Intro
Learn about Tie My Tubes aka tubal ligation, a permanent birth control method. Discover the procedure, benefits, and risks of getting your tubes tied, including recovery and potential complications, in this informative guide on female sterilization and family planning options.
Getting a tubal ligation, also known as "tying your tubes," is a highly effective and permanent form of birth control for women. This surgical procedure involves cutting or blocking the fallopian tubes to prevent pregnancy. With over 700,000 women in the United States undergoing tubal ligation each year, it's essential to understand the benefits, risks, and what to expect from this procedure.
The decision to get a tubal ligation is a personal one, often made by women who have completed their families or are certain they do not want to become pregnant in the future. The procedure is typically performed on an outpatient basis, and most women can return to their normal activities within a few days. However, it's crucial to carefully consider the permanence of this birth control method, as reversing a tubal ligation can be challenging and may not always be successful.
Tubal ligation has been a popular form of birth control for decades, offering a high level of effectiveness and convenience. Unlike other birth control methods, such as the pill or condoms, which require daily or frequent use, a tubal ligation provides a one-time solution to prevent pregnancy. This can be especially appealing to women who have experienced unintended pregnancies or have concerns about the side effects of hormonal birth control methods.
What is Tubal Ligation?
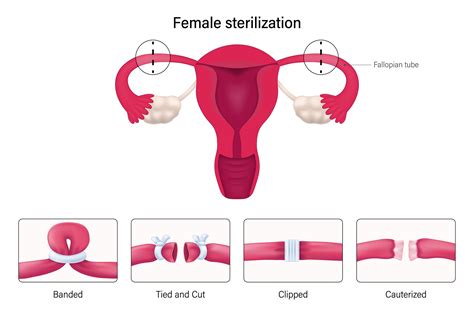
Tubal ligation is a surgical procedure that involves cutting, blocking, or tying the fallopian tubes to prevent pregnancy. The fallopian tubes are the passageways that connect the ovaries to the uterus, and they play a crucial role in fertilization. By blocking the fallopian tubes, sperm are unable to reach the egg, and fertilization cannot occur. There are several types of tubal ligation procedures, including laparoscopic, mini-laparotomy, and postpartum tubal ligation.
Types of Tubal Ligation Procedures
The type of tubal ligation procedure used depends on the individual woman's needs and medical history. Laparoscopic tubal ligation is a minimally invasive procedure that involves making small incisions in the abdomen and using a laparoscope to visualize the fallopian tubes. Mini-laparotomy, on the other hand, involves making a small incision in the abdomen to access the fallopian tubes. Postpartum tubal ligation is typically performed after childbirth, while the woman is still in the hospital.Benefits of Tubal Ligation
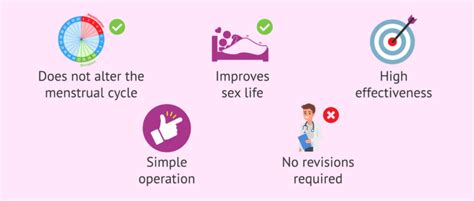
The benefits of tubal ligation are numerous, making it a popular choice for many women. Some of the advantages of this procedure include:
- High effectiveness: Tubal ligation is over 99% effective in preventing pregnancy.
- Permanent solution: Unlike other birth control methods, tubal ligation provides a one-time solution to prevent pregnancy.
- Convenience: Once the procedure is complete, women do not need to worry about taking birth control pills or using other forms of contraception.
- Reduced risk of ovarian cancer: Some studies have shown that tubal ligation may reduce the risk of ovarian cancer.
Risks and Complications
While tubal ligation is generally a safe procedure, there are some risks and complications to be aware of. These may include: * Infection: As with any surgical procedure, there is a risk of infection with tubal ligation. * Adverse reaction to anesthesia: Some women may experience an adverse reaction to the anesthesia used during the procedure. * Ectopic pregnancy: Although rare, it is possible for a woman to become pregnant after a tubal ligation. If this occurs, the pregnancy is likely to be ectopic, which can be life-threatening. * Regret: Some women may experience regret after having a tubal ligation, particularly if they change their mind about having more children.What to Expect During the Procedure

The tubal ligation procedure typically takes about 30 minutes to an hour to complete, and most women can return home the same day. The procedure is usually performed under general anesthesia, which means the woman will be asleep during the procedure. The surgeon will make small incisions in the abdomen and use a laparoscope to visualize the fallopian tubes. The tubes will then be cut, blocked, or tied to prevent pregnancy.
Recovery and Aftercare
After the procedure, women may experience some discomfort, cramping, and bleeding. It's essential to follow the surgeon's instructions for aftercare, which may include: * Resting for several days after the procedure * Avoiding heavy lifting or strenuous activities * Taking pain medication as directed * Attending follow-up appointments to ensure proper healingReversing a Tubal Ligation

Reversing a tubal ligation is possible, but it can be a challenging and expensive procedure. The success of the reversal depends on various factors, including the type of tubal ligation procedure used, the length of the remaining fallopian tube, and the woman's age. Women who are considering reversing a tubal ligation should consult with a fertility specialist to discuss their options and the potential success rate.
Alternatives to Tubal Ligation
For women who are not ready for a permanent form of birth control, there are several alternatives to tubal ligation. These may include: * Birth control pills or patches * Intrauterine devices (IUDs) * Condoms * Diaphragms * Cervical capsConclusion and Next Steps

Tubal ligation is a highly effective and permanent form of birth control that can provide peace of mind for women who have completed their families. While the procedure is generally safe, it's essential to carefully consider the risks and benefits and to discuss any concerns with a healthcare provider. For women who are considering a tubal ligation, it's crucial to:
- Consult with a healthcare provider to discuss the procedure and any concerns
- Carefully consider the permanence of the procedure
- Explore alternative forms of birth control
- Follow the surgeon's instructions for aftercare and recovery
We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences with tubal ligation in the comments below. If you have any questions or concerns, please don't hesitate to ask. You can also share this article with others who may be considering a tubal ligation.
What is the success rate of tubal ligation?
+Tubal ligation is over 99% effective in preventing pregnancy.
Can a tubal ligation be reversed?
+Yes, a tubal ligation can be reversed, but the success of the procedure depends on various factors, including the type of tubal ligation used and the woman's age.
What are the risks and complications of tubal ligation?
+The risks and complications of tubal ligation include infection, adverse reaction to anesthesia, ectopic pregnancy, and regret.
