Intro
Understanding thyroid blood check results is crucial for individuals who have undergone thyroid function tests. The thyroid gland plays a vital role in regulating metabolism, energy levels, and overall health. Abnormal thyroid function can lead to various health issues, making it essential to comprehend the test results. In this article, we will delve into the world of thyroid blood check results, exploring what they mean, how to interpret them, and the necessary steps to take after receiving the results.
Thyroid function tests are commonly used to diagnose and monitor thyroid disorders, such as hypothyroidism (underactive thyroid) and hyperthyroidism (overactive thyroid). The tests measure the levels of thyroid hormones, including triiodothyronine (T3) and thyroxine (T4), as well as thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) produced by the pituitary gland. These hormone levels help healthcare professionals assess thyroid function and determine the best course of treatment.
The importance of understanding thyroid blood check results cannot be overstated. By grasping the meaning behind the numbers, individuals can take control of their health, make informed decisions, and work closely with their healthcare providers to manage their condition. In the following sections, we will break down the components of thyroid blood check results, discuss the normal ranges, and explore the implications of abnormal results.
Understanding Thyroid Hormones
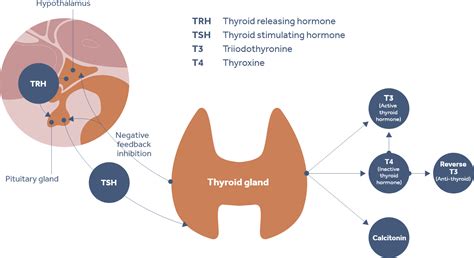
Triiodothyronine (T3)
T3 is the most active form of thyroid hormone, responsible for regulating metabolism, energy production, and nerve function. Abnormal T3 levels can indicate thyroid dysfunction, which may lead to symptoms such as weight loss or gain, fatigue, and mood changes.Thyroxine (T4)
T4 is the inactive form of thyroid hormone, which is converted to T3 in the body. T4 levels are often measured to assess thyroid function, as they can indicate hypothyroidism or hyperthyroidism.Thyroid-Stimulating Hormone (TSH)
TSH is produced by the pituitary gland and regulates the production of T3 and T4 by the thyroid gland. Abnormal TSH levels can indicate thyroid dysfunction, which may lead to symptoms such as fatigue, weight changes, and mood disturbances.Interpreting Thyroid Blood Check Results
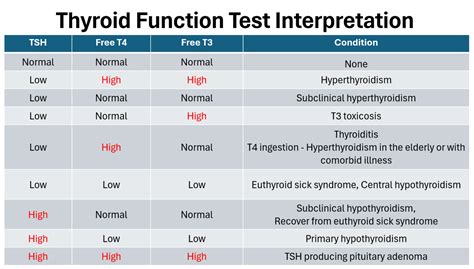
Normal Ranges
The normal ranges for thyroid hormones vary depending on the laboratory and the individual's age, sex, and medical history. Generally, the normal ranges are:- T3: 80-180 ng/dL
- T4: 4.5-12.5 μg/dL
- TSH: 0.4-4.5 μU/mL
Abnormal Results
Abnormal thyroid blood check results can indicate thyroid dysfunction, which may lead to various health issues. The possible causes of abnormal results include:- Hypothyroidism: elevated TSH levels, decreased T3 and T4 levels
- Hyperthyroidism: decreased TSH levels, elevated T3 and T4 levels
- Thyroiditis: inflammation of the thyroid gland, leading to abnormal T3 and T4 levels
- Thyroid nodules or cancer: abnormal T3 and T4 levels, possibly accompanied by elevated TSH levels
Managing Thyroid Disorders

Treatment Options
The treatment options for thyroid disorders depend on the underlying cause and severity of the condition. The possible treatment options include:- Medication: synthetic thyroid hormones, such as levothyroxine (T4) and liothyronine (T3), to replace or supplement the natural hormones
- Radioactive iodine: to destroy part or all of the thyroid gland, used to treat hyperthyroidism
- Surgery: to remove part or all of the thyroid gland, used to treat thyroid cancer or nodules
Lifestyle Changes
Lifestyle changes play a crucial role in managing thyroid disorders. The following changes can help alleviate symptoms and improve overall health:- Dietary changes: avoiding foods that can interfere with thyroid function, such as soy and cruciferous vegetables
- Exercise: regular physical activity to improve metabolism and energy levels
- Stress management: techniques such as meditation and yoga to reduce stress and promote relaxation
Monitoring Thyroid Function

Regular Monitoring
Regular monitoring of thyroid function is crucial for managing thyroid disorders. The frequency of monitoring depends on the individual's condition and treatment plan. Generally, thyroid function tests are performed:- Every 6-12 months for individuals with hypothyroidism or hyperthyroidism
- Every 3-6 months for individuals with thyroid cancer or nodules
Complications of Untreated Thyroid Disorders
Untreated thyroid disorders can lead to various complications, including:- Cardiovascular disease: increased risk of heart disease, high blood pressure, and stroke
- Osteoporosis: increased risk of bone fractures and osteoporosis
- Infertility: increased risk of infertility and miscarriage
Conclusion and Next Steps

We invite you to share your experiences and questions about thyroid blood check results in the comments section below. Your input can help others better understand their results and take control of their health. Additionally, please share this article with anyone who may benefit from this information.
What is the normal range for TSH levels?
+The normal range for TSH levels is 0.4-4.5 μU/mL, but this can vary depending on the laboratory and individual factors.
What are the symptoms of hypothyroidism?
+The symptoms of hypothyroidism include fatigue, weight gain, dry skin, hair loss, and cold intolerance.
How often should I have my thyroid function tested?
+The frequency of thyroid function tests depends on your individual condition and treatment plan, but generally, tests are performed every 6-12 months for individuals with hypothyroidism or hyperthyroidism.
