Intro
Discover the recommended Thiamine maximum daily dose, essential for nerve function and energy production, with related vitamins and nutrients like Vitamin B1, Beriberi prevention, and dietary supplements.
Thiamine, also known as vitamin B1, is an essential nutrient that plays a critical role in energy production, nerve function, and heart health. The human body requires thiamine to convert carbohydrates into energy, and it is also necessary for the proper functioning of the nervous system. Thiamine deficiency can lead to a range of health problems, including beriberi, a condition that affects the heart, digestive system, and nervous system. In this article, we will explore the importance of thiamine, its benefits, and the maximum daily dose recommended by health experts.
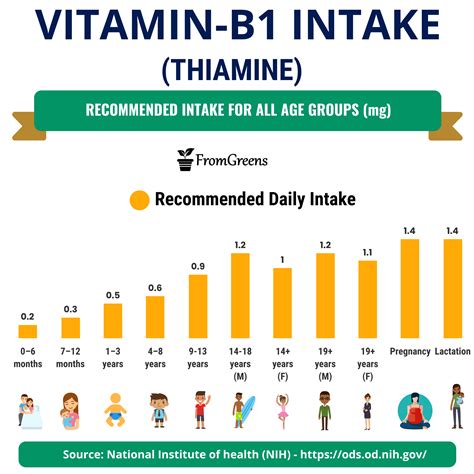
Thiamine is found in a variety of foods, including whole grains, legumes, nuts, and seeds. However, many people do not get enough thiamine from their diet alone, and may require supplements to meet their daily needs. The recommended daily intake of thiamine varies based on age, sex, and other factors, but most adults need around 1-2 milligrams per day. Thiamine supplements are available in a range of forms, including tablets, capsules, and injections. While thiamine is generally considered safe, high doses can cause adverse effects, such as nausea, dizziness, and headaches.
Thiamine has been shown to have numerous health benefits, including reducing the risk of heart disease, improving cognitive function, and supporting nerve health. It is also essential for the proper functioning of the immune system, and may help to reduce the severity of infections. Additionally, thiamine has been used to treat a range of medical conditions, including beriberi, Wernicke-Korsakoff syndrome, and certain types of neuropathy. With its wide range of health benefits and relatively low risk of adverse effects, thiamine is an essential nutrient that should be included in a healthy diet.
Thiamine Benefits

Thiamine has been used to treat a range of medical conditions, including beriberi, Wernicke-Korsakoff syndrome, and certain types of neuropathy. Beriberi is a condition that affects the heart, digestive system, and nervous system, and is caused by a severe deficiency of thiamine. Wernicke-Korsakoff syndrome is a condition that affects the brain and nervous system, and is caused by a combination of thiamine deficiency and excessive alcohol consumption. Thiamine has also been used to treat certain types of neuropathy, including diabetic neuropathy and alcoholic neuropathy.
Thiamine Deficiency
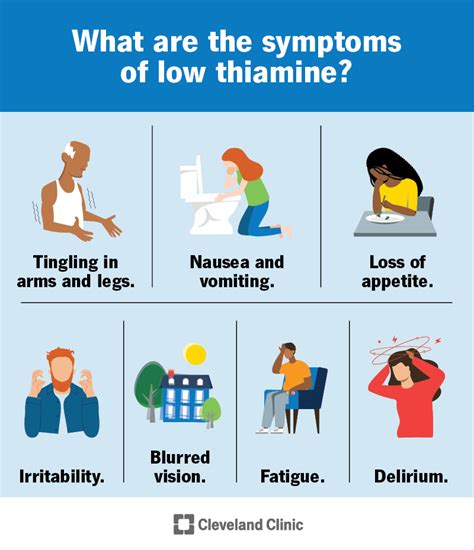
Thiamine deficiency can be caused by a range of factors, including a poor diet, certain medical conditions, and excessive alcohol consumption. People who are at risk of thiamine deficiency include those who eat a diet that is high in processed foods and low in whole grains, legumes, and nuts. Certain medical conditions, such as celiac disease and Crohn's disease, can also increase the risk of thiamine deficiency. Excessive alcohol consumption can also cause thiamine deficiency, as alcohol can interfere with the absorption of thiamine from food.
Thiamine Food Sources

