Intro
Detect Helicobacter Pylori infection with accurate antigen detection methods, including stool tests and breath analysis, to diagnose gastric symptoms and prevent complications like ulcers and cancer.
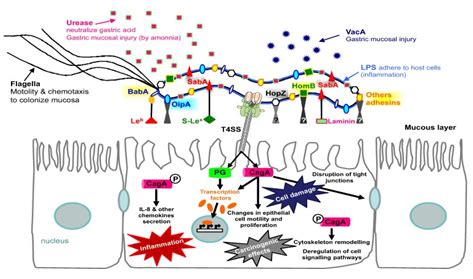
The discovery of Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) has revolutionized our understanding of gastrointestinal diseases, particularly peptic ulcers and gastric cancer. This bacterium is known to infect the stomach lining of approximately 50% of the global population, making it a significant public health concern. The detection of H. pylori antigens has become a crucial diagnostic tool in managing and treating related diseases. In this article, we will delve into the importance of H. pylori antigen detection, its benefits, working mechanisms, and the various methods employed to identify this bacterium.
H. pylori infection is often asymptomatic, but it can lead to severe conditions such as gastritis, peptic ulcers, and even gastric cancer. The bacterium's ability to evade the host's immune system and persist in the stomach lining makes it a challenging target for diagnosis and treatment. Traditional diagnostic methods, such as endoscopy and biopsy, are invasive and may not always detect the presence of H. pylori. This is where antigen detection comes into play, offering a non-invasive and accurate means of identifying the bacterium.
The significance of H. pylori antigen detection lies in its ability to provide a rapid and reliable diagnosis, enabling healthcare professionals to initiate appropriate treatment and prevent long-term complications. Antigen detection tests can be performed on stool, urine, or blood samples, making them a convenient and patient-friendly option. Furthermore, these tests can also be used to monitor the effectiveness of treatment and confirm the eradication of the bacterium.
H. Pylori Antigen Detection Methods
Several methods are employed to detect H. pylori antigens, each with its advantages and limitations. The most commonly used tests include:
- Stool antigen test (SAT): This test detects the presence of H. pylori antigens in stool samples and is considered one of the most accurate non-invasive tests.
- Urine antigen test: This test detects the presence of H. pylori antigens in urine samples and is often used in conjunction with other diagnostic methods.
- Blood tests: These tests detect the presence of antibodies against H. pylori in the blood and can indicate current or past infection.
Stool Antigen Test (SAT)
The SAT is a widely used and recommended test for detecting H. pylori antigens. It involves collecting a stool sample and testing it for the presence of H. pylori antigens using an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) or a rapid test. The SAT is highly sensitive and specific, making it an ideal choice for diagnosing H. pylori infection.Benefits of H. Pylori Antigen Detection
The benefits of H. pylori antigen detection are numerous and significant. Some of the most notable advantages include:
- Rapid diagnosis: Antigen detection tests provide quick results, enabling healthcare professionals to initiate treatment promptly.
- Non-invasive: These tests are non-invasive, making them a convenient and patient-friendly option.
- High accuracy: Antigen detection tests are highly sensitive and specific, reducing the risk of false positives or false negatives.
- Cost-effective: Compared to traditional diagnostic methods, antigen detection tests are relatively inexpensive and cost-effective.
Working Mechanisms of H. Pylori Antigen Detection
The working mechanisms of H. pylori antigen detection involve the use of antibodies or other molecules that bind specifically to H. pylori antigens. These antibodies or molecules are labeled with enzymes, fluorescent dyes, or other detectable markers, allowing for the detection of the antigen-antibody complex. The most commonly used methods include ELISA, rapid tests, and immunochromatographic assays.Steps Involved in H. Pylori Antigen Detection
The steps involved in H. pylori antigen detection vary depending on the test used. However, the general steps include:
- Sample collection: A stool, urine, or blood sample is collected from the patient.
- Sample preparation: The sample is prepared for testing, which may involve centrifugation, filtration, or other processing steps.
- Antigen detection: The prepared sample is then tested for the presence of H. pylori antigens using a specific detection method, such as ELISA or a rapid test.
- Result interpretation: The results are interpreted, and a diagnosis is made based on the presence or absence of H. pylori antigens.
