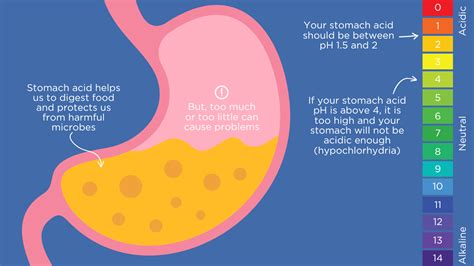
Intro
Discover vomiting stomach acid symptoms, causes, and remedies. Learn to manage acid reflux, heartburn, and digestive issues with expert advice and natural treatments.
Vomiting stomach acid can be a distressing and painful experience, often leaving individuals feeling weak, dehydrated, and anxious about when it might happen again. The symptoms associated with vomiting stomach acid can vary from person to person, but there are common signs and symptoms that can help in identifying and managing the condition. Understanding these symptoms is crucial for seeking the right medical attention and implementing effective treatment strategies.
The sensation of vomiting stomach acid is often accompanied by a burning feeling in the chest and throat, which can be quite uncomfortable. This burning sensation is usually a result of the stomach acid flowing back up into the esophagus, a condition known as acid reflux. When stomach acid is vomited, it can also lead to tooth erosion due to the high acidity, causing pain and sensitivity in the teeth. Furthermore, the act of vomiting itself can lead to dehydration, especially if the individual is unable to keep fluids down, further complicating the situation.
Vomiting stomach acid can be triggered by a variety of factors, including eating certain foods, lying down after eating, or having conditions like gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD). The symptoms can be managed through lifestyle changes, dietary adjustments, and in some cases, medication. However, it's essential to consult a healthcare provider to determine the underlying cause of the vomiting and to receive appropriate treatment. Early diagnosis and treatment can significantly improve the quality of life for individuals experiencing these symptoms.
Vomiting Stomach Acid Causes
Understanding the causes of vomiting stomach acid is vital for effective management and prevention. Several factors can contribute to this condition, including dietary habits, lifestyle choices, and underlying health conditions. Consuming large or heavy meals, especially those high in fats, can put extra pressure on the stomach, leading to acid reflux and potentially vomiting stomach acid. Additionally, foods and drinks that are known to trigger acid reflux, such as citrus fruits, tomatoes, chocolate, and alcohol, can exacerbate the symptoms in susceptible individuals.
Lifestyle factors, such as smoking, wearing tight clothing, and being overweight or obese, can also increase the risk of experiencing vomiting stomach acid. Smoking can relax the lower esophageal sphincter, allowing stomach acid to flow more easily into the esophagus, while tight clothing can put pressure on the stomach, causing its contents to rise into the esophagus. Being overweight can increase pressure on the stomach, making it easier for stomach acid to escape into the esophagus.
Underlying Health Conditions
Certain health conditions can predispose individuals to vomiting stomach acid. Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) is a chronic condition where the stomach acid flows back into the tube connecting the mouth and stomach (esophagus). This backwash (acid reflux) can irritate the lining of the esophagus, causing discomfort. Other conditions like gastritis, an inflammation of the stomach lining, and peptic ulcers, sores on the lining of the stomach or the first part of the small intestine, can also lead to vomiting stomach acid.Symptoms of Vomiting Stomach Acid
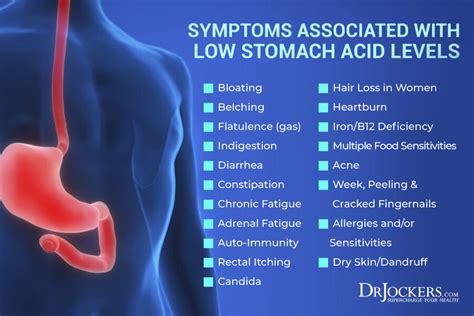
The symptoms of vomiting stomach acid can range from mild to severe and may include a sour taste in the mouth, difficulty swallowing, and a sensation of food getting stuck in the throat. Heartburn, a burning sensation in the chest that often spreads to the throat, along with chest pain, are common complaints. Some individuals may experience hoarseness, a chronic cough, or wheezing due to the acid reflux reaching the upper airway.
In severe cases, vomiting stomach acid can lead to complications such as esophagitis, an inflammation of the esophagus, or esophageal stricture, a narrowing of the esophagus that can cause difficulty swallowing. These symptoms necessitate immediate medical attention to prevent long-term damage to the esophagus and to manage the underlying cause effectively.
Diagnosis and Treatment
Diagnosing the cause of vomiting stomach acid involves a combination of medical history, physical examination, and diagnostic tests such as endoscopy, ambulatory acid probe tests, or esophageal pH monitoring. Treatment strategies often include lifestyle modifications, such as dietary changes, weight loss, and avoiding triggers. Medications like antacids, histamine-2 (H2) blockers, and proton pump inhibitors (PPIs) can help reduce acid production or neutralize stomach acid.In some cases, surgery may be necessary to strengthen the lower esophageal sphincter or to repair a hiatal hernia, which can contribute to acid reflux. It's crucial for individuals experiencing frequent or severe symptoms of vomiting stomach acid to consult with a healthcare provider to determine the best course of treatment and to prevent potential complications.
Management and Prevention

