Intro
Discover causes and symptoms of high Urea Nitrogen BUN levels, including kidney function, dehydration, and liver disease, and learn how to manage and reduce elevated BUN levels for optimal health.
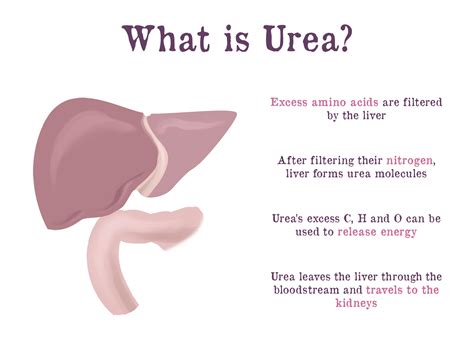
The importance of understanding urea nitrogen bun high levels cannot be overstated, as it plays a critical role in assessing kidney function and overall health. Urea nitrogen, also known as blood urea nitrogen (BUN), is a waste product that occurs in the blood when the body breaks down protein. Normally, the kidneys filter out this waste, but high levels can indicate kidney problems or other health issues. In this article, we will delve into the world of urea nitrogen bun high levels, exploring what they mean, their causes, symptoms, and treatment options.
High levels of urea nitrogen in the blood can be a cause for concern, as they may signal that the kidneys are not functioning properly. The kidneys play a vital role in filtering waste and excess fluids from the blood, and when they are not working correctly, waste products like urea nitrogen can build up. This can lead to a range of health problems, from mild to severe. Understanding the causes and consequences of high urea nitrogen levels is essential for maintaining good health and preventing potential complications.
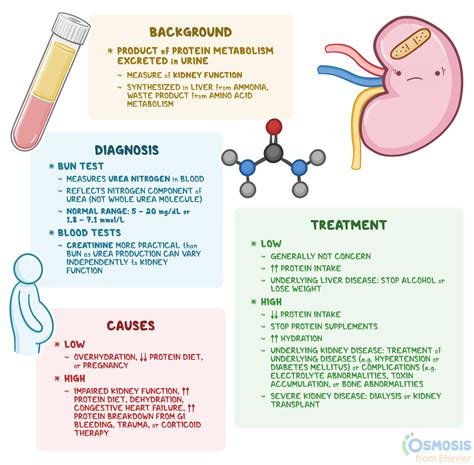
The urea nitrogen bun test is a common laboratory test used to assess kidney function. The test measures the levels of urea nitrogen in the blood, which can help doctors diagnose kidney problems, monitor kidney function, and adjust treatment plans accordingly. High levels of urea nitrogen can indicate kidney disease, kidney failure, or other health issues, such as dehydration, heart failure, or liver disease. By understanding the results of the urea nitrogen bun test, individuals can take proactive steps to manage their health and prevent potential complications.
What is Urea Nitrogen?
Causes of High Urea Nitrogen Levels
There are several causes of high urea nitrogen levels, including: * Kidney disease or kidney failure * Dehydration * Heart failure * Liver disease * Diabetes * High blood pressure * Certain medications, such as antibiotics and diuretics * Blood loss or trauma * Inadequate diet or malnutrition These causes can lead to a range of health problems, from mild to severe. Understanding the underlying causes of high urea nitrogen levels is essential for developing effective treatment plans and preventing potential complications.Symptoms of High Urea Nitrogen Levels

Treatment Options for High Urea Nitrogen Levels
Treatment options for high urea nitrogen levels depend on the underlying cause and severity of the condition. Common treatment options include: * Medications to manage underlying conditions, such as diabetes or high blood pressure * Dialysis or kidney transplantation for kidney failure * Fluid replacement or diuretics to manage dehydration or fluid overload * Dietary changes, such as reducing protein intake or increasing fluid intake * Lifestyle modifications, such as quitting smoking or exercising regularly * Monitoring and adjusting treatment plans as needed By working with a healthcare provider, individuals can develop effective treatment plans to manage high urea nitrogen levels and prevent potential complications.Prevention and Management
Complications of High Urea Nitrogen Levels
High urea nitrogen levels can lead to a range of complications, including: * Kidney failure or end-stage renal disease * Heart disease or stroke * Fluid overload or dehydration * Electrolyte imbalances or acid-base disorders * Malnutrition or weight loss * Anemia or blood disorders * Increased risk of infections or sepsis These complications can be severe and even life-threatening. By understanding the risks and consequences of high urea nitrogen levels, individuals can take proactive steps to manage their health and prevent potential complications.Conclusion and Next Steps

We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences with urea nitrogen bun high levels in the comments section below. Your input can help others better understand this complex health issue and take proactive steps to manage their health. Additionally, feel free to share this article with others who may benefit from this information.
What is the normal range for urea nitrogen levels?
+The normal range for urea nitrogen levels is typically between 6 and 24 mg/dL, but this can vary depending on the laboratory and individual factors.
What are the symptoms of high urea nitrogen levels?
+The symptoms of high urea nitrogen levels can include fatigue, nausea, loss of appetite, weight loss, swelling, and shortness of breath, among others.
How can I lower my urea nitrogen levels?
+To lower urea nitrogen levels, individuals can stay hydrated, eat a balanced diet, exercise regularly, manage underlying conditions, and get regular check-ups with their healthcare provider.
What are the complications of high urea nitrogen levels?
+The complications of high urea nitrogen levels can include kidney failure, heart disease, fluid overload, electrolyte imbalances, and malnutrition, among others.
How often should I get my urea nitrogen levels checked?
+The frequency of urea nitrogen level checks depends on individual factors, such as underlying health conditions and risk factors. Consult with a healthcare provider to determine the best schedule for your needs.