Practical Examples of H. Pylori Antigen Detection
Practical examples of H. pylori antigen detection include: * A 45-year-old man presenting with symptoms of peptic ulcer disease. A stool antigen test is performed, and the results indicate the presence of H. pylori antigens. The patient is subsequently treated with antibiotics, and a follow-up test confirms the eradication of the bacterium. * A 30-year-old woman with a family history of gastric cancer. A urine antigen test is performed as part of a screening program, and the results indicate the presence of H. pylori antigens. The patient is referred for further evaluation and treatment.Statistical Data on H. Pylori Antigen Detection
Statistical data on H. pylori antigen detection highlight the importance of this diagnostic tool. For example:
- A study published in the Journal of Clinical Microbiology found that the stool antigen test had a sensitivity of 95% and a specificity of 98% in detecting H. pylori infection.
- Another study published in the American Journal of Gastroenterology found that the urine antigen test had a positive predictive value of 92% and a negative predictive value of 95% in detecting H. pylori infection.
Future Directions in H. Pylori Antigen Detection
Future directions in H. pylori antigen detection include the development of more sensitive and specific tests, as well as the use of novel technologies such as molecular diagnostics and point-of-care testing. Additionally, there is a need for more research on the epidemiology and transmission of H. pylori infection, as well as the development of effective prevention and treatment strategies.Challenges and Limitations of H. Pylori Antigen Detection
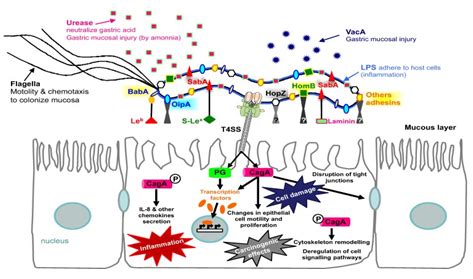
Despite the benefits of H. pylori antigen detection, there are several challenges and limitations to consider. These include:
- False positive results: Antigen detection tests can produce false positive results, particularly in patients with other gastrointestinal infections or conditions.
- False negative results: Conversely, antigen detection tests can also produce false negative results, particularly in patients with low bacterial loads or those who have recently received antibiotics.
- Limited availability: Antigen detection tests may not be widely available in all regions, particularly in resource-poor settings.
Solutions to Overcome Challenges and Limitations
To overcome the challenges and limitations of H. pylori antigen detection, several solutions can be implemented. These include: * Improving test sensitivity and specificity: Researchers can develop more sensitive and specific tests to reduce the risk of false positive and false negative results. * Increasing test availability: Efforts can be made to increase the availability of antigen detection tests in resource-poor settings, particularly in regions with high prevalence rates of H. pylori infection. * Providing education and training: Healthcare professionals can receive education and training on the proper use and interpretation of antigen detection tests, reducing the risk of errors and misdiagnosis.Conclusion and Recommendations

In conclusion, H. pylori antigen detection is a crucial diagnostic tool in the management and treatment of H. pylori-related diseases. The benefits of antigen detection include rapid diagnosis, non-invasive testing, high accuracy, and cost-effectiveness. However, there are also challenges and limitations to consider, including false positive and false negative results, limited availability, and the need for education and training. To overcome these challenges, researchers and healthcare professionals can work together to develop more sensitive and specific tests, increase test availability, and provide education and training on the proper use and interpretation of antigen detection tests.
What is H. pylori antigen detection?
+H. pylori antigen detection is a diagnostic test used to detect the presence of Helicobacter pylori antigens in stool, urine, or blood samples.
What are the benefits of H. pylori antigen detection?
+The benefits of H. pylori antigen detection include rapid diagnosis, non-invasive testing, high accuracy, and cost-effectiveness.
What are the challenges and limitations of H. pylori antigen detection?
+The challenges and limitations of H. pylori antigen detection include false positive and false negative results, limited availability, and the need for education and training.
We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences with H. pylori antigen detection in the comments section below. If you found this article informative and helpful, please consider sharing it with others who may benefit from this information. Additionally, if you have any questions or concerns about H. pylori antigen detection, please do not hesitate to reach out to us. We are committed to providing you with accurate and reliable information to support your health and well-being.
