Intro
Dietary fiber boosts health, aiding digestion, weight loss, and blood sugar control with high-fiber foods like fruits, vegetables, and whole grains.
The importance of fiber in our diets cannot be overstated. With the rise of processed and convenience foods, many of us are not getting enough fiber in our daily meals. However, fiber plays a crucial role in maintaining a healthy digestive system, preventing chronic diseases, and even supporting weight management. In this article, we will delve into the world of fiber, exploring its benefits, types, and ways to incorporate it into our diets.
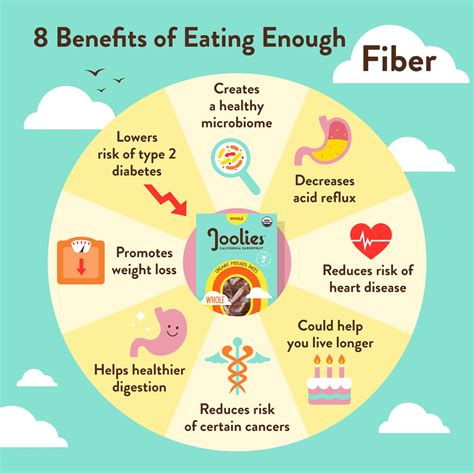
A high-fiber diet has been shown to have numerous health benefits, from reducing the risk of heart disease and type 2 diabetes to promoting regular bowel movements and preventing constipation. Fiber also helps to keep us feeling full and satisfied, making it an excellent tool for weight management. Moreover, a diet rich in fiber can help to support healthy blood sugar levels and even reduce the risk of certain cancers. With so many benefits, it's no wonder that health experts and nutritionists recommend increasing our daily fiber intake.
Despite the many advantages of fiber, many of us are still not getting enough. The average adult consumes only about 15 grams of fiber per day, which is significantly less than the recommended daily intake of 25-30 grams. This can be attributed to the prevalence of processed and low-fiber foods in our diets. However, with a little knowledge and planning, it's easy to boost our fiber intake and start enjoying the many benefits that come with it. In the following sections, we will explore the different types of fiber, how to incorporate them into our diets, and provide tips and tricks for increasing our daily fiber intake.
What Is Fiber?

Types of Fiber
There are many different types of fiber, each with its unique benefits and characteristics. Some of the most common types of fiber include: * Pectin: found in fruits such as apples and berries * Gums: found in legumes such as beans and lentils * Cellulose: found in plant cell walls * Hemicellulose: found in plant cell walls * Lignin: found in plant cell walls * Beta-glucan: found in oats and barleyBenefits of Fiber
How Fiber Works
Fiber works by adding bulk to stool and helping to move food through the digestive system. Soluble fiber forms a gel-like substance that helps to slow down the digestion of carbohydrates and prevent spikes in blood sugar levels. Insoluble fiber, on the other hand, helps to add bulk to stool and prevent constipation. Fiber also helps to feed the good bacteria in the gut, supporting a healthy gut microbiome.Increasing Fiber Intake

Fiber-Rich Foods
Some of the richest sources of fiber include: * Fruits: apples, bananas, berries * Vegetables: broccoli, carrots, sweet potatoes * Whole grains: brown rice, quinoa, whole wheat bread * Legumes: beans, lentils, chickpeas * Nuts and seeds: almonds, chia seeds, flaxseedsFiber and Weight Management

Tips for Weight Management
Here are some tips for using fiber to support weight management: * Eat a high-fiber breakfast: try oatmeal with fruit and nuts * Incorporate fiber-rich snacks into your diet: try apple slices with almond butter or carrot sticks with hummus * Add fiber to your meals: try adding beans or lentils to your favorite dishes * Drink plenty of water: fiber can help to regulate bowel movements, but it's also important to stay hydratedFiber and Chronic Diseases

Reducing Inflammation
Fiber can help to reduce inflammation in the body by: * Regulating blood sugar levels * Improving insulin sensitivity * Reducing the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines * Supporting healthy gut bacteriaFiber and Gut Health

Supporting Healthy Gut Bacteria
Here are some ways that fiber supports healthy gut bacteria: * Feeding the good bacteria: fiber acts as a prebiotic, feeding the good bacteria in the gut and helping them to thrive * Reducing inflammation: fiber can help to reduce inflammation in the gut, creating a healthy environment for gut bacteria to grow * Improving gut motility: fiber can help to regulate bowel movements, preventing constipation and supporting healthy gut motilityWhat are the benefits of a high-fiber diet?
+A high-fiber diet can help to promote regular bowel movements, reduce the risk of heart disease and type 2 diabetes, support healthy blood sugar levels, aid in weight management, and reduce the risk of certain cancers.
How much fiber should I eat per day?
+The recommended daily intake of fiber is 25-30 grams per day. However, the average adult consumes only about 15 grams of fiber per day.
What are some high-fiber foods that I can add to my diet?
+Some high-fiber foods that you can add to your diet include fruits, vegetables, whole grains, legumes, and nuts and seeds. Some specific examples include apples, bananas, broccoli, carrots, brown rice, quinoa, and almonds.
In conclusion, fiber is a crucial component of a healthy diet, providing numerous benefits for digestive health, chronic disease prevention, and weight management. By incorporating more fiber-rich foods into our diets and taking steps to increase our daily fiber intake, we can take a significant step towards improving our overall health and wellbeing. We encourage you to share your experiences with fiber and provide any tips or tricks you have for increasing your daily fiber intake. Let's work together to prioritize our health and wellbeing, one fiber-rich meal at a time!