Managing and preventing vomiting stomach acid involves making conscious lifestyle and dietary choices. Eating smaller, more frequent meals can reduce pressure on the stomach, while avoiding trigger foods and drinks can help minimize acid reflux episodes. Raising the head of the bed by 6 inches can prevent stomach acid from flowing into the esophagus during sleep, and quitting smoking can significantly reduce the risk of GERD and its symptoms.
Maintaining a healthy weight, avoiding tight clothing, and managing stress through relaxation techniques such as meditation or deep breathing exercises can also contribute to reducing the frequency and severity of vomiting stomach acid. By understanding personal triggers and taking proactive steps to manage symptoms, individuals can significantly improve their quality of life and reduce the risk of complications associated with acid reflux.
Dietary Adjustments
Making dietary adjustments is a crucial part of managing vomiting stomach acid. Identifying and avoiding trigger foods, eating a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains, and staying hydrated can help alleviate symptoms. Foods that are low in fat, high in fiber, and not too spicy or acidic are generally well-tolerated. Keeping a food diary can help individuals track which foods exacerbate their symptoms, allowing them to make informed dietary choices.Complications of Untreated Vomiting Stomach Acid
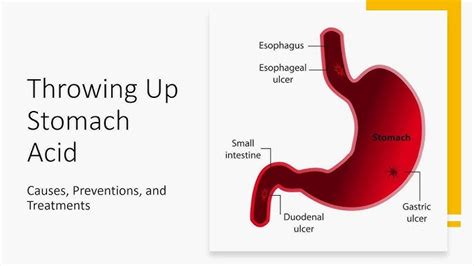
Untreated vomiting stomach acid can lead to several complications, including esophageal stricture, Barrett's esophagus, and an increased risk of esophageal cancer. Esophageal stricture, a narrowing of the esophagus due to scar tissue from chronic acid exposure, can cause difficulty swallowing, leading to malnutrition and weight loss. Barrett's esophagus, a condition in which the esophageal lining changes to resemble the intestine, is a precursor to esophageal cancer and requires regular monitoring.
It's essential for individuals experiencing symptoms of vomiting stomach acid to seek medical attention to prevent these complications and to improve their quality of life. Early diagnosis and treatment can significantly reduce the risk of long-term damage to the esophagus and other related health issues.
Psychological Impact
The psychological impact of vomiting stomach acid should not be underestimated. The unpredictability of symptoms, fear of vomiting in public, and the discomfort associated with acid reflux can lead to anxiety, depression, and social isolation. Addressing these psychological aspects through counseling, support groups, or stress management techniques can be an integral part of the treatment plan, helping individuals cope with their condition more effectively.Future Perspectives and Research

Research into the causes and treatments of vomiting stomach acid continues to evolve, with ongoing studies focusing on new medications, surgical techniques, and lifestyle interventions. The development of more effective treatments with fewer side effects is a key area of research, aiming to improve the management of GERD and related conditions. Additionally, there is a growing interest in the role of the gut microbiome in gastrointestinal health, which may lead to new therapeutic approaches in the future.
Understanding the genetic factors that predispose individuals to GERD and vomiting stomach acid can also lead to personalized treatment plans, tailored to an individual's specific needs and genetic profile. As our understanding of the complex interplay between dietary, environmental, and genetic factors improves, so too will our ability to prevent and treat vomiting stomach acid effectively.
Advancements in Diagnostic Techniques
Advancements in diagnostic techniques, such as improved endoscopy equipment and more sensitive pH monitoring devices, will enable healthcare providers to diagnose and monitor vomiting stomach acid more accurately. These advancements can lead to earlier interventions, reducing the risk of complications and improving patient outcomes.Conclusion and Final Thoughts

In conclusion, vomiting stomach acid is a complex condition with a range of causes, symptoms, and potential complications. By understanding the underlying factors and taking proactive steps towards management and prevention, individuals can significantly improve their quality of life. It's crucial for those experiencing symptoms to seek medical attention to receive an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment, preventing long-term damage to the esophagus and related health issues.
We invite readers to share their experiences and thoughts on managing vomiting stomach acid. Your insights can help others understand the condition better and find effective ways to cope. Please feel free to comment below, and let's work together to raise awareness about this common yet often misunderstood condition.
What are the common symptoms of vomiting stomach acid?
+The common symptoms include a sour taste in the mouth, difficulty swallowing, heartburn, and a sensation of food getting stuck in the throat.
How can vomiting stomach acid be managed and prevented?
+Management and prevention involve making lifestyle and dietary changes, such as eating smaller meals, avoiding trigger foods, raising the head of the bed, and maintaining a healthy weight.
What are the potential complications of untreated vomiting stomach acid?
+Potential complications include esophageal stricture, Barrett's esophagus, and an increased risk of esophageal cancer. It's essential to seek medical attention to prevent these complications.
