Intro
The weight of an average newborn is a topic of great interest to expecting parents, healthcare professionals, and anyone curious about the miracle of birth. As we delve into this fascinating subject, we'll explore the various factors that influence a newborn's weight, the average weight range, and what this means for the baby's health and development. Whether you're a soon-to-be parent or simply interested in learning more about human biology, this article will provide you with a comprehensive understanding of the weight of an average newborn.
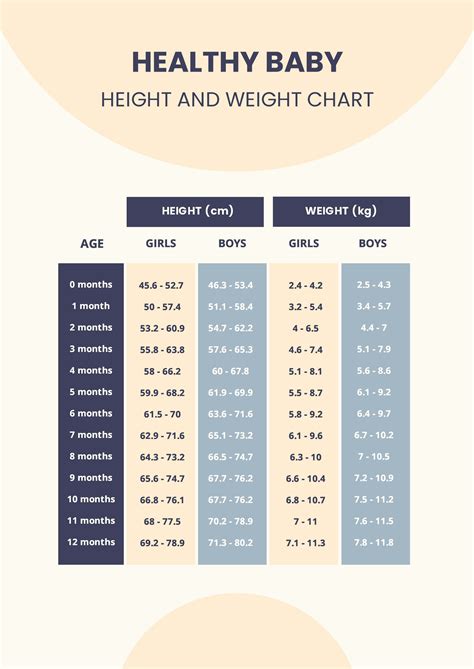
The weight of a newborn baby is a significant indicator of their overall health and well-being. A baby's birth weight is influenced by a combination of genetic and environmental factors, including the mother's nutrition, lifestyle, and health during pregnancy. On average, a newborn baby weighs between 5.5 and 8.8 pounds (2.5 to 4 kilograms), with the average weight being around 7.9 pounds (3.6 kilograms). However, it's essential to note that a normal birth weight can vary significantly, and babies born at a weight outside of this range may still be perfectly healthy.
As we explore the topic of newborn weight, it's crucial to understand the factors that contribute to a baby's birth weight. The mother's diet, overall health, and lifestyle choices during pregnancy play a significant role in determining the baby's weight. For example, a mother who consumes a balanced diet rich in essential nutrients, such as folic acid, iron, and calcium, is more likely to give birth to a baby with a healthy weight. Additionally, a mother's pre-pregnancy weight, age, and medical conditions, such as gestational diabetes or hypertension, can also impact the baby's birth weight.
Understanding Newborn Weight Ranges

Newborn weight ranges can be categorized into several groups, each with its unique characteristics and potential health implications. The World Health Organization (WHO) defines the following weight ranges for newborns: low birth weight (less than 5.5 pounds or 2.5 kilograms), normal birth weight (5.5-8.8 pounds or 2.5-4 kilograms), and high birth weight (more than 8.8 pounds or 4 kilograms). Understanding these weight ranges is essential for healthcare professionals to identify potential health risks and provide appropriate care to newborns.
Factors Influencing Newborn Weight
The factors that influence a newborn's weight are complex and multifaceted. Some of the key factors include: * Genetics: The baby's genetic makeup plays a significant role in determining their birth weight. * Maternal nutrition: A mother's diet during pregnancy can significantly impact the baby's weight. * Maternal health: Pre-existing medical conditions, such as gestational diabetes or hypertension, can affect the baby's weight. * Lifestyle choices: A mother's lifestyle choices, such as smoking or substance abuse, can also impact the baby's weight.The Importance of Monitoring Newborn Weight

Monitoring a newborn's weight is crucial for identifying potential health risks and providing appropriate care. Healthcare professionals use a baby's birth weight, along with other factors, such as length and head circumference, to assess their overall health and development. Regular weight checks can help identify any potential issues, such as growth restriction or excessive weight gain, allowing for early intervention and treatment.
Benefits of Optimal Newborn Weight
A newborn's optimal weight is essential for their overall health and development. Some of the benefits of optimal newborn weight include: * Reduced risk of health complications: Babies born at a healthy weight are less likely to experience health complications, such as respiratory distress or hypoglycemia. * Improved cognitive development: Optimal birth weight has been linked to improved cognitive development and better academic performance in childhood. * Enhanced physical development: A healthy birth weight can also impact a baby's physical development, with optimal weight babies tend to have better motor skills and coordination.Consequences of Low or High Newborn Weight

Low or high newborn weight can have significant consequences for a baby's health and development. Low birth weight babies are at a higher risk of health complications, such as respiratory distress, hypoglycemia, and infections. On the other hand, high birth weight babies may experience complications during delivery, such as shoulder dystocia, and are at a higher risk of developing conditions like obesity and diabetes later in life.
Risks Associated with Low Newborn Weight
Some of the risks associated with low newborn weight include: * Respiratory distress: Low birth weight babies may experience respiratory distress, which can lead to long-term health complications. * Hypoglycemia: Low birth weight babies are at a higher risk of hypoglycemia, which can cause seizures, brain damage, and other health complications. * Infections: Low birth weight babies are more susceptible to infections, which can be life-threatening if left untreated.Supporting Healthy Newborn Weight
Supporting healthy newborn weight is crucial for a baby's overall health and development. Expecting mothers can take several steps to support a healthy birth weight, including:
- Eating a balanced diet: A diet rich in essential nutrients, such as folic acid, iron, and calcium, can help support a healthy birth weight.
- Staying hydrated: Drinking plenty of water and other fluids can help support fetal development and overall health.
- Avoiding harmful substances: Avoiding substances like tobacco, alcohol, and illicit drugs can help reduce the risk of low birth weight and other health complications.
Role of Prenatal Care in Supporting Newborn Weight
Prenatal care plays a critical role in supporting healthy newborn weight. Regular prenatal check-ups can help identify potential health risks and allow for early intervention and treatment. Some of the ways prenatal care can support healthy newborn weight include: * Monitoring fetal growth: Regular ultrasounds and fetal monitoring can help track a baby's growth and development. * Identifying health risks: Prenatal care can help identify potential health risks, such as gestational diabetes or hypertension, which can impact a baby's birth weight.Conclusion and Next Steps
In conclusion, the weight of an average newborn is a complex and multifaceted topic. Understanding the factors that influence a baby's birth weight, the benefits of optimal newborn weight, and the consequences of low or high newborn weight is essential for supporting healthy newborn development. By taking steps to support healthy newborn weight, expecting mothers can help give their baby the best possible start in life.
We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences on this topic. Have you or someone you know had a baby with a low or high birth weight? What steps did you take to support a healthy newborn weight? Share your story in the comments below, and let's work together to promote healthy newborn development.
What is the average weight of a newborn baby?
+The average weight of a newborn baby is around 7.9 pounds (3.6 kilograms), with a normal weight range of 5.5-8.8 pounds (2.5-4 kilograms).
What factors influence a newborn's weight?
+The factors that influence a newborn's weight include genetics, maternal nutrition, maternal health, and lifestyle choices.
What are the consequences of low or high newborn weight?
+Low birth weight babies are at a higher risk of health complications, such as respiratory distress and hypoglycemia, while high birth weight babies may experience complications during delivery and are at a higher risk of developing conditions like obesity and diabetes later in life.
