus can increase the risk of respiratory infections, such as pneumonia * Other complications: Norovirus can also increase the risk of other complications, such as kidney damage, seizures, and deathNorovirus Prevention

Vaccines and Norovirus
Researchers are working to develop vaccines against norovirus. While there are currently no licensed vaccines available, several candidates are in development. These vaccines aim to provide protection against norovirus by stimulating an immune response against the virus.Norovirus Outbreaks

Investigating Norovirus Outbreaks
Investigating norovirus outbreaks requires a coordinated effort from public health officials, healthcare providers, and other stakeholders. Some strategies include: * Identifying the source of the outbreak: Public health officials work to identify the source of the outbreak, such as contaminated food or water * Collecting and testing samples: Samples are collected from affected individuals and tested for the presence of norovirus * Implementing control measures: Control measures, such as increased hygiene and sanitation, are implemented to prevent further spread of the virusNorovirus and Vulnerable Populations
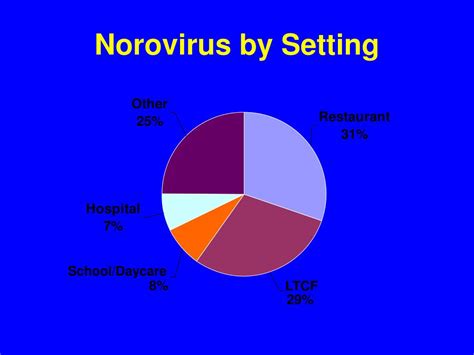
Protecting Vulnerable Populations
Protecting vulnerable populations from norovirus requires special attention to hygiene and sanitation. Some strategies include: * Implementing infection control measures: Infection control measures, such as increased hygiene and sanitation, can help prevent the spread of norovirus * Providing education and support: Education and support can help vulnerable populations understand the risks of norovirus and take steps to protect themselves * Ensuring access to healthcare: Ensuring access to healthcare can help vulnerable populations receive prompt and effective treatment for norovirus illnessWhat are the symptoms of norovirus?
+Norovirus symptoms can include diarrhea, vomiting, stomach cramps, fever, headache, fatigue, and muscle aches.
How is norovirus transmitted?
+Norovirus can be transmitted through contaminated food and water, close contact with an infected person, and contaminated surfaces.
Can norovirus be prevented?
+Yes, norovirus can be prevented by practicing good hygiene and sanitation, such as washing hands frequently and avoiding close contact with infected individuals.
What is the treatment for norovirus?
+Treatment for norovirus typically focuses on managing symptoms and preventing dehydration, and may include fluid replacement, rest, and medications.
Can norovirus cause complications?
+Yes, norovirus can cause complications, particularly in vulnerable populations, such as dehydration, malnutrition, and respiratory infections.
As we move into 2025, it is essential to remain vigilant and take steps to prevent the spread of norovirus. By understanding the symptoms, transmission, and prevention of norovirus, we can work together to reduce the impact of this illness on public health. If you have any questions or concerns about norovirus, please do not hesitate to reach out to a healthcare professional or public health official. Share this article with others to help spread awareness about norovirus and its prevention. Together, we can make a difference and create a healthier, safer community for everyone.
