Intro
Identify 7 key preeclampsia symptoms, including high blood pressure, proteinuria, and severe headaches, to ensure timely diagnosis and treatment, preventing pregnancy complications like eclampsia and placental abruption.
Preeclampsia is a pregnancy complication characterized by high blood pressure and often accompanied by significant amounts of protein in the urine. This condition can lead to serious complications for both the mother and the baby if not promptly diagnosed and managed. Understanding the symptoms of preeclampsia is crucial for early detection and intervention. Despite its severity, preeclampsia can be asymptomatic in its early stages, making regular prenatal check-ups vital for identifying the condition before it progresses.
The importance of recognizing preeclampsia symptoms cannot be overstated. Early detection allows for timely medical intervention, which can significantly improve outcomes for both the mother and the baby. Preeclampsia affects a significant number of pregnancies worldwide, and while the exact cause remains unclear, research continues to uncover factors that contribute to its development. Factors such as a history of high blood pressure, kidney disease, and certain medical conditions can increase the risk of preeclampsia. Given the potential severity of this condition, it is essential for pregnant individuals to be aware of the signs and symptoms that may indicate its presence.
Preeclampsia can manifest in various ways, and its symptoms may resemble those of other conditions, making diagnosis challenging. However, being informed about the common symptoms associated with preeclampsia empowers pregnant individuals to seek medical attention if they experience any unusual changes in their health. The management and treatment of preeclampsia depend on the severity of the condition and the gestational age at diagnosis. In mild cases, close monitoring may be sufficient, while more severe cases may require hospitalization and, in some instances, premature delivery. Understanding the symptoms and the importance of prompt medical evaluation is key to navigating this pregnancy complication effectively.
Preeclampsia Overview
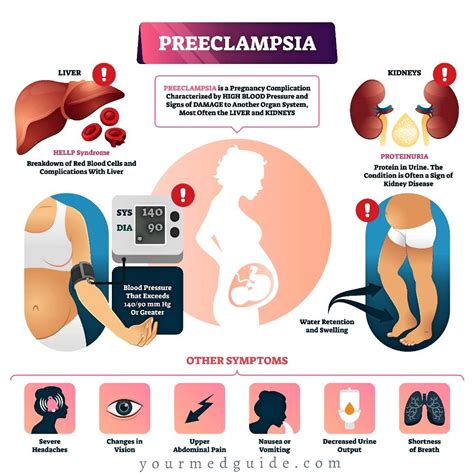
Understanding Preeclampsia
Understanding preeclampsia involves recognizing its potential impact on pregnancy. The condition can lead to premature birth and has been associated with an increased risk of maternal and fetal complications. Pregnant individuals with preeclampsia may need to undergo more frequent prenatal check-ups to monitor their condition and the well-being of the baby. In cases where preeclampsia is severe, hospitalization may be necessary to closely monitor the mother's and baby's health and to intervene promptly if complications arise.Symptoms of Preeclampsia
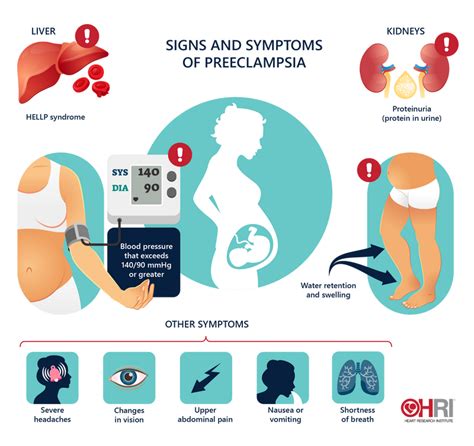
Severe Preeclampsia Symptoms
Severe preeclampsia is characterized by more pronounced symptoms and can lead to life-threatening complications if not managed promptly. Symptoms of severe preeclampsia include: - Very high blood pressure - Severe headache or vision disturbances - Severe abdominal pain - Vomiting - Decreased urine output - Severe nauseaRisk Factors for Preeclampsia

Prevention and Management
While preeclampsia cannot be completely prevented, certain measures can reduce the risk. These include: - Maintaining a healthy weight - Following a balanced diet - Engaging in regular physical activity - Managing stress - Attending all scheduled prenatal appointments for early detection and managementDiagnosis of Preeclampsia
Treatment Options
The treatment of preeclampsia depends on the severity of the condition and the gestational age of the baby. For mild preeclampsia, close monitoring may be sufficient, while more severe cases may require hospitalization. Treatment options include: - Bed rest - Medications to lower blood pressure - Corticosteroids to promote fetal lung maturity - In severe cases, delivery may be necessary, even if the baby is prematureComplications of Preeclampsia
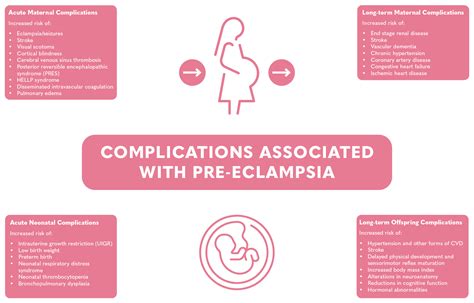
Long-term Effects
The long-term effects of preeclampsia can vary. Women who have had preeclampsia are at a higher risk for future cardiovascular disease and may need to take preventive measures. Regular health check-ups and maintaining a healthy lifestyle can mitigate these risks.Living with Preeclampsia
Coping Mechanisms
Coping with preeclampsia involves not only managing the physical aspects of the condition but also dealing with the emotional and psychological challenges it presents. Strategies for coping include: - Staying informed about the condition - Following the treatment plan - Practicing stress-reduction techniques - Seeking support from loved ones and support groupsWhat are the first signs of preeclampsia?
+The first signs of preeclampsia often include high blood pressure and protein in the urine, which can be detected during routine prenatal visits.
Can preeclampsia be prevented?
+While preeclampsia cannot be completely prevented, maintaining a healthy lifestyle, including a balanced diet and regular physical activity, can reduce the risk.
What are the risks of untreated preeclampsia?
+Untreated preeclampsia can lead to serious complications, including premature birth, low birth weight, and in severe cases, eclampsia and HELLP syndrome, which can be life-threatening for both the mother and the baby.
In conclusion, understanding the symptoms, risks, and management of preeclampsia is crucial for pregnant individuals and their healthcare providers. By being aware of the potential signs of preeclampsia and taking proactive steps towards a healthy pregnancy, individuals can reduce their risk and ensure the best possible outcomes for themselves and their babies. If you or someone you know is experiencing symptoms of preeclampsia, it is essential to seek medical attention promptly. Share this article with others to spread awareness about preeclampsia and encourage open discussions about pregnancy health. Together, we can work towards healthier pregnancies and better outcomes for all.
