Intro
Discover how West Nile Encephalitis spreads through mosquito bites, contaminated blood, and organ transplants, highlighting prevention methods and symptoms of this viral disease, including neuroinvasive infection and meningitis.
West Nile encephalitis, also known as West Nile virus (WNV), is a serious disease that affects the central nervous system and is primarily transmitted through the bite of an infected mosquito. The disease has been a significant public health concern in recent years, with cases reported in various parts of the world, including the United States, Europe, and Africa. Understanding how West Nile encephalitis spreads is crucial in preventing and controlling the disease. In this article, we will explore the five main ways West Nile encephalitis spreads and provide insights into the disease's transmission dynamics.
The importance of understanding West Nile encephalitis transmission cannot be overstated. The disease can have severe consequences, including meningitis, encephalitis, and acute flaccid paralysis, which can lead to long-term disability or even death. Moreover, the disease can have significant economic and social impacts, particularly in areas where outbreaks occur. By grasping the modes of transmission, individuals can take necessary precautions to protect themselves and their loved ones from the disease.
The transmission of West Nile encephalitis is a complex process that involves multiple factors, including the mosquito vector, the virus itself, and the environment. The disease is typically spread through the bite of an infected mosquito, which acquires the virus from feeding on infected birds or other animals. However, there are other ways West Nile encephalitis can spread, and it is essential to be aware of these modes of transmission to prevent the disease.
Introduction to West Nile Encephalitis Transmission
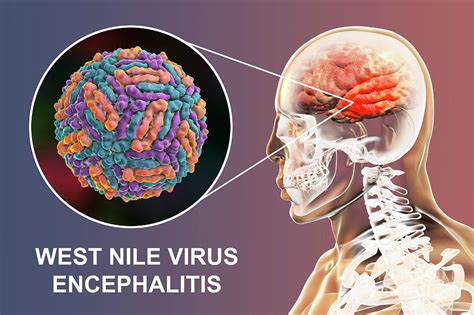
West Nile encephalitis transmission is a multifaceted process that involves various factors, including the mosquito vector, the virus, and the environment. The disease is typically spread through the bite of an infected mosquito, which acquires the virus from feeding on infected birds or other animals. However, there are other ways West Nile encephalitis can spread, and it is essential to be aware of these modes of transmission to prevent the disease.
Mosquito-Borne Transmission
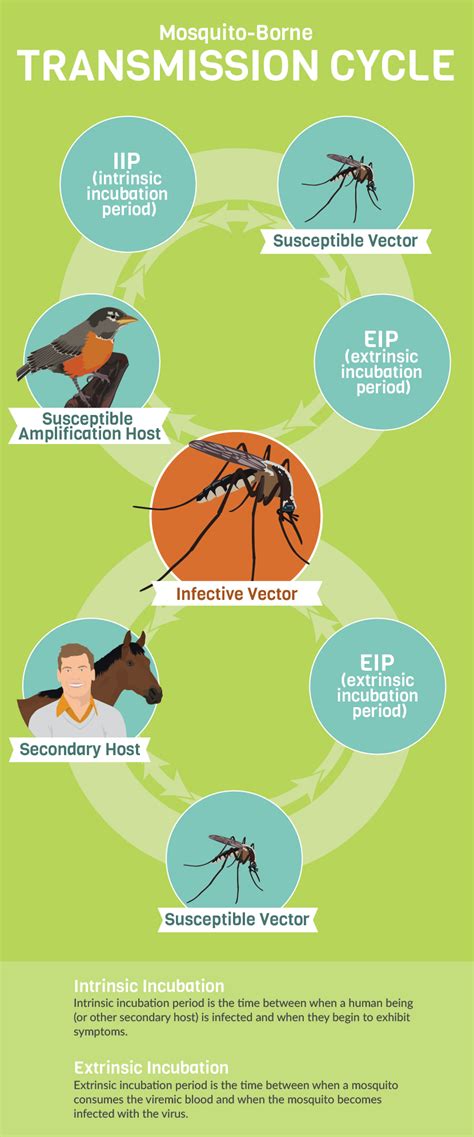
The primary mode of West Nile encephalitis transmission is through the bite of an infected mosquito. Mosquitoes become infected with the virus when they feed on infected birds or other animals. The virus then replicates within the mosquito, and when the mosquito feeds on another host, it can transmit the virus through its saliva. This mode of transmission is the most common way West Nile encephalitis spreads, and it is essential to take precautions to prevent mosquito bites.
Preventing Mosquito-Borne Transmission
To prevent mosquito-borne transmission, individuals can take several precautions, including: * Using insect repellents that contain DEET, picaridin, or oil of lemon eucalyptus * Wearing protective clothing, such as long-sleeved shirts and pants, when outdoors * Installing or repairing screens on windows and doors to prevent mosquitoes from entering homes * Eliminating standing water around homes to prevent mosquito breedingTransfusion-Associated Transmission
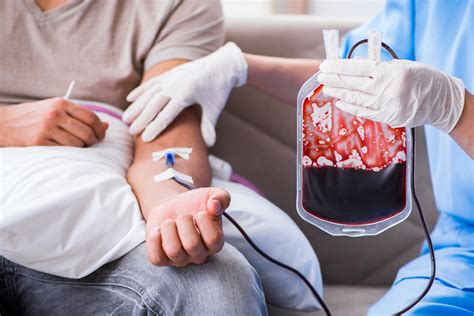
West Nile encephalitis can also be transmitted through blood transfusions. If an infected person donates blood, the virus can be transmitted to the recipient. This mode of transmission is rare, but it can occur if the donated blood is not properly screened for the virus.