It is generally recommended to get thiamine from food sources rather than supplements, as this can help to ensure that you are getting a balanced intake of all the necessary nutrients. However, if you are unable to get enough thiamine from your diet, supplements may be necessary. Thiamine supplements are available in a range of forms, including tablets, capsules, and injections.
Thiamine Supplements

When choosing a thiamine supplement, it is generally recommended to opt for a high-quality supplement that is made by a reputable manufacturer. It is also important to follow the recommended dosage instructions, as high doses of thiamine can cause adverse effects. It is also important to note that thiamine supplements should not be used as a replacement for a healthy diet, but rather as a supplement to a balanced diet.
Thiamine Maximum Daily Dose
High doses of thiamine can cause adverse effects, such as nausea, dizziness, and headaches. It is generally recommended to start with a low dose and gradually increase as needed, under the guidance of a healthcare professional. It is also important to note that thiamine supplements should not be used for extended periods of time, as this can cause dependence and other adverse effects.
Thiamine Side Effects

It is generally recommended to start with a low dose and gradually increase as needed, under the guidance of a healthcare professional. It is also important to note that thiamine supplements should not be used for extended periods of time, as this can cause dependence and other adverse effects. If you experience any side effects while taking thiamine supplements, it is important to seek medical attention immediately.
Thiamine Interactions

Thiamine can also interact with certain foods, including foods that are high in sulfur, such as garlic and onions. Foods that are high in sugar can also interfere with the absorption of thiamine. It is generally recommended to eat a balanced diet that is rich in whole grains, legumes, nuts, and seeds, and to avoid foods that are high in processed ingredients and added sugars.
Thiamine Overdose

Treatment for thiamine overdose typically involves supportive care, such as hydration and rest, as well as monitoring for any potential side effects. In severe cases, hospitalization may be necessary. It is generally recommended to consult with a healthcare professional before taking thiamine supplements, especially if you are taking any medications or have any underlying medical conditions.
Thiamine Deficiency Prevention

If you are at risk of thiamine deficiency, it is generally recommended to consult with a healthcare professional before taking any supplements. They can help to determine the best course of treatment, and can monitor for any potential side effects. Additionally, regular blood tests can help to monitor thiamine levels, and can detect any potential deficiencies before they become severe.
What is the recommended daily intake of thiamine?
+The recommended daily intake of thiamine is around 1-2 milligrams per day for most adults.
What are the symptoms of thiamine deficiency?
+The symptoms of thiamine deficiency can include fatigue, weakness, numbness or tingling in the hands and feet, and difficulty walking.
Can thiamine supplements interact with other medications?
+Yes, thiamine supplements can interact with certain medications, including diuretics and certain antibiotics.
How can I prevent thiamine deficiency?
+Preventing thiamine deficiency can be achieved by eating a balanced diet that is rich in whole grains, legumes, nuts, and seeds, and avoiding foods that are high in processed ingredients and added sugars.
What are the potential side effects of thiamine supplements?
+The potential side effects of thiamine supplements can include nausea, dizziness, and headaches, as well as more serious side effects, such as anaphylaxis and seizures.
In summary, thiamine is an essential nutrient that plays a critical role in energy production, nerve function, and heart health. Thiamine deficiency can cause a range of health problems, including beriberi, Wernicke-Korsakoff syndrome, and certain types of neuropathy. Thiamine supplements can be used to treat these conditions, as well as to prevent thiamine deficiency in people who are at risk. However, high doses of thiamine can cause adverse effects, and it is generally recommended to start with a low dose and gradually increase as needed, under the guidance of a healthcare professional. We hope this article has provided you with a comprehensive understanding of thiamine and its importance for overall health. If you have any further questions or concerns, please do not hesitate to comment or share this article with others.
