Intro
Discover the symptoms and diagnosis of celiac disease, including blood tests, intestinal biopsies, and genetic testing, to accurately detect gluten intolerance and sensitivity.
Celiac disease is a chronic autoimmune disorder that affects the small intestine and is caused by a reaction to gluten, a protein found in wheat, barley, and rye. The disease can cause a range of symptoms, from mild to severe, and can lead to complications such as malnutrition, osteoporosis, and increased risk of other autoimmune disorders. Testing for celiac disease is crucial for accurate diagnosis and timely treatment. In this article, we will delve into the importance of testing for celiac disease, the various testing methods available, and what to expect from the testing process.
The importance of testing for celiac disease cannot be overstated. Celiac disease can be difficult to diagnose, as the symptoms can be similar to those of other conditions, such as irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) or inflammatory bowel disease (IBD). Furthermore, some people with celiac disease may not experience any symptoms at all, making it even more challenging to diagnose. Testing for celiac disease can help identify the condition early on, allowing for prompt treatment and preventing long-term complications.
Testing for celiac disease is also essential for individuals who are at high risk of developing the condition. This includes people with a family history of celiac disease, those with other autoimmune disorders, such as type 1 diabetes or thyroid disease, and individuals with certain genetic markers. Additionally, testing for celiac disease can help identify people who are at risk of developing the condition, even if they are not currently experiencing symptoms.
Understanding Celiac Disease
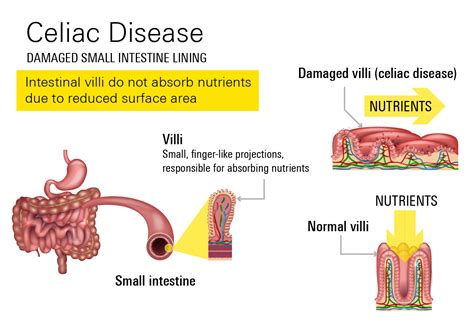
Causes and Risk Factors
Celiac disease is caused by a reaction to gluten, which is found in wheat, barley, and rye. The exact mechanisms of this reaction are not fully understood, but it is believed to involve an immune response that damages the lining of the small intestine. Several factors can increase the risk of developing celiac disease, including: * Family history: Having a family history of celiac disease increases the risk of developing the condition. * Genetic markers: Certain genetic markers, such as HLA-DQ2 and HLA-DQ8, can increase the risk of developing celiac disease. * Other autoimmune disorders: Having other autoimmune disorders, such as type 1 diabetes or thyroid disease, can increase the risk of developing celiac disease.Testing Methods

Blood Tests
Blood tests are the most common method of testing for celiac disease. These tests detect the presence of certain antibodies in the blood, which are associated with celiac disease. The most common blood tests used to diagnose celiac disease include: * Tissue transglutaminase antibody (tTGA) test: This test detects the presence of antibodies against tissue transglutaminase, an enzyme found in the small intestine. * Endomysial antibody (EMA) test: This test detects the presence of antibodies against the endomysium, a protein found in the small intestine. * Gliadin antibody test: This test detects the presence of antibodies against gliadin, a protein found in wheat.Intestinal Biopsy

Genetic Testing
Genetic testing can identify certain genetic markers that increase the risk of developing celiac disease. The most common genetic markers associated with celiac disease include: * HLA-DQ2: This genetic marker is found in the majority of people with celiac disease. * HLA-DQ8: This genetic marker is found in a smaller percentage of people with celiac disease.Treatment and Management

Dietary Changes
Making dietary changes can be challenging, but there are many resources available to help. Some tips for following a gluten-free diet include: * Reading food labels carefully to ensure that the food does not contain gluten. * Avoiding cross-contamination with gluten-containing foods. * Eating a variety of gluten-free foods, including fruits, vegetables, meats, and whole grains.Complications and Risks
Long-term Health Consequences
The long-term health consequences of celiac disease can be significant if left untreated. Some potential long-term health consequences include: * Increased risk of osteoporosis and fractures. * Increased risk of other autoimmune disorders. * Increased risk of certain types of cancer, such as lymphoma.Living with Celiac Disease

Coping with Emotional Challenges
Celiac disease can be emotionally challenging, particularly when it comes to managing dietary restrictions and dealing with social situations. Some tips for coping with emotional challenges include: * Seeking support from friends and family. * Connecting with others who have celiac disease. * Practicing stress-reducing techniques, such as meditation or yoga.What are the symptoms of celiac disease?
+The symptoms of celiac disease can vary, but common symptoms include abdominal pain, diarrhea, fatigue, and weight loss.
How is celiac disease diagnosed?
+Celiac disease is diagnosed using a combination of blood tests, intestinal biopsy, and genetic testing.
What is the treatment for celiac disease?
+The primary treatment for celiac disease is a strict gluten-free diet.
Can celiac disease be cured?
+Celiac disease cannot be cured, but it can be managed with a gluten-free diet and careful attention to nutrition.
Is celiac disease a common condition?
+Celiac disease is a relatively common condition, affecting approximately 1 in 100 people worldwide.
In conclusion, testing for celiac disease is a crucial step in diagnosing and managing the condition. By understanding the causes and risk factors of celiac disease, as well as the various testing methods available, individuals can take control of their health and well-being. If you suspect that you or a loved one may have celiac disease, it is essential to consult with a healthcare provider to discuss testing and treatment options. We encourage you to share this article with others who may be affected by celiac disease and to comment below with any questions or concerns you may have. By working together, we can raise awareness and promote understanding of this important health condition.