Preventing Transfusion-Associated Transmission
To prevent transfusion-associated transmission, blood banks and transfusion centers must screen donated blood for West Nile virus. This can be done using nucleic acid testing (NAT) or other screening methods. Additionally, individuals can reduce their risk of transfusion-associated transmission by: * Donating blood only through reputable blood banks and transfusion centers * Ensuring that donated blood is properly screened for West Nile virus * Avoiding blood transfusions unless absolutely necessaryOrgan Transplantation Transmission
West Nile encephalitis can also be transmitted through organ transplantation. If an infected person donates an organ, the virus can be transmitted to the recipient. This mode of transmission is rare, but it can occur if the donated organ is not properly screened for the virus.
Preventing Organ Transplantation Transmission
To prevent organ transplantation transmission, organ procurement organizations and transplant centers must screen donated organs for West Nile virus. This can be done using NAT or other screening methods. Additionally, individuals can reduce their risk of organ transplantation transmission by: * Ensuring that donated organs are properly screened for West Nile virus * Avoiding organ transplantation unless absolutely necessary * Donating organs only through reputable organ procurement organizations and transplant centersVertical Transmission

West Nile encephalitis can also be transmitted from mother to child during pregnancy or breastfeeding. This mode of transmission is rare, but it can occur if the mother is infected with the virus.
Preventing Vertical Transmission
To prevent vertical transmission, pregnant women and breastfeeding mothers can take several precautions, including: * Avoiding mosquito bites by using insect repellents and wearing protective clothing * Ensuring that their homes are free of standing water to prevent mosquito breeding * Avoiding contact with infected birds or animals * Getting tested for West Nile virus if they experience symptoms or have been exposed to the virusLab-Associated Transmission
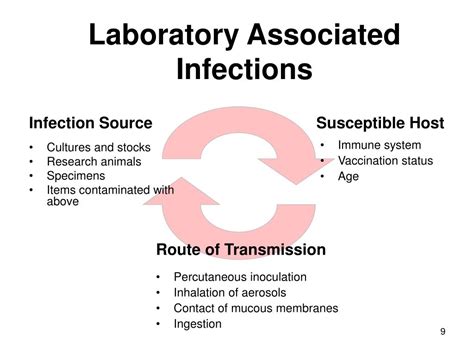
Finally, West Nile encephalitis can be transmitted in laboratory settings, where workers may be exposed to the virus through contact with infected samples or equipment. This mode of transmission is rare, but it can occur if laboratory workers do not follow proper safety protocols.
Preventing Lab-Associated Transmission
To prevent lab-associated transmission, laboratory workers can take several precautions, including: * Wearing personal protective equipment, such as gloves and masks, when handling infected samples or equipment * Following proper safety protocols when working with infected samples or equipment * Ensuring that laboratory equipment is properly cleaned and disinfected * Getting vaccinated against West Nile virus if they work with infected samples or equipmentIn summary, West Nile encephalitis can spread through various modes of transmission, including mosquito-borne transmission, transfusion-associated transmission, organ transplantation transmission, vertical transmission, and lab-associated transmission. By understanding these modes of transmission, individuals can take necessary precautions to protect themselves and their loved ones from the disease.
To further understand the transmission dynamics of West Nile encephalitis, it is essential to consider the following factors:
- The role of mosquitoes in transmitting the disease
- The importance of screening donated blood and organs for West Nile virus
- The risks associated with vertical transmission and lab-associated transmission
- The effectiveness of preventive measures, such as insect repellents and personal protective equipment
By considering these factors, individuals can reduce their risk of contracting West Nile encephalitis and prevent the disease from spreading.
What is West Nile encephalitis?
+West Nile encephalitis is a serious disease that affects the central nervous system and is primarily transmitted through the bite of an infected mosquito.
How is West Nile encephalitis transmitted?
+West Nile encephalitis can be transmitted through mosquito-borne transmission, transfusion-associated transmission, organ transplantation transmission, vertical transmission, and lab-associated transmission.
What are the symptoms of West Nile encephalitis?
+The symptoms of West Nile encephalitis can range from mild to severe and include fever, headache, vomiting, and muscle weakness.
How can I prevent West Nile encephalitis?
+To prevent West Nile encephalitis, individuals can take several precautions, including using insect repellents, wearing protective clothing, installing or repairing screens on windows and doors, and eliminating standing water around homes.
Is there a vaccine available for West Nile encephalitis?
+There is no vaccine available for West Nile encephalitis, but individuals can reduce their risk of contracting the disease by taking preventive measures, such as using insect repellents and wearing protective clothing.
In
